What are the disadvantages of financial statements?
While financial statements are crucial for assessing the financial health and performance of a business, they also have some disadvantages and limitations. It's important to be aware of these drawbacks when using financial statements for analysis. Here are some of the disadvantages of financial statements:
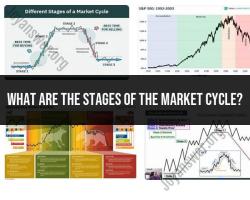
Historical Information: Financial statements provide historical data about a company's financial performance. They reflect the past and may not necessarily predict future trends or market changes.
Limited Scope: Financial statements focus primarily on quantitative data, such as numbers, figures, and monetary values. They may not capture qualitative factors like management quality, employee morale, or customer satisfaction.
Estimates and Assumptions: Financial statements often involve estimates and assumptions, particularly in areas like depreciation, valuation of assets, and accounting for contingencies. These estimates can vary and impact the accuracy of the statements.
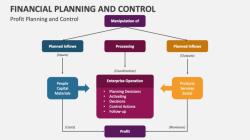
Simplification: To make financial data understandable and comparable, financial statements use simplifications and conventions. While these are necessary, they can lead to oversimplification and may not fully reflect the complexity of a business.
Timing Issues: Financial statements are prepared at specific intervals, such as quarterly or annually. They may not capture short-term fluctuations or sudden changes in a company's financial position.
Manipulation and Fraud: Financial statements can be manipulated or misrepresented through creative accounting practices, leading to fraudulent reporting or misrepresentation of a company's financial health.
No Context: Financial statements provide numbers without context. To interpret them accurately, users need to consider industry benchmarks, economic conditions, and company-specific factors.
Lack of Non-Financial Information: Financial statements do not include information on non-financial aspects like a company's market position, brand reputation, or competitive advantage.
Aggregation of Data: Information on financial statements is often aggregated, which can mask important details or variations within the business.
No Future Orientation: Financial statements do not provide forward-looking information. Investors and analysts often need to rely on additional tools like financial forecasting to assess a company's future prospects.
Complexity: Financial statements can be complex, especially for non-financial professionals. Interpreting them accurately requires financial literacy and expertise.
External Factors: Financial statements may not account for external factors, such as changes in regulations, shifts in market conditions, or unexpected events like natural disasters, which can impact a company's financial performance.
Despite these disadvantages, financial statements remain a fundamental tool for financial analysis and decision-making. To mitigate some of these limitations, financial professionals often use supplementary information and analysis techniques to gain a more comprehensive understanding of a company's financial position and prospects.