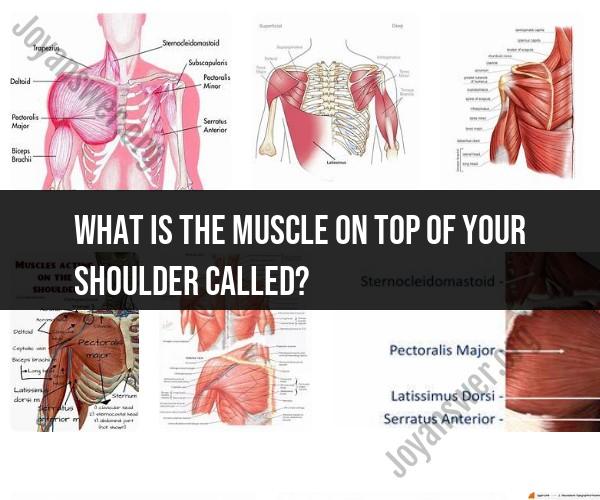
What is the muscle on top of your shoulder called?
The muscle on top of your shoulder is called the trapezius muscle. The trapezius is a large, flat muscle that extends from the base of the skull, along the vertebral column, and to the shoulder blades. It has a trapezoid-like shape, which is how it gets its name.
The trapezius muscle plays a crucial role in moving and stabilizing the shoulder girdle. It has three main parts or regions:
Upper Trapezius: This portion of the muscle originates from the base of the skull and extends down to the upper thoracic spine. It is involved in elevating and shrugging the shoulders, such as when you raise your shoulders towards your ears.
Middle Trapezius: This part of the muscle spans from the upper thoracic spine to the scapula (shoulder blade). It is responsible for retracting or pulling the shoulder blades together. This action is often used when squeezing your shoulder blades together as in good posture.
Lower Trapezius: The lower trapezius originates from the lower thoracic spine and extends to the scapula. It plays a role in depressing or lowering the shoulder blades and also helps with scapular rotation and stabilization.
Overall, the trapezius muscle is essential for various shoulder and neck movements and helps maintain proper posture. It is commonly engaged in activities such as lifting, carrying, and rotating the arms and shoulders.
Unveiling the Deltoid Muscle: What's the Muscle on Top of Your Shoulder Called?
The muscle on top of your shoulder is called the deltoid muscle. It is a triangular-shaped muscle that covers the glenohumeral joint, which is the ball-and-socket joint that connects your arm to your shoulder blade.
The deltoid muscle has three parts: the anterior (front) part, the medial (middle) part, and the posterior (back) part. Each part of the deltoid muscle has a different function.
- The anterior deltoid abducts (lifts to the side) the arm.
- The medial deltoid abducts and internally rotates (turns inward) the arm.
- The posterior deltoid extends (straightens) and externally rotates (turns outward) the arm.
The deltoid muscle is a very important muscle for shoulder movement and stability. It is used in many everyday activities, such as reaching, lifting, and dressing. It is also used in many sports and recreational activities, such as swimming, tennis, and baseball.
Anatomy of the Shoulder: Learning About the Deltoid Muscle
The deltoid muscle is a superficial muscle, meaning that it is close to the surface of the skin. It is also a pennate muscle, meaning that its muscle fibers are arranged at an angle to the tendon. This arrangement allows the deltoid muscle to generate a lot of force.
The deltoid muscle originates from three different bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the acromion process of the scapula (shoulder blade), and the spine of the scapula. It inserts onto the deltoid tuberosity, which is a bony prominence on the lateral (outer) aspect of the humerus (upper arm bone).
The deltoid muscle is innervated by the axillary nerve, which is a branch of the brachial plexus. The axillary nerve supplies motor and sensory innervation to the deltoid muscle and other muscles of the shoulder and upper arm.
Strengthening and Caring for Your Deltoid Muscle: Shoulder Health Tips
There are many things you can do to strengthen and care for your deltoid muscle, including:
- Exercise regularly. Exercise helps to keep your muscles strong and healthy. There are many different exercises that can target the deltoid muscle, such as shoulder presses, lateral raises, and front raises.
- Warm up before exercise. Warming up helps to prepare your muscles for exercise and reduce your risk of injury. A simple warm-up for the deltoid muscle might include arm circles and shoulder rolls.
- Cool down after exercise. Cooling down helps your muscles to recover from exercise. A simple cool-down for the deltoid muscle might include static stretches, such as the overhead triceps stretch and the chest stretch.
- Listen to your body. If you experience any pain, stop exercising and consult with a doctor or physical therapist.
Here are some additional tips for caring for your deltoid muscle:
- Avoid repetitive overhead activities. Repetitive overhead activities can put stress on the deltoid muscle and lead to injury. If you have to do overhead activities at work or during sports, make sure to take breaks and stretch your shoulders regularly.
- Maintain a good posture. Good posture helps to keep your shoulders aligned and reduces the risk of injury. When you are standing, make sure to keep your back straight and your shoulders relaxed. When you are sitting, make sure to keep your feet flat on the floor and your shoulders relaxed.
- Eat a healthy diet. A healthy diet provides your muscles with the nutrients they need to recover and grow. Make sure to eat plenty of protein, fruits, and vegetables.
By following these tips, you can help to keep your deltoid muscles strong and healthy.