What is meant by a bottleneck?
In the context of population genetics, a "bottleneck" refers to a significant and sudden reduction in the size of a population due to a random and often catastrophic event. This reduction in population size can have profound effects on the genetic diversity and composition of the population. Bottlenecks are a key concept in the study of genetic drift, which is one of the mechanisms of evolution.
Here are some key points to understand about bottlenecks in population genetics:
Population Contraction: A bottleneck occurs when a population undergoes a sharp and temporary decrease in size. This can result from various events, such as natural disasters (e.g., earthquakes, floods, wildfires), disease outbreaks, habitat destruction, or human activities (e.g., hunting, habitat destruction).
Genetic Consequences: When a population experiences a bottleneck, the genetic diversity within the population is drastically reduced. Many alleles (different versions of genes) are lost from the gene pool, leading to a population that is more genetically homogenous.
Founder Effect: A bottleneck can lead to a phenomenon known as the "founder effect" when a small subset of individuals survives the bottleneck and goes on to establish a new population. This subset carries only a fraction of the genetic diversity present in the original population. As a result, the new population may have a different genetic makeup than the original population.
Increased Genetic Drift: Genetic drift, which is the random change in allele frequencies over time, becomes more pronounced in small populations. In bottlenecked populations, genetic drift can lead to the fixation of certain alleles (where one allele becomes the only version of the gene in the population) and the loss of others.
Reduced Adaptive Potential: Reduced genetic diversity in bottlenecked populations can limit their ability to adapt to changing environmental conditions or resist diseases. This can make these populations more vulnerable to future challenges.
Long-Term Effects: The genetic consequences of a bottleneck event can persist for generations. Even if the population size later increases, the genetic diversity may remain low, which can have long-term implications for the population's viability and evolutionary potential.
It's important to note that bottlenecks are a natural part of the evolutionary process, and they can occur in both small and large populations. However, the severity and duration of a bottleneck can vary widely, and their impact on a population depends on factors such as the initial genetic diversity, the size of the surviving population, and the rate of subsequent gene flow (migration) with other populations.
In conservation biology, the study of bottlenecks is essential for understanding the genetic health of endangered species and developing strategies for their protection and recovery, such as genetic rescue programs and maintaining genetic diversity in captive populations.
Understanding Bottlenecks: What Does it Mean in Different Contexts?
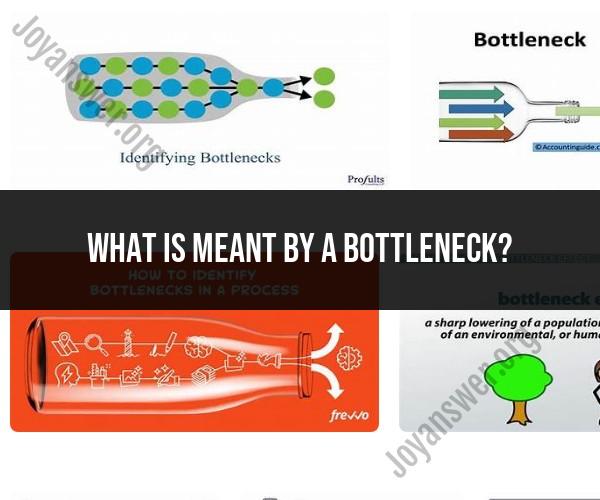
A bottleneck is a point in a process where the flow of work is slowed down or stopped. It can be caused by a variety of factors, such as a lack of resources, inefficient processes, or poor communication.
Bottlenecks can occur in any kind of process, from manufacturing to customer service to software development. In a manufacturing setting, a bottleneck might be a machine that is running at full capacity and cannot process any more work. In a customer service setting, a bottleneck might be a long wait time for customers to speak to a representative. In a software development setting, a bottleneck might be a team that is working on a critical feature that is blocking other teams from making progress.
Identifying Bottlenecks: Factors that Hinder Efficiency and Flow
There are a number of factors that can hinder efficiency and flow and lead to bottlenecks. Some of the most common factors include:
- Lack of resources: If a process does not have the necessary resources, such as people, equipment, or materials, it is likely to experience bottlenecks.
- Inefficient processes: If a process is not designed efficiently, it can create bottlenecks. For example, if a process has a lot of steps or handoffs, it is more likely to experience bottlenecks.
- Poor communication: Poor communication between team members or departments can also lead to bottlenecks. For example, if one team is not informed about a delay from another team, it can cause a bottleneck in the overall process.
Breaking Through Bottlenecks: Strategies for Smoother Processes
There are a number of strategies that can be used to break through bottlenecks and improve the flow of work. Some of the most common strategies include:
- Identify the bottleneck: The first step to breaking through a bottleneck is to identify it. Once the bottleneck has been identified, the root cause of the problem can be addressed.
- Increase resources: If the bottleneck is caused by a lack of resources, the resources can be increased. This may involve hiring more people, purchasing new equipment, or obtaining more materials.
- Improve processes: If the bottleneck is caused by inefficient processes, the processes can be improved. This may involve streamlining steps, eliminating handoffs, or automating tasks.
- Improve communication: If the bottleneck is caused by poor communication, communication can be improved. This may involve establishing clear communication channels, setting expectations, and providing regular updates.
By following these strategies, organizations can break through bottlenecks and improve the flow of work. This can lead to increased efficiency, productivity, and customer satisfaction.
Here are some additional tips for breaking through bottlenecks:
- Use data to identify and track bottlenecks. This will help you to understand the root cause of the problem and to measure the effectiveness of your solutions.
- Get input from stakeholders. People who are involved in the process on a daily basis can provide valuable insights into the bottlenecks and how to solve them.
- Be proactive. Don't wait until bottlenecks occur to address them. By identifying and addressing bottlenecks early, you can prevent them from causing major disruptions.
Breaking through bottlenecks is an ongoing process. It is important to regularly review your processes and identify any new bottlenecks that may have emerged.