What are the causes of blisters on the hands?
Blisters on the hands can occur due to various reasons, typically involving friction, burns, allergic reactions, infections, or certain medical conditions. Some common causes include:
Friction: Continuous rubbing or friction against the skin, especially when performing tasks like using tools, handling sports equipment, or repetitive motions, can cause blisters.
Burns: Thermal burns from touching hot surfaces or liquids, chemical burns from exposure to certain substances, or sunburns can lead to blisters on the hands.
Allergic Reactions: Contact dermatitis caused by exposure to irritants or allergens like certain soaps, detergents, cosmetics, or plants (such as poison ivy or poison oak) can result in blisters.
Infections: Viral infections like herpes simplex (cold sores) or bacterial infections such as impetigo can cause blisters on the hands.
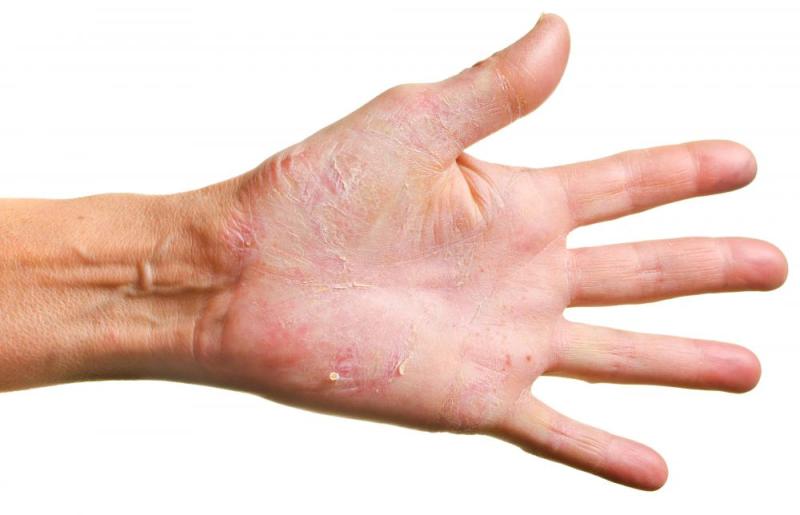
Skin Conditions: Conditions like eczema, psoriasis, or dyshidrotic eczema (a specific type of eczema affecting the hands and feet) can lead to the formation of blisters.
Insect Bites or Stings: Certain insect bites or stings, like those from ants, bees, or wasps, can cause localized allergic reactions resulting in blisters.
Medical Treatments: Certain medical treatments, such as radiation therapy or certain medications, can cause skin reactions leading to blisters.
Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like pemphigus or bullous pemphigoid, which are autoimmune disorders affecting the skin, can cause blister formation.
The treatment for blisters on the hands depends on the underlying cause. In most cases, it's advisable to avoid further irritation, keep the area clean, and protect the blister to prevent infection. Over-the-counter remedies like bandages, antiseptic creams, or cold compresses can help alleviate discomfort.
However, if blisters are severe, recurrent, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms like fever, pain, or signs of infection, it's essential to seek medical attention for proper evaluation and treatment.
Medical Conditions Causing Hand Blisters
Dyshidrotic Eczema: A skin condition characterized by tiny, fluid-filled blisters on the palms, sides of the fingers, and sometimes the soles of the feet. The exact cause is unknown, but it may be triggered by stress, sweating, or exposure to certain chemicals or allergens.
Pompholyx: A less common skin condition similar to dyshidrotic eczema, but the blisters are larger and deeper. The cause of pompholyx is also unknown, but it may be linked to allergies or autoimmune disorders.
Contact Dermatitis: An allergic reaction to a substance that touches the skin, causing inflammation, redness, and blisters. Common culprits include latex, nickel, fragrances, and certain plants.
Herpes Simplex Virus: The virus that causes cold sores can also cause blisters on the hands, especially near the fingers. The blisters are typically small and painful, and they may appear in clusters.
Impetigo: A bacterial skin infection that causes small, fluid-filled blisters that can rupture and form a honey-colored crust. It is more common in children and is often spread through direct contact.
External Factors Causing Hand Blisters
Friction: Repetitive friction against the skin, especially from tools, sports equipment, or musical instruments, can cause blisters to form. The friction rubs against the outer layers of the skin, causing them to separate and form fluid-filled pockets.
Repetitive Motion: Engaging in repetitive hand movements, such as typing, writing, or using tools, can lead to friction and blister formation. The constant rubbing and pressure can irritate and damage the skin, making it more susceptible to blisters.
Heat and Moisture: Hot and humid environments can soften the skin, making it more vulnerable to friction and blister formation. Sweat can also increase friction and contribute to blister development.
Ill-fitting Gloves: Wearing gloves that are too tight or too loose can increase friction and rubbing against the skin, leading to blisters. Proper-fitting gloves can help prevent friction and protect the hands.
Chemical Exposure: Exposure to harsh chemicals or detergents can irritate and damage the skin, making it more prone to blister formation. It is essential to wear gloves and protective clothing when handling chemicals.
Prevention of Hand Blisters
Avoid Friction: Minimize friction against the hands by using proper tools, wearing protective gloves, and taking breaks from repetitive activities.
Moisturize Regularly: Keep the hands well-moisturized to maintain skin integrity and reduce susceptibility to blisters.
Protect from Heat and Moisture: Avoid prolonged exposure to hot and humid environments, and wear breathable gloves when necessary.
Treat Underlying Conditions: If blisters are caused by a medical condition, seek treatment to manage the underlying issue and prevent recurrences.
Seek Medical Attention: If blisters are severe, painful, or do not heal on their own, consult a doctor or dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment.