How do interest rates affect municipal bond prices?
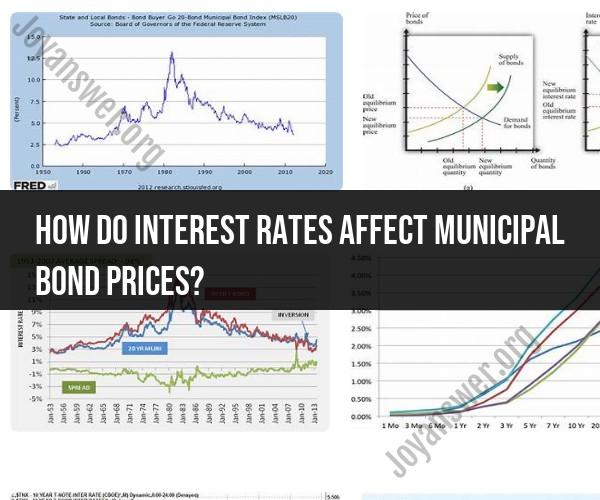
Interest rates have a significant impact on municipal bond prices. Municipal bonds, often referred to as "munis," are debt securities issued by state, local, or municipal governments to raise funds for various public projects or operational needs. The relationship between interest rates and municipal bond prices is generally inverse; when interest rates rise, bond prices tend to fall, and vice versa. Here's how it works:
Interest Rate Risk: Municipal bond prices are sensitive to changes in interest rates, particularly market interest rates. This sensitivity is known as "interest rate risk." When market interest rates increase, newly issued bonds pay higher coupon (interest) rates, making existing bonds with lower coupon rates less attractive to investors. As a result, the prices of existing municipal bonds with lower coupon rates tend to decrease to compete with new, higher-yielding bonds.
Coupon Rate vs. Market Interest Rate: The coupon rate of a municipal bond is the fixed interest rate that the issuer pays to bondholders. If the coupon rate on an existing bond is lower than the prevailing market interest rate, the bond will trade at a discount to its face value (par value). This discount is necessary to make the bond's effective yield competitive with current market rates.
Inverse Relationship: The relationship between interest rates and bond prices is inverse. When market interest rates fall, existing bonds with higher coupon rates become more attractive to investors, leading to an increase in their prices. This price increase can result in a premium above the bond's face value.
Yield and Price: It's essential to understand the concept of yield. Yield is the annual return on a bond, and it moves inversely to the bond's price. When bond prices rise due to falling interest rates, the yield on the bond decreases, and when bond prices fall due to rising interest rates, the yield increases.
Duration: The sensitivity of a municipal bond's price to changes in interest rates is also influenced by its duration. Duration is a measure of a bond's sensitivity to interest rate changes. Bonds with longer durations are generally more sensitive to interest rate fluctuations and may experience more significant price changes in response to interest rate movements.
Call Features: Some municipal bonds have call features that allow the issuer to redeem the bonds before maturity. These features can introduce additional complexity to the relationship between interest rates and bond prices, as issuers may choose to call bonds when it is financially advantageous to do so.
In summary, interest rates and municipal bond prices have an inverse relationship. When market interest rates rise, existing bond prices generally fall, and when interest rates fall, bond prices tend to rise. This inverse relationship is important for investors to consider when making decisions about buying, selling, or holding municipal bonds, as it can impact the total return on their investments.
Interest Rates and Municipal Bond Prices: Understanding the Connection
Interest rates and municipal bond prices have an inverse relationship. This means that when interest rates rise, municipal bond prices fall, and vice versa.
There are two main reasons for this relationship:
- New issues: When interest rates rise, new municipal bonds are issued with higher yields. This makes existing municipal bonds with lower yields less attractive to investors, and therefore, their prices fall.
- Reinvested proceeds: When municipal bonds mature, investors can reinvest the proceeds in new bonds with higher yields. This also makes existing municipal bonds with lower yields less attractive to investors, and therefore, their prices fall.
Municipal Bond Pricing: The Impact of Interest Rates
The impact of interest rates on municipal bond prices can vary depending on a number of factors, such as the type of bond, the maturity of the bond, and the overall market conditions.
In general, however, bonds with longer maturities are more sensitive to changes in interest rates than bonds with shorter maturities. This is because bonds with longer maturities have more time to be affected by changes in interest rates.
For example, if interest rates rise by 1%, the price of a 10-year municipal bond is likely to fall by more than the price of a 2-year municipal bond.
Navigating Municipal Bond Markets: Interest Rate Dynamics
Investors who are considering investing in municipal bonds should be aware of the impact of interest rates on bond prices. Investors who are concerned about rising interest rates may want to consider shorter-maturity bonds or floating-rate bonds.
Floating-rate bonds are bonds that have a variable interest rate that is reset periodically. This means that the interest rate on a floating-rate bond will rise or fall along with market interest rates.
Investors should also consider their investment goals and risk tolerance before investing in municipal bonds. Municipal bonds can be a good option for investors who are looking for a low-risk investment with tax advantages. However, investors should be aware that municipal bond prices can fall if interest rates rise.
Conclusion
Interest rates and municipal bond prices have an inverse relationship. This means that when interest rates rise, municipal bond prices fall, and vice versa. Investors should be aware of this relationship before investing in municipal bonds.