What is right lower quad?
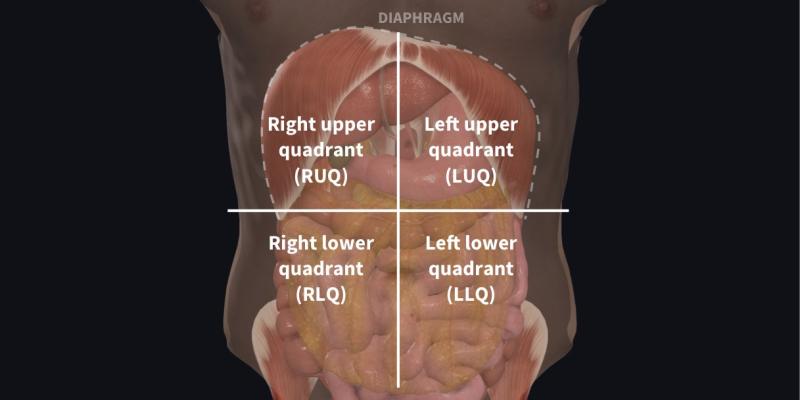
The right lower quadrant (RLQ) is one of four imaginary sections used by medical professionals to divide the abdomen.
Anatomy of the Right Lower Quadrant
The RLQ is bordered on the left by a vertical line running down the center of the abdomen (through the belly button) and above by a horizontal line that also passes through the belly button.
The main organs located in the right lower quadrant are:
Appendix: The appendix is a small, finger-like pouch attached to the large intestine.
Cecum: The first part of the large intestine, where it connects to the small intestine.
Ascending colon: The section of the large intestine that travels upwards toward the right upper quadrant.
Right ovary and fallopian tube: These are key parts of the female reproductive system.
Right ureter: The tube that carries urine from the right kidney to the bladder.
Small intestine: The last portion of the small intestine, known as the ileum, is located here before it joins the large intestine.
Clinical Significance
Pain in the right lower quadrant is a significant symptom for diagnosing several conditions, with appendicitis being the most well-known.
Because of the critical organs located in this area, any persistent or severe pain in the right lower quadrant warrants prompt medical evaluation.
Understanding the Right Lower Quadrant (RLQ) in Anatomy: Location, Organs, Pain Causes, and Health Impact
The right lower quadrant (RLQ) of the abdomen is a key anatomical region often discussed in medical examinations and diagnostic imaging. Understanding its location, the organs within it, and the conditions that can cause pain in this area is essential for both healthcare professionals and patients. This article explores RLQ anatomy, its organs, clinical evaluation methods, common causes of pain, and potential impacts on overall health.
What Is the Right Lower Quadrant (RLQ) in Anatomy?
In medical terminology, the right lower quadrant (RLQ) refers to one of the four sections of the abdomen, as divided by vertical and horizontal lines through the umbilicus (navel). It lies below the umbilical region on the right side of the body.
The RLQ is commonly referenced in physical examinations because it contains several vital organs and structures, and pain here can indicate various medical conditions.
Which Organs Are Located in the RLQ?
The RLQ contains parts of several important organs and anatomical structures, including:
Appendix – A small, tube-shaped pouch attached to the cecum.
Cecum – The first part of the large intestine.
Terminal ileum – The end portion of the small intestine.
Right ureter – Part of the urinary tract carrying urine from the kidney to the bladder.
Reproductive organs (in females) – Right ovary and fallopian tube.
Blood vessels and lymphatic structures – Supplying and draining the lower abdominal region.
The exact structures involved may vary depending on individual anatomy and surgical history.
How Is Pain in the RLQ Evaluated Clinically?
Doctors use a combination of history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests to evaluate RLQ pain:
Medical history – Includes onset, duration, severity, and nature of the pain.
Physical examination – Palpation (gentle pressing) to check for tenderness, guarding, or rebound pain.
Laboratory tests – Blood tests, urinalysis, or pregnancy tests (for females) to identify underlying causes.
Imaging studies – Ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to visualize internal structures.
One of the most well-known RLQ pain assessments is checking for McBurney’s point tenderness, which can suggest appendicitis.
What Are Common Causes of RLQ Pain?
Several conditions can cause pain in the RLQ, including:
Appendicitis – Inflammation of the appendix; often an emergency.
Kidney stones – Stones in the right ureter causing sharp flank-to-groin pain.
Gastrointestinal issues – Such as Crohn’s disease, constipation, or bowel obstruction.
Gynecological conditions (females) – Ovarian cysts, ectopic pregnancy, or pelvic inflammatory disease.
Hernias – Inguinal hernias can cause localized discomfort.
Proper diagnosis is essential because the treatment varies greatly depending on the underlying cause.
How Can RLQ Issues Affect Overall Health?
Problems in the RLQ can significantly impact overall health if not addressed promptly:
Delayed treatment risks – Untreated appendicitis can lead to rupture and life-threatening infection.
Chronic digestive issues – Conditions like Crohn’s disease may cause long-term nutrient absorption problems.
Reproductive health implications – Gynecological disorders in the RLQ may affect fertility.
Pain and mobility limitations – Persistent RLQ pain can reduce daily activity and quality of life.
Early medical evaluation of RLQ pain is crucial to prevent complications and maintain good health.
In summary, the right lower quadrant is an important anatomical region with critical structures. Awareness of its organs, pain evaluation methods, and possible health issues can help in early detection and treatment of medical problems.