Does NIST SP 800-63-3 recognize the four levels of assurance model?
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication 800-63-3 provides guidelines for digital identity assurance. These guidelines are organized into different assurance levels, each designed to meet specific security requirements for various applications. In this guide, we'll explore the assurance levels defined in NIST SP 800-63-3 and their significance.
Understanding Assurance Levels
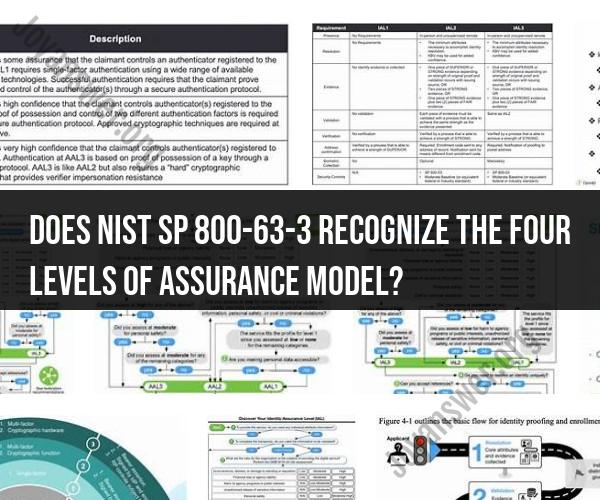
Assurance levels in NIST SP 800-63-3 represent the strength of identity proofing and authentication processes. They are categorized as Levels 1, 2, and 3, with each level having distinct security requirements and measures.
Assurance Level 1 (AL1)
AL1 is the lowest assurance level. It requires minimal identity proofing and is suitable for applications with low-security risk. Examples include accessing public information or basic online services. AL1 authentication typically involves a single factor, such as a password.
Assurance Level 2 (AL2)
AL2 requires higher identity proofing compared to AL1. It is appropriate for applications with moderate-security risk. AL2 authentication involves two factors: something the user knows (password) and something the user has (smartcard or token).
Assurance Level 3 (AL3)
AL3 represents the highest assurance level defined in NIST SP 800-63-3. It requires strong identity proofing and is suitable for applications with high-security risk. AL3 authentication involves multiple factors, including something the user knows, something the user has, and something the user is (biometric data).
Key Considerations
Choosing the appropriate assurance level depends on the security requirements and risk assessment of the application. Higher assurance levels offer stronger authentication but may involve more complex processes and higher costs.
Benefits of NIST SP 800-63-3 Assurance Levels
The assurance levels provide a standardized framework for evaluating the strength of identity proofing and authentication methods. This ensures consistency and comparability across different systems and applications. It also helps organizations implement appropriate security measures based on the sensitivity of the data and the potential consequences of a security breach.
Conclusion
Navigating the assurance levels in NIST SP 800-63-3 is crucial for implementing effective identity proofing and authentication practices. By understanding the differences between AL1, AL2, and AL3, organizations can make informed decisions about the level of security required for their applications while promoting user trust and data protection.