What are the different types of differentiation?
In mathematics, differentiation refers to the process of finding the derivative of a function, which represents the rate of change of the function with respect to its independent variable. Differentiation has several types and rules associated with it. Here are some of the different types of differentiation:
Ordinary Differentiation: Ordinary differentiation is the most common type and involves finding the derivative of a function with respect to a single independent variable. The result is a single derivative or slope of the function.
Partial Differentiation: Partial differentiation is used when a function has more than one independent variable. It involves finding the derivative with respect to one of the independent variables while treating the others as constants. This is often used in multivariable calculus to analyze functions of multiple variables.
Implicit Differentiation: Implicit differentiation is used when an equation involves both dependent and independent variables and cannot be easily solved for the dependent variable explicitly. It involves finding the derivative of the equation implicitly by differentiating each term and treating the dependent variable as a function of the independent variable.
Higher-Order Differentiation: Higher-order differentiation involves finding the second, third, or higher derivatives of a function. The second derivative represents the rate of change of the rate of change (acceleration), and higher-order derivatives provide information about further rates of change.
Parametric Differentiation: Parametric differentiation is used when a function is defined parametrically, meaning that both the dependent and independent variables are expressed in terms of a third parameter. Differentiation is carried out with respect to this parameter.
Total Differentiation: Total differentiation, also known as the differential, considers the changes in both the dependent and independent variables. It results in a differential equation that relates changes in the variables.
Logarithmic Differentiation: Logarithmic differentiation is a technique used to differentiate functions that involve products, quotients, and powers of functions. It involves taking the natural logarithm of both sides of an equation, simplifying the expression, and then differentiating.
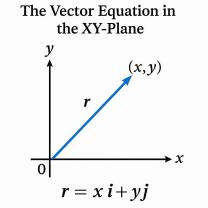
Vector Differentiation: Vector differentiation deals with differentiation in vector calculus, where functions are vectors or vector-valued functions. It includes operations like the gradient (nabla) operator, divergence, and curl.
Differentiation Rules: Differentiation also involves various rules and techniques, such as the product rule, quotient rule, chain rule, and trigonometric differentiation rules, to differentiate specific types of functions.
Numerical Differentiation: In numerical analysis, numerical differentiation methods are used to estimate derivatives numerically using data points and finite differences.
The specific type of differentiation used depends on the nature of the function and the problem being addressed. Each type of differentiation has its applications in various fields of mathematics, science, engineering, and economics.
Differentiation in Education: Exploring Various Approaches
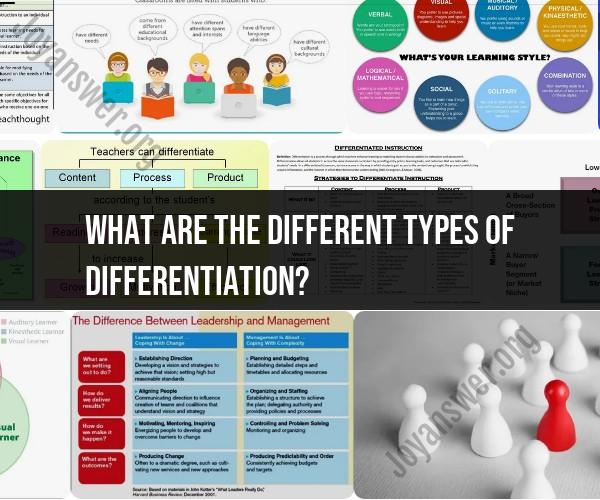
Differentiation in education is a pedagogical approach that involves tailoring instruction to meet the individual needs of learners. It recognizes that all learners are different and that they learn in different ways. Differentiation can be achieved through a variety of approaches, such as:
- Content differentiation: This involves providing students with different content to learn, or different ways to access and engage with content. For example, a teacher might provide students with different reading materials at different levels, or offer students different ways to complete a project.
- Process differentiation: This involves providing students with different ways to learn the same content. For example, a teacher might provide students with different learning activities, or allow students to work at their own pace.
- Product differentiation: This involves providing students with different ways to demonstrate their learning. For example, a teacher might allow students to choose between writing a report, creating a presentation, or making a video to demonstrate their understanding of a topic.
Understanding Differentiation as a Pedagogical Strategy
Differentiation is not about making things easier or harder for some students. It is about providing all students with the opportunity to learn and succeed. Differentiation is a way to ensure that all students are challenged and engaged, and that they are able to reach their full potential.
Types and Models of Differentiation in Classroom Instruction
There are many different types and models of differentiation in classroom instruction. Some common types include:
- Tiered instruction: This model involves providing students with different levels of support, based on their readiness level. For example, a teacher might provide students with different worksheets or different groups of practice problems.
- Flexible grouping: This model involves grouping students together based on their interests, learning needs, or skill levels. For example, a teacher might group students together to work on a project, or to complete a learning activity.
- Compacting: This model involves accelerating the pace of instruction for students who have mastered the material quickly. This allows students to learn more challenging material or to move on to new topics earlier.
- Enrichment: This model involves providing students with additional opportunities to learn and grow. This can be done through independent projects, extracurricular activities, or field trips.
Implementing Differentiated Instruction for Diverse Learners
Differentiation can be implemented in a variety of ways to meet the needs of diverse learners. Here are a few tips:
- Get to know your students. The first step to differentiating instruction is to get to know your students and their individual needs. This can be done through formal assessments, informal observations, and conversations with students and their families.
- Plan for differentiation from the start. When planning lessons and activities, think about how you can differentiate for different learners. This will help you to be more efficient and effective in your teaching.
- Provide students with choices. Students learn best when they have choices about their learning. Give students choices about the content they learn, the process they use to learn, and the product they create to demonstrate their learning.
- Be flexible. Be prepared to adjust your plans as needed. Students may need different levels of support than you originally anticipated.
- Monitor student progress. It is important to monitor student progress to ensure that differentiation is working. This can be done through formal assessments, informal observations, and conversations with students and their families.
Success Stories and Best Practices in Educational Differentiation
There are many success stories and best practices in educational differentiation. Here are a few examples:
- One teacher used tiered instruction to help her students learn about the water cycle. She provided students with different levels of support, based on their readiness level. For example, she provided some students with a graphic organizer to help them organize their thoughts, while she provided other students with more challenging reading materials.
- Another teacher used flexible grouping to help her students learn about different types of government. She grouped students together based on their interests and learning needs. For example, she grouped students together who were interested in learning about the United States government, and she grouped students together who were interested in learning about the government of their home country.
- A third teacher used enrichment to help her students learn about different cultures. She provided students with additional opportunities to learn and grow, such as through independent projects, extracurricular activities, and field trips. For example, she organized a field trip to a local museum of world culture.
Differentiation is a powerful tool that can help all students learn and succeed. By implementing differentiation in your classroom, you can create a more inclusive and equitable learning environment.