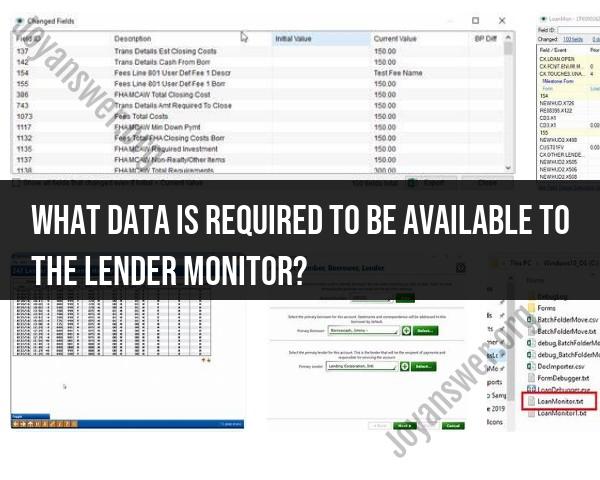
What data is required to be available to the lender monitor?
Lender monitoring is an essential component of the lending and credit industry, particularly in the context of regulatory compliance and risk management. The specific data required for lender monitoring can vary depending on the regulatory environment, the type of lending institution, and the lender's internal policies. However, there are several key categories of data that lenders typically monitor to ensure compliance and assess risk. These may include:
Borrower Information:
- Personal information: Name, address, Social Security number, and other identifying details.
- Credit history: Credit scores, credit reports, and credit payment history.
- Employment and income details: Employment status, income level, and stability of income.
Loan Documentation:
- Loan agreements: Details of the loan agreement, including the loan amount, interest rate, term, and repayment schedule.
- Collateral details: If the loan is secured, information about the collateral, including its value and condition.
Regulatory Compliance Data:
- Regulatory documentation: Lenders must comply with various laws and regulations, such as the Equal Credit Opportunity Act (ECOA), Truth in Lending Act (TILA), and others. Monitoring compliance with these laws may involve checking the required disclosures and documentation.
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) Data:
- Lenders are often required to collect information on borrowers to prevent money laundering and verify the identity of customers. This includes gathering identification documents, verifying the source of funds, and conducting due diligence.
Loan Performance Data:
- Payment history: Lenders monitor whether borrowers are making timely payments and track any missed or late payments.
- Loan delinquency and default data: This includes data on loans that are past due, as well as those that have gone into default.
Credit Risk Data:
- Credit risk models: Lenders use various models to assess the credit risk of borrowers. This data is used to determine interest rates and loan approvals.
- Risk management strategies: Data on how the lender is managing and mitigating credit risk, including underwriting guidelines, credit policies, and risk assessment procedures.
Market Data:
- Economic conditions: Information on local and national economic conditions that may impact borrowers' ability to repay loans.
- Housing and real estate market data: For mortgage lenders, data on property values and market conditions is crucial.
Complaint and Dispute Resolution Data:
- Records of customer complaints and disputes: Lenders monitor and track customer complaints and how they are resolved.
Financial Performance Data:
- Lender's financial statements: Regulators may require lenders to provide financial statements and reports as part of compliance monitoring.
Consumer Protection Data:
- Data on consumer protection measures and adherence to consumer protection laws.
It's important to note that the specific data required for lender monitoring can vary not only by the type of lender (e.g., bank, credit union, online lender) but also by the specific lending products offered (e.g., mortgages, personal loans, credit cards). Lenders must stay informed about regulatory requirements and internal policies to ensure they collect and monitor the necessary data effectively. Failure to do so can result in regulatory non-compliance and increased risk.
Lender Monitoring: What Data Is Required to Be Available
The specific data that lenders are required to have available for monitoring will vary depending on the type of loan and the regulatory environment. However, some common data elements that are required include:
- Applicant information: This may include the applicant's name, address, income, debt-to-income ratio, credit score, and loan purpose.
- Loan information: This may include the loan amount, interest rate, term, and type of loan.
- Performance data: This may include the borrower's payment history, delinquency status, and foreclosure history.
Regulatory Requirements for Lender Oversight and Reporting
Lenders are subject to a variety of regulatory requirements related to oversight and reporting. These requirements are designed to protect consumers and ensure that lenders are operating in a fair and responsible manner.
Some of the key regulatory requirements for lender oversight and reporting include:
- The Equal Credit Opportunity Act (ECOA): ECOA prohibits lenders from discriminating against borrowers on the basis of race, color, religion, national origin, sex, marital status, age, receipt of income from a public assistance program, or because an applicant has exercised in good faith any right under the Consumer Credit Protection Act.
- The Fair Housing Act (FHA): The FHA prohibits discrimination in housing on the basis of race, color, religion, national origin, sex, familial status, and disability.
- The Home Mortgage Disclosure Act (HMDA): HMDA requires lenders to collect and report data on mortgage loans. This data is used to identify and address patterns of discrimination in lending.
Data Transparency in Financial Institutions
Financial institutions are increasingly recognizing the importance of data transparency. Data transparency can help to build trust with customers, reduce risk, and improve decision-making.
One way to promote data transparency is to provide customers with access to their own data. This can be done through online portals or mobile apps. Financial institutions can also make their data more transparent by publishing it on their websites or releasing it to third-party developers.
Ensuring Accountability in Lending Practices
Accountability is essential for ensuring that lenders are operating in a fair and responsible manner. Lenders should have clear policies and procedures in place to ensure that all borrowers are treated fairly.
Lenders should also have a process in place for handling complaints from borrowers. This process should be fair and efficient, and it should allow borrowers to have their complaints resolved in a timely manner.
The Role of Data in Mitigating Risk
Data can play a vital role in helping lenders to mitigate risk. By analyzing data, lenders can identify patterns and trends that can be used to predict which borrowers are more likely to default on their loans.
Lenders can also use data to develop risk-based pricing models. These models can be used to set interest rates and other loan terms in a way that reflects the borrower's risk level.
By using data to mitigate risk, lenders can reduce their losses and protect their customers.
Overall, data is essential for lender monitoring, regulatory compliance, data transparency, accountability, and risk mitigation. Lenders that use data effectively can better serve their customers and protect their own interests.