What are the properties of solids?
Exploring the properties of solids is an essential aspect of material science and physics. Solids are one of the three fundamental states of matter, along with liquids and gases. Understanding the properties of solids helps us comprehend their behavior, characteristics, and applications in various fields. Here's a comprehensive overview of the properties of solids:
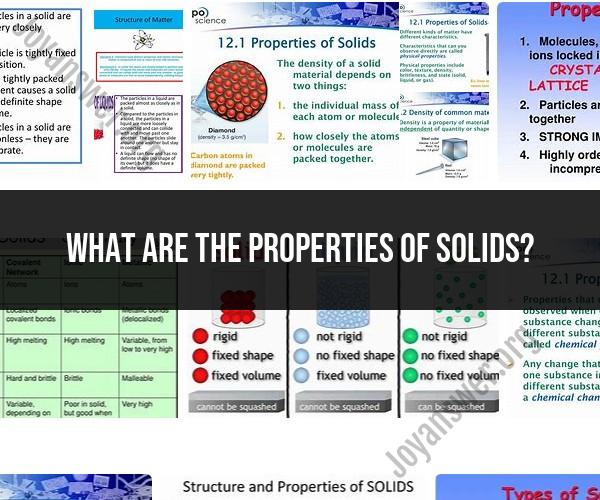
Density: Solids have a relatively high density compared to liquids and gases. Density is the mass per unit volume and is a measure of how tightly the particles are packed within a solid.
Particle Arrangement: In solids, particles are closely packed and arranged in a regular and repeating pattern. This arrangement contributes to the solid's stability and shape.
Shape and Volume: Solids have a definite shape and volume. The strong intermolecular forces hold the particles in fixed positions, allowing solids to maintain their shape unless external forces are applied.
Rigidity and Incompressibility: Solids are rigid and do not easily compress. The arrangement of particles and strong intermolecular forces prevent significant changes in volume under pressure.
Mechanical Properties:
- Strength: Solids exhibit varying levels of strength, which depends on the type of solid and the forces between particles.
- Hardness: Hardness refers to a solid's resistance to deformation or scratching. Different materials have different hardness levels.
- Elasticity: Solids can deform under stress, but many return to their original shape when the stress is removed due to elastic behavior.
Thermal Properties:
- Melting Point: The temperature at which a solid changes to a liquid is called its melting point. Different materials have different melting points.
- Heat Conductivity: Solids can conduct heat. Some materials are good conductors (metals), while others are poor conductors (insulators).
- Thermal Expansion: Solids expand when heated and contract when cooled. This property is used in various engineering applications.
Electrical Properties:
- Conductivity: Some solids are good conductors of electricity (metals), while others are insulators or semiconductors.
- Band Gap: In semiconductors, the band gap determines the energy required for electrons to move from the valence band to the conduction band, allowing electrical conductivity.
Optical Properties:
- Transparency and Opacity: Solids can be transparent, translucent, or opaque based on how they interact with light.
- Refraction and Reflection: Some solids exhibit refraction and reflection of light, contributing to their optical properties.
Crystal Structure: Solids can have different crystal structures, such as cubic, tetragonal, hexagonal, and more. The arrangement of particles within these structures affects the material's properties.
Magnetic Properties: Solids can be magnetic (ferromagnetic, paramagnetic, diamagnetic) based on the alignment of electron spins and the presence of unpaired electrons.
Chemical Reactivity: Solids can react with other substances, undergo phase changes, and form compounds through chemical reactions.
Phonons: Solids transmit vibrations through lattice vibrations known as phonons, which affect thermal conductivity and other properties.
In summary, exploring the properties of solids involves understanding their density, particle arrangement, mechanical, thermal, electrical, and optical properties, as well as crystal structures, chemical reactivity, and more. The unique characteristics of different solids play a crucial role in their applications across various industries, from materials science to electronics and engineering.