What is the temperature at altitude?
The temperature at altitude varies depending on several factors, including the altitude itself, time of day, season, and geographical location. There is no single fixed temperature for a given altitude because temperature changes with altitude due to the lapse rate, which is the rate at which temperature decreases with increasing altitude in the Earth's atmosphere. The lapse rate is not constant and can vary.
However, we can provide a general idea of how temperature changes with altitude using a standard atmospheric model. This model assumes a typical lapse rate:
- On average, the temperature decreases by about 2°C (3.6°F) for every 1,000 feet (300 meters) of altitude gained. This is a common approximation known as the "standard lapse rate."
For example, if the temperature at sea level (0 feet or 0 meters) is 20°C (68°F), you can estimate the temperature at an altitude of 5,000 feet (1,524 meters) using the standard lapse rate:
- Temperature at 5,000 feet ≈ 20°C - (5,000 feet / 1,000 feet) * 2°C = 10°C (50°F)
Keep in mind that this is a simplified model, and actual temperature variations with altitude can be influenced by local weather patterns, geographic features, and other factors. In reality, temperature profiles in the atmosphere can be more complex.
To obtain accurate temperature information at a specific altitude and location, it's best to consult local weather reports, aviation charts, or meteorological data sources that provide temperature profiles for the region of interest. These sources will offer more precise and up-to-date information for the altitude you are concerned about.
Calculating Temperature at Altitude: Methods and Formulas
There are two main methods for calculating temperature at altitude:
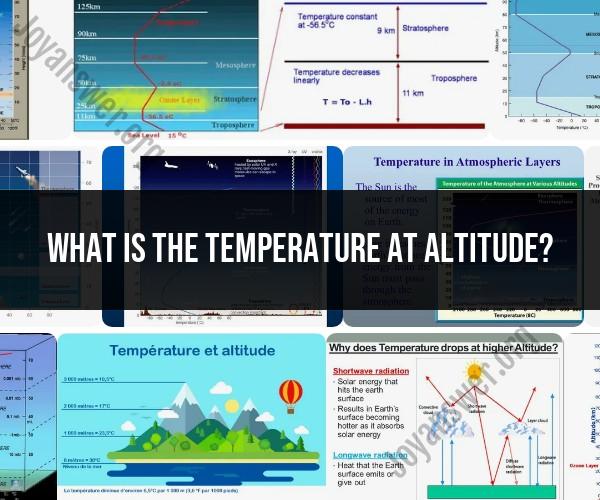
- The standard atmosphere model: The standard atmosphere model is a theoretical model of the Earth's atmosphere that is based on average temperature and pressure measurements at different altitudes. The standard atmosphere model can be used to calculate temperature at altitude using the following formula:
T = T_0 - 0.0065 * h
where:
T is the temperature at altitude h (in meters)
T_0 is the temperature at sea level (15 °C)
The lapse rate method: The lapse rate method is a more accurate method for calculating temperature at altitude, but it requires knowledge of the current temperature and the lapse rate. The lapse rate is the rate at which temperature decreases with altitude. The lapse rate varies depending on the location and the time of year, but it is typically around 6.5 °C/km.
To calculate temperature at altitude using the lapse rate method, use the following formula:
T = T_0 - L * h
where:
- T is the temperature at altitude h (in meters)
- T_0 is the current temperature
- L is the lapse rate
Determining Atmospheric Temperature Variations with Altitude
Atmospheric temperature variations with altitude are caused by a number of factors, including:
- Solar radiation: Solar radiation heats the Earth's atmosphere, but the amount of solar radiation that reaches a particular altitude decreases with altitude. This is because the atmosphere absorbs some of the solar radiation before it reaches the ground.
- Greenhouse gases: Greenhouse gases trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere. The concentration of greenhouse gases decreases with altitude, so the temperature also decreases with altitude.
- Adiabatic cooling: Adiabatic cooling is the cooling that occurs when air is forced to rise. As air rises, it expands and cools. This is because the pressure of the air decreases as it rises.
The Relationship Between Altitude and Temperature
The relationship between altitude and temperature is negative. This means that temperature decreases with altitude. The rate at which temperature decreases with altitude is called the lapse rate. The lapse rate varies depending on the location and the time of year, but it is typically around 6.5 °C/km.
The decrease in temperature with altitude is due to a number of factors, including the absorption of solar radiation by the atmosphere, the decrease in the concentration of greenhouse gases with altitude, and adiabatic cooling.
Temperature at Altitude
The temperature at altitude can vary depending on a number of factors, including:
- Location: The temperature at altitude is typically lower in colder climates than in warmer climates.
- Time of year: The temperature at altitude is typically lower in the winter than in the summer.
- Time of day: The temperature at altitude is typically lower at night than during the day.
- Weather conditions: The temperature at altitude can be affected by weather conditions, such as clouds and precipitation.
Conclusion
Calculating temperature at altitude is a complex process that requires knowledge of a number of factors, including the standard atmosphere model, the lapse rate, and the current weather conditions. However, there are a number of resources available online and in libraries that can help you to calculate temperature at altitude.