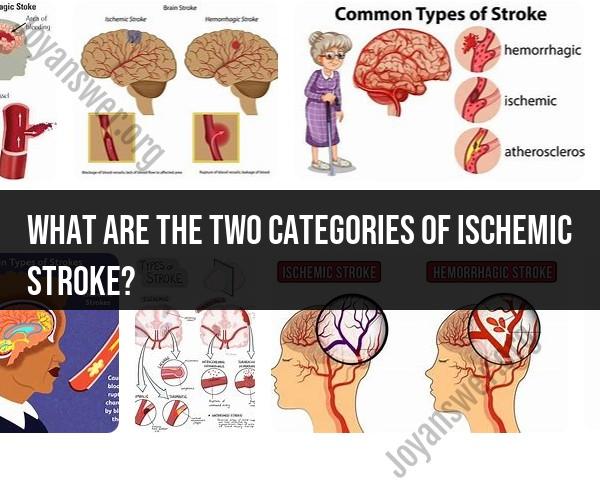
What are the two categories of ischemic stroke?
Ischemic strokes, which are the most common type of stroke, are typically categorized into two main categories based on their underlying causes:
Thrombotic Stroke:
- Thrombotic strokes occur when a blood clot (thrombus) forms within an artery that supplies blood to the brain. These clots often develop in areas where arteries have been narrowed or damaged by atherosclerosis (the buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries). Thrombotic strokes can be further divided into two subcategories:
- Large-Vessel Thrombosis: This type of thrombotic stroke occurs when a clot forms in one of the larger arteries supplying blood to the brain.
- Small-Vessel Thrombosis (Lacunar Stroke): Small-vessel thrombosis involves the formation of a clot in one of the brain's smaller blood vessels. These strokes are often associated with conditions like hypertension (high blood pressure).
- Thrombotic strokes occur when a blood clot (thrombus) forms within an artery that supplies blood to the brain. These clots often develop in areas where arteries have been narrowed or damaged by atherosclerosis (the buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries). Thrombotic strokes can be further divided into two subcategories:
Embolic Stroke:
- Embolic strokes occur when a blood clot or other debris, such as plaque or cholesterol particles, originates from a different location in the body (usually the heart or large arteries) and travels through the bloodstream until it becomes lodged in a smaller artery within the brain. These clots are called emboli. Embolic strokes can be caused by various factors, including atrial fibrillation (a heart rhythm disorder), heart valve issues, or other conditions that promote blood clot formation.
These two categories, thrombotic and embolic strokes, represent the clot-based causes of ischemic strokes. Both types result in a blockage of blood flow to a part of the brain, leading to a lack of oxygen and nutrients, which can cause brain tissue damage. Prompt medical intervention is essential in the case of ischemic strokes to restore blood flow and minimize brain damage.
Types of Ischemic Strokes: Thrombotic and Embolic
Ischemic strokes are the most common type of stroke, accounting for about 87% of all strokes. They occur when a blood clot blocks or narrows an artery leading to the brain, depriving the brain of oxygen and nutrients.
There are two main types of ischemic strokes: thrombotic and embolic.
Thrombotic strokes are caused by a blood clot that forms inside a blood vessel in the brain. This can happen due to a number of factors, including:
- Atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries)
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Smoking
Embolic strokes are caused by a blood clot that travels from another part of the body, such as the heart or legs, to the brain. The most common source of emboli is the heart, especially in people with atrial fibrillation, a condition that causes the heart to beat irregularly.
Differences Between Thrombotic and Embolic Ischemic Strokes
The main difference between thrombotic and embolic ischemic strokes is the source of the blood clot. Thrombotic strokes are caused by a blood clot that forms inside a blood vessel in the brain, while embolic strokes are caused by a blood clot that travels to the brain from another part of the body.
Another difference is that thrombotic strokes are more likely to occur in the morning, while embolic strokes can occur at any time.
Symptoms and Treatment of Thrombotic vs Embolic Strokes
The symptoms of thrombotic and embolic strokes are very similar. They can include:
- Sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body
- Sudden confusion, trouble speaking or understanding speech
- Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes
- Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination
- Sudden severe headache with no known cause
If you or someone you know is experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to call 911 immediately.
The treatment for thrombotic and embolic strokes is also similar. The goal of treatment is to restore blood flow to the brain as quickly as possible. This may involve medications to break up the blood clot or surgery to remove the clot.
In addition to emergency treatment, people who have had a stroke may also need rehabilitation to help them regain their lost abilities. This may involve physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy.
Prevention
The best way to prevent ischemic strokes is to reduce your risk factors for atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases. This includes:
- Controlling your blood pressure
- Managing your cholesterol levels
- Keeping your blood sugar levels under control
- Quitting smoking
- Eating a healthy diet
- Exercising regularly
If you have a history of atrial fibrillation or other heart conditions, it is important to work with your doctor to manage your condition and reduce your risk of stroke.