What is considered severe hypothyroidism?
Severe hypothyroidism refers to a significant and profound deficiency of thyroid hormone levels in the body. Thyroid hormones play a crucial role in regulating various metabolic processes, and when their levels are markedly low, it can lead to a range of severe symptoms and potential complications.
The severity of hypothyroidism is often assessed based on the degree of hormone deficiency, clinical symptoms, and the impact on overall health. The following are key indicators that may be associated with severe hypothyroidism:
Extremely Low Thyroid Hormone Levels: Laboratory tests, including measurements of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), free thyroxine (FT4), and free triiodothyronine (FT3), are used to assess thyroid function. In severe hypothyroidism, TSH levels are usually elevated, while FT4 and FT3 levels are significantly reduced.
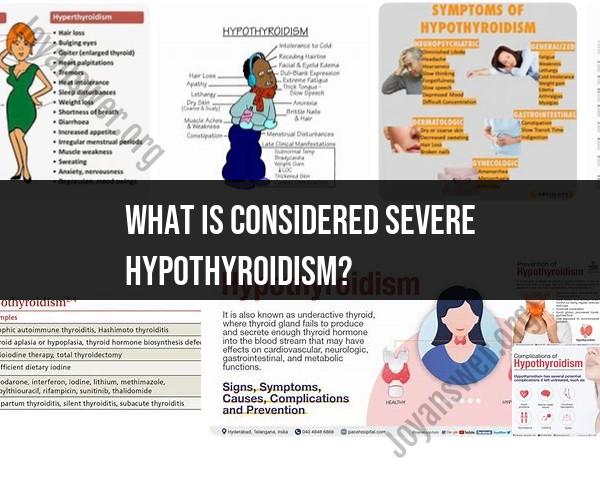
Profound Clinical Symptoms: Severe hypothyroidism is often characterized by a wide range of severe and debilitating symptoms. These may include extreme fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, constipation, brittle nails, dry skin, hair loss, muscle weakness, and depression.
Myxedema: In extreme cases of severe hypothyroidism, a condition known as myxedema may develop. Myxedema is a rare but serious complication characterized by swelling of the face, hands, and feet, along with other symptoms such as hypothermia, slowed heart rate, and altered mental status. Myxedema coma is an advanced and life-threatening form of myxedema.
It's important to note that hypothyroidism exists on a spectrum, ranging from mild to severe. The severity of the condition can vary among individuals, and the impact on overall health depends on factors such as the underlying cause, duration, and individual health status.
Treatment for severe hypothyroidism typically involves thyroid hormone replacement therapy, often with synthetic thyroid hormones such as levothyroxine. The goal of treatment is to restore thyroid hormone levels to normal and alleviate symptoms. In severe cases, hospitalization and supportive care may be necessary, especially if complications like myxedema coma are present.
If there are concerns about hypothyroidism or its severity, it is important to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and appropriate management. Thyroid function tests and clinical evaluation by a healthcare professional are essential for determining the severity of the condition and planning the appropriate course of treatment.
Severe Hypothyroidism: A Closer Look
1. Defining Severe Hypothyroidism
Severe hypothyroidism, also known as myxedema, is a rare but life-threatening condition that occurs when the thyroid gland produces very little or no thyroid hormone. This can lead to a significant slowdown in the body's metabolic processes, impacting numerous bodily functions.
2. Symptoms of Severe Hypothyroidism
Severe hypothyroidism can cause a range of alarming symptoms, including:
- Extreme fatigue and lethargy
- Severe cold intolerance
- Significant weight gain
- Dry, coarse skin and hair
- Puffy face and eyelids
- Slow heart rate and weak pulse
- Deepened, hoarse voice
- Confusion and memory problems
- Muscle weakness and cramps
- Depression and anxiety
3. Treatment for Severe Hypothyroidism
The treatment for severe hypothyroidism is hospitalization and immediate treatment with thyroid hormone medication. Levothyroxine is administered intravenously to quickly replenish the body's thyroid hormone levels. Other supportive care may also be necessary, such as treatment for hypothermia, low blood pressure, and other complications.
4. Complications of Untreated Severe Hypothyroidism
Untreated severe hypothyroidism can lead to life-threatening complications, including:
- Myxedema coma: A life-threatening condition with coma, dangerously low body temperature, and respiratory failure.
- Heart failure: Slowed heart rate and weakened muscles can lead to heart failure.
- Pneumonia: Increased susceptibility to respiratory infections due to weakened immune system.
- Seizures: In rare cases, severe hormone deficiency can trigger seizures.
- Death: If left untreated, myxedema coma can be fatal.
5. Health Issues Associated with Severe Hypothyroidism
Severe hypothyroidism can also contribute to various long-term health issues if not managed effectively:
- Infertility: Difficulty getting pregnant due to hormonal imbalance.
- Miscarriage: Increased risk of pregnancy loss during early stages.
- Birth defects: Potential for fetal development complications in pregnant women with untreated hypothyroidism.
- Depression and anxiety: Persistent mood problems due to ongoing hormone imbalance.
- Osteoporosis: Increased risk of bone fractures due to weakened bones.
Early diagnosis and proper treatment are crucial in managing severe hypothyroidism and preventing these serious complications. Consulting a doctor promptly if you experience any of the mentioned symptoms is vital for ensuring timely intervention and improving your health outcomes.
Conclusion
Severe hypothyroidism is a serious condition that can have life-threatening complications if left untreated. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are essential for managing this condition and preventing long-term health problems.