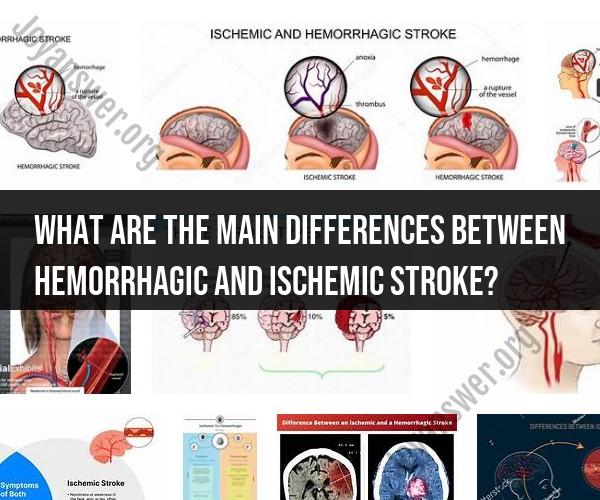
What are the main differences between hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke?
Hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes are two different types of strokes, and they have distinct causes and characteristics:
Cause:
Ischemic Stroke: Ischemic strokes occur when a blood clot (thrombus) or a plaque buildup (embolus) blocks a blood vessel in the brain, cutting off the blood supply to a part of the brain.
Hemorrhagic Stroke: Hemorrhagic strokes happen when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures or leaks, causing bleeding into or around the brain. This can result from conditions like an aneurysm, arteriovenous malformation (AVM), or hypertension.
Type of Bleeding:
Ischemic Stroke: There is no bleeding involved in ischemic strokes. Instead, a clot or blockage prevents blood flow to a specific area of the brain.
Hemorrhagic Stroke: Hemorrhagic strokes involve bleeding within the brain (intracerebral hemorrhage) or into the space between the brain and the skull (subarachnoid hemorrhage).
Symptoms:
Ischemic Stroke: Symptoms of an ischemic stroke may include sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking, confusion, trouble seeing, and loss of coordination.
Hemorrhagic Stroke: Symptoms of a hemorrhagic stroke can include a severe headache, sudden weakness or numbness, nausea and vomiting, loss of balance, and a decreased level of consciousness.
Treatment:
Ischemic Stroke: Treatment for ischemic strokes often involves medications to dissolve clots (thrombolytics) and procedures like mechanical thrombectomy to remove the clot. Time is crucial in ischemic stroke treatment.
Hemorrhagic Stroke: Managing hemorrhagic strokes focuses on controlling bleeding and preventing further damage. Treatment may involve surgery to repair the damaged blood vessel or control bleeding.
Risk Factors:
Ischemic Stroke: Risk factors for ischemic strokes include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, high cholesterol, and a history of heart disease.
Hemorrhagic Stroke: Risk factors for hemorrhagic strokes include hypertension, aneurysms, AVMs, and certain blood-thinning medications.
Prevention:
Ischemic Stroke: Prevention strategies for ischemic strokes often involve lifestyle changes like maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, managing blood pressure, and not smoking.
Hemorrhagic Stroke: Prevention of hemorrhagic strokes may include managing conditions like hypertension and seeking treatment for aneurysms or AVMs.
It's important to note that both types of strokes are medical emergencies, and early recognition and prompt medical attention are crucial to minimize damage and improve outcomes. The specific treatment and prognosis can vary depending on the individual and the circumstances of the stroke.