What is the definition of a sample space in statistics?
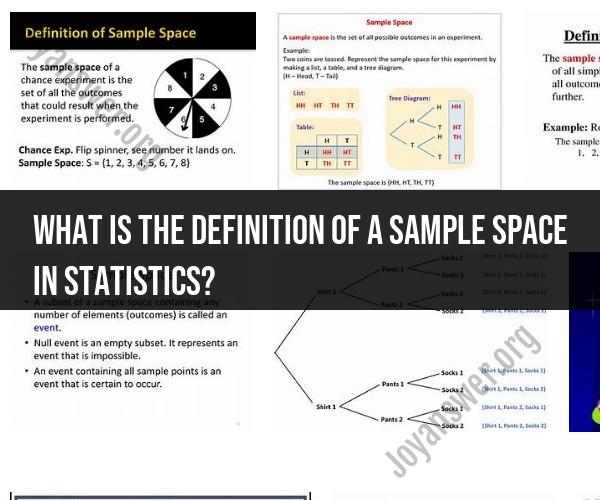
In statistics and probability theory, a sample space is the set of all possible outcomes or results of a random experiment or process. It represents the complete set of events that can occur when a random phenomenon is observed or studied. The sample space is a fundamental concept because it forms the basis for defining probabilities and conducting statistical analysis.
The sample space is typically denoted by the symbol "S" and consists of individual outcomes, which are often denoted using descriptive variables. These outcomes encompass all the possible scenarios or observations that could occur. The sample space can be finite, countably infinite, or uncountably infinite, depending on the nature of the random experiment.
For example, consider rolling a six-sided fair die. The sample space for this experiment would be:
S = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
In this case, there are six possible outcomes, each corresponding to one of the six faces of the die. The sample space lists all the potential results of rolling the die.
Understanding the sample space is essential in probability theory because it allows you to define events (subsets of the sample space) and calculate probabilities associated with those events. By analyzing the sample space and defining events within it, statisticians and probabilists can make predictions and draw conclusions about random processes.