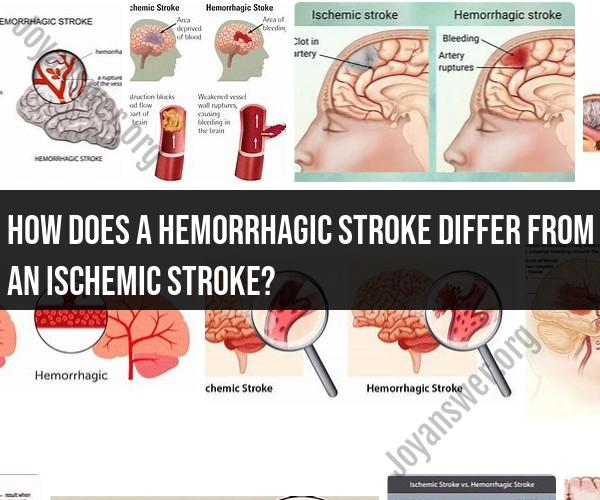
How does a hemorrhagic stroke differ from an ischemic stroke?
Hemorrhagic strokes and ischemic strokes are two primary types of strokes, and they differ in their underlying causes and characteristics. Here are the key differences between them:
1. Cause:
Hemorrhagic Stroke: This type of stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures or leaks, leading to bleeding within the brain (intracerebral hemorrhage) or into the space surrounding the brain (subarachnoid hemorrhage). The most common cause of hemorrhagic strokes is high blood pressure (hypertension), but they can also result from aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), or bleeding disorders.
Ischemic Stroke: Ischemic strokes are caused by a blockage or clot that reduces or completely halts blood flow to a part of the brain. The blockage can occur due to a blood clot forming within a blood vessel in the brain (thrombotic stroke) or a clot traveling from another part of the body to the brain (embolic stroke). Common risk factors for ischemic strokes include atherosclerosis, heart disease, and atrial fibrillation.
2. Location of Brain Damage:
Hemorrhagic Stroke: In a hemorrhagic stroke, brain damage occurs due to the direct effects of bleeding, which can lead to increased pressure and damage to surrounding brain tissue. The extent of damage depends on the location and size of the bleed.
Ischemic Stroke: Ischemic strokes result in brain damage in areas downstream from the blocked blood vessel. Without a steady supply of oxygen and nutrients, brain cells in the affected area can quickly become damaged or die.
3. Symptoms:
Hemorrhagic Stroke: Common symptoms of a hemorrhagic stroke may include a sudden and severe headache, nausea and vomiting, weakness or numbness on one side of the body, vision changes, confusion, and loss of consciousness.
Ischemic Stroke: Ischemic strokes often present with sudden symptoms such as facial drooping, arm weakness, speech difficulties (slurred speech or difficulty speaking), confusion, trouble walking, and loss of coordination.
4. Diagnosis:
Hemorrhagic Stroke: Diagnosis of a hemorrhagic stroke is typically made through imaging tests such as a CT scan or MRI, which can reveal the presence of bleeding within the brain.
Ischemic Stroke: Ischemic strokes are also diagnosed using imaging tests, such as CT or MRI scans, which can show the blocked blood vessel or the area of reduced blood flow.
5. Treatment:
Hemorrhagic Stroke: Treatment for a hemorrhagic stroke aims to control bleeding, reduce pressure within the brain, and address the underlying cause. This may involve surgery to repair the blood vessel, medications to lower blood pressure, and other supportive measures.
Ischemic Stroke: Treatment for an ischemic stroke is often focused on restoring blood flow to the affected area of the brain. This may involve the use of clot-busting medications (thrombolytics) or mechanical procedures such as thrombectomy to remove the clot.
Both types of strokes are medical emergencies that require immediate attention. The specific treatment approach and outcome can vary depending on the individual case, the location of the stroke, and how quickly medical intervention is sought. Recognizing the symptoms of a stroke and seeking prompt medical attention can significantly improve the chances of a positive outcome.
Hemorrhagic vs. Ischemic Stroke: Key Differences in Stroke Types
A stroke is a medical emergency that occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients. This can damage or kill brain cells. There are two main types of stroke: hemorrhagic stroke and ischemic stroke.
Hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures or bursts, causing bleeding into the brain tissue. This can be caused by a number of factors, including high blood pressure, aneurysms, and arteriovenous malformations (AVMs).
Ischemic stroke occurs when a blood clot blocks a blood vessel leading to the brain, or when a blood vessel in the brain becomes narrowed or blocked. This can be caused by a number of factors, including atherosclerosis, heart disease, and diabetes.
Key differences between hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke:
| Feature | Hemorrhagic stroke | Ischemic stroke |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Bleeding into the brain | Blockage of a blood vessel leading to the brain |
| Symptoms | Sudden, severe headache; nausea and vomiting; confusion and disorientation; weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body; difficulty speaking or understanding speech; vision problems; loss of balance or coordination | Sudden onset of weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body; confusion and disorientation; difficulty speaking or understanding speech; vision problems; loss of balance or coordination |
| Treatment | Emergency surgery or other procedures to stop the bleeding and reduce pressure on the brain | Medication to dissolve the blood clot or surgery to open the blocked blood vessel |
Exploring the Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of Hemorrhagic Stroke
Causes of hemorrhagic stroke:
- High blood pressure
- Aneurysms
- Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs)
- Head injury
- Blood thinners
- Certain medical conditions, such as liver disease and leukemia
Symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke:
- Sudden, severe headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Confusion and disorientation
- Weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Vision problems
- Loss of balance or coordination
Treatment for hemorrhagic stroke:
Hemorrhagic stroke is a medical emergency and requires immediate medical attention. Treatment may involve surgery to stop the bleeding and reduce pressure on the brain. Other treatments may include medication to control blood pressure, pain, and seizures.
Understanding Ischemic Stroke: Prevention and Recovery Strategies
Causes of ischemic stroke:
- Atherosclerosis
- Heart disease
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Family history of stroke
Symptoms of ischemic stroke:
- Sudden onset of weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body
- Confusion and disorientation
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Vision problems
- Loss of balance or coordination
Prevention strategies for ischemic stroke:
- Control high blood pressure
- Manage diabetes
- Quit smoking
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Exercise regularly
- Eat a healthy diet
Recovery strategies for ischemic stroke:
Recovery from a stroke varies depending on the severity of the stroke and the area of the brain that was damaged. Some people make a full recovery within a few weeks or months, while others may experience permanent disabilities.
Recovery strategies may include:
- Physical therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Speech therapy
- Medication
- Support groups
If you think you or someone you know is having a stroke, call 911 immediately. Every second counts when it comes to stroke treatment.