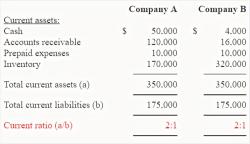
What do you have to pay for a home loan?
When obtaining a home loan, there are various costs and fees associated with the process. It's important for borrowers to understand these costs to make informed financial decisions. Here are some common costs associated with a home loan:
Interest Rate:The interest rate is the cost of borrowing money and is typically expressed as an annual percentage rate (APR). It is a crucial factor in determining the overall cost of the loan. The interest rate can be fixed or variable.
Loan Origination Fees:Lenders may charge loan origination fees to cover the administrative costs of processing the loan. This fee is usually a percentage of the loan amount.
Points:Points are fees paid to the lender at closing in exchange for a lower interest rate. Each point typically costs 1% of the loan amount and can be an upfront cost to reduce long-term interest payments.
Appraisal Fees:Before approving a loan, lenders often require an appraisal of the property to determine its value. Borrowers typically pay for this appraisal, and the cost can vary.
Credit Report Fees:Lenders check the credit history of borrowers, and there may be fees associated with obtaining a credit report.
Title Insurance:Title insurance protects the lender and the borrower against any issues with the property's title. Both lender's title insurance and, in some cases, owner's title insurance may be required.
Homeowners Insurance:Borrowers are generally required to have homeowners insurance to protect the property and the lender's interest in it. The cost of insurance can vary based on the property and its location.
Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI):If the down payment is less than 20% of the home's purchase price, lenders may require private mortgage insurance. This insurance protects the lender in case the borrower defaults on the loan.
Property Taxes:Property taxes are assessed by local governments, and homeowners typically pay them annually or as part of their monthly mortgage payments. Lenders may collect property tax payments and hold them in an escrow account.
Homeowners Association (HOA) Fees:If the property is part of a homeowners association, the borrower may need to pay monthly or annual HOA fees for community maintenance and amenities.
Closing Costs:Closing costs include a variety of fees, such as legal fees, document preparation fees, and settlement fees. The buyer is usually responsible for these costs, and they can be negotiated as part of the home purchase process.
It's important for borrowers to carefully review the Loan Estimate and Closing Disclosure provided by the lender, which outline the estimated and final costs associated with the home loan. Additionally, borrowers should be aware that ongoing costs such as property taxes, homeowners insurance, and, if applicable, PMI and HOA fees, will continue throughout the life of the loan. Consulting with a mortgage advisor or financial professional can help borrowers understand these costs and make informed decisions.
What expenses are involved in obtaining a home loan?
Obtaining a home loan involves various expenses that borrowers should be aware of and factor into their financial planning. These expenses can be broadly categorized into upfront costs and ongoing costs.
Upfront Costs
Down payment: This is a significant upfront payment typically ranging from 10% to 20% of the property's purchase price. It demonstrates the buyer's financial commitment and reduces the amount borrowed from the lender.
Closing costs: These are fees incurred during the loan closing process, typically ranging from 2% to 5% of the loan amount. They cover various services, including appraisals, title insurance, lender fees, and government taxes.
Origination fee: This is a fee charged by the lender for processing and originating the loan. It typically ranges from 1% to 2% of the loan amount.
Discount points: These are optional fees paid upfront by the borrower to lower the interest rate on the loan. Each point typically reduces the interest rate by 0.25%.
Home inspection fee: This fee is paid for a professional inspection of the property to identify potential structural, mechanical, or safety issues.
Credit report fee: This fee is paid to obtain a copy of the borrower's credit report, which the lender reviews to assess creditworthiness.
Appraisal fee: This fee is paid for a professional appraisal of the property's value to ensure it aligns with the purchase price.
Title insurance: This protects the lender from financial losses if there are any title defects or liens on the property.
Survey fee: This fee is paid for a professional survey of the property's boundaries and property lines.
HOA fees (if applicable): Homeowners' association fees are recurring charges paid by homeowners in communities with HOAs to maintain common areas and amenities.
Ongoing Costs
Mortgage payments: These are monthly payments that cover the principal amount borrowed, interest, and any additional fees or charges.
Property taxes: These are annual taxes levied by local governments based on the property's assessed value.
Homeowners insurance: This protects the property from financial losses due to damage, theft, or other perils.
Private mortgage insurance (PMI): This is required for mortgages with a down payment of less than 20%. It protects the lender in case of borrower default.
Maintenance and repairs: These are ongoing expenses associated with upkeep and repairs of the property, such as plumbing, electrical, and roofing maintenance.
Utilities: These include monthly or bi-monthly charges for essential services like electricity, water, gas, and garbage collection.
HOA fees (if applicable): These recurring charges are used for maintaining common areas, amenities, and enforcing community rules in HOA communities.
By understanding and budgeting for these expenses, borrowers can make informed decisions about homeownership and manage their finances effectively.