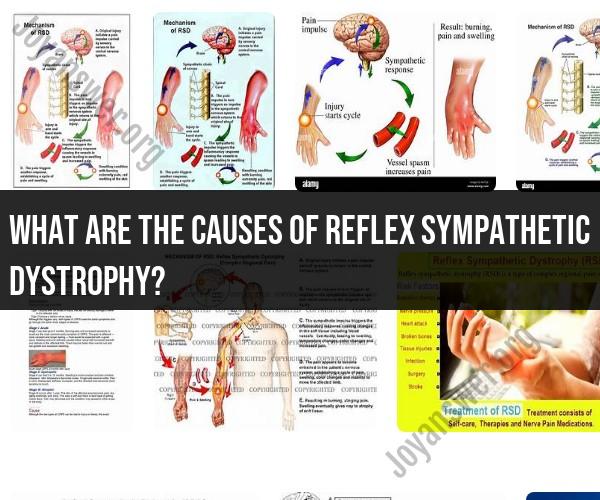
What are the causes of reflex sympathetic dystrophy?
The exact cause of reflex sympathetic dystrophy (RSD) is unknown, but it is thought to be caused by an injury or trauma to a nerve or limb. The injury can be minor or major, and it can occur anywhere in the body.
Some of the most common triggers for RSD include:
- Fractures: Fractures to the bones of the wrist, ankle, or shoulder are particularly common triggers for RSD.
- Soft tissue injuries: Injuries to the soft tissues, such as tendons, ligaments, and muscles, can also trigger RSD.
- Surgery: Surgery can also trigger RSD, especially if the surgery involves the nerves or limbs.
- Burns: Burns can also trigger RSD, especially if the burn is severe.
- Immunizations: In rare cases, immunizations can trigger RSD.
It is important to note that not everyone who experiences an injury or trauma will develop RSD. It is thought that there may be a genetic predisposition to RSD, and that certain people are more likely to develop the condition than others.
The exact mechanism by which RSD develops is also unknown. However, it is thought that the injury or trauma triggers an overactive sympathetic nervous system response. The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for the body's fight-or-flight response. When the sympathetic nervous system is overactive, it can lead to a number of problems, including pain, swelling, and changes in skin temperature and color.
RSD is a complex condition, and there is no single cure. However, there are a number of treatments that can help to manage the symptoms and improve function. These treatments may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, pain management, and psychological therapy.
If you think you may have RSD, it is important to see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to improve your chances of a better outcome.
Unraveling the Causes of Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy
The exact cause of reflex sympathetic dystrophy (RSD) is unknown, but it is thought to be caused by a combination of factors, including:
- Damage to the nerves: RSD often occurs after an injury to a nerve, such as a fracture, dislocation, or surgery.
- Autonomic nervous system dysfunction: The autonomic nervous system is responsible for regulating involuntary bodily functions, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and sweating. In RSD, the autonomic nervous system malfunctions, leading to changes in blood flow, sweating, and other bodily functions.
- Psychological factors: Stress, anxiety, and depression can all contribute to the development of RSD.
What Triggers Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy? Investigating the Factors
While the exact cause of RSD is unknown, there are a number of factors that can trigger the condition, including:
- Physical injury: As mentioned above, RSD often occurs after an injury to a nerve. This can be any type of injury, from a minor sprain to a major fracture.
- Surgery: RSD can also occur after surgery, especially surgery on the hand or foot.
- Repetitive strain injury: Repetitive strain injuries, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, can also trigger RSD.
- Trauma: Emotional trauma, such as the death of a loved one or a serious illness, can also trigger RSD.
Understanding the Origins and Contributors to Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy
The origins of RSD are thought to lie in the way that the body responds to injury. When a nerve is damaged, the body releases chemicals that cause inflammation and pain. In people with RSD, this inflammation and pain become exaggerated and spread to other areas of the body.
The exact mechanisms that cause this exaggerated inflammation and pain are not fully understood. However, it is thought that the sympathetic nervous system plays a role. The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for the "fight or flight" response. In RSD, the sympathetic nervous system becomes overactive, which leads to changes in blood flow, sweating, and other bodily functions.
Psychological factors can also play a role in the development and maintenance of RSD. Stress, anxiety, and depression can all make RSD symptoms worse.
It is important to note that not everyone who experiences an injury or other trigger will develop RSD. The exact reason why some people develop RSD and others do not is unknown.
Researchers are still working to understand the causes of RSD and to develop better treatments for the condition.