How to calculate hourly pay correctly for your employees?
Calculating hourly pay correctly for employees involves considering various factors, including the agreed-upon wage rate, the number of hours worked, and any applicable overtime rates. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you calculate hourly pay accurately:
Determine the Employee's Wage Rate:
- Identify the employee's hourly wage rate. This is the amount the employee earns per hour of work. Ensure that this rate complies with local minimum wage laws and any other relevant employment regulations.
Identify Regular and Overtime Hours:
- Differentiate between regular hours and overtime hours. In many jurisdictions, overtime is applicable when an employee works more than a certain number of hours in a week. Commonly, overtime begins after 40 hours in a workweek, but this can vary.
Calculate Regular Earnings:
For regular hours worked (usually up to 40 hours in a workweek), multiply the number of hours by the employee's hourly wage rate.
Calculate Overtime Earnings (if applicable):
If the employee has worked overtime, calculate the overtime earnings. In many cases, overtime is paid at a rate of 1.5 times the regular hourly wage.
Add Regular and Overtime Earnings:
Combine the regular and overtime earnings to determine the total gross pay.
Consider Additional Pay Elements:
- If there are other elements of pay, such as bonuses or commissions, factor them into the calculation. Ensure that you comply with any applicable laws or employment agreements regarding these additional pay components.
Deduct Taxes and Withholdings:
- Deduct applicable taxes, Social Security, Medicare, and any other withholdings. The net pay is the amount the employee receives after these deductions.
Check Employment Agreements and Regulations:
- Ensure that your calculations align with any employment agreements or collective bargaining agreements in place. Additionally, be aware of and comply with relevant labor laws and regulations governing minimum wage, overtime, and other employment-related matters.
Provide Detailed Pay Statements:
- Clearly communicate the breakdown of hours worked, rates, and any deductions on the employee's pay statement. Transparency helps employees understand how their pay is calculated.
Keep Accurate Records:
- Maintain accurate records of hours worked, rates, and pay calculations. This documentation is crucial for compliance with labor laws and for resolving any potential disputes.
It's essential to stay informed about applicable labor laws and regulations, as they can vary by location and industry. If you have specific concerns or if the pay structure is more complex, consider seeking guidance from a payroll professional or employment law expert.
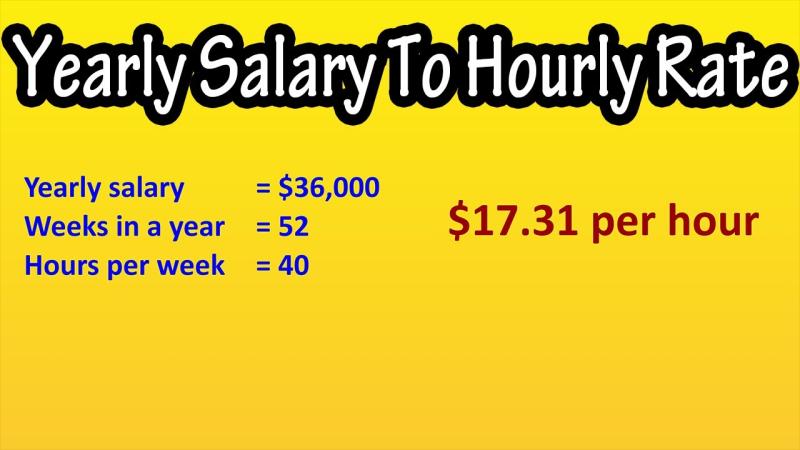
What is the formula for calculating hourly pay for employees?
The standard formula for calculating hourly pay for employees is:
Hourly Pay = Total Pay / Total Work Hours
Where:
Total Pay is the total compensation earned by an employee during a specific period, such as a week, month, or year.
Total Work Hours is the total number of hours an employee works during the same period. This typically includes regular work hours, overtime hours, and any paid time off.
For example, if an employee earns a total of $1,000 per week and works 40 hours per week, their hourly pay would be:
Hourly Pay = $1,000 / 40 hours = $25 per hour
Are there legal considerations when calculating hourly pay for employees?
Yes, there are various legal considerations when calculating hourly pay for employees. These considerations are primarily based on labor laws and regulations that aim to protect employee rights and ensure fair compensation. Here are some key legal aspects to consider:
Minimum Wage: Many countries and jurisdictions have established minimum wage laws that set a mandatory minimum hourly pay rate for employees. Employers are legally obligated to pay at least the minimum wage to all non-exempt employees.
Overtime Pay: Overtime pay regulations typically require employers to pay employees at a higher rate for hours worked beyond a certain limit, often 40 hours per week. The overtime pay rate is usually 1.5 or double the standard hourly wage.
Exempt and Non-Exempt Employees: Labor laws often categorize employees as exempt or non-exempt. Exempt employees are generally not entitled to overtime pay, while non-exempt employees must be compensated for overtime hours.
Deductions and Taxes: Employers may have legal obligations to deduct certain amounts from employee paychecks, such as taxes, social security contributions, and health insurance premiums. These deductions should be clearly communicated to employees and adhere to relevant laws and regulations.
How do factors like overtime and bonuses affect hourly pay calculations?
Overtime and bonuses can significantly impact hourly pay calculations. Overtime pay raises the effective hourly wage for hours worked beyond the standard limit. For instance, if an employee's standard hourly wage is $25 and they work 5 overtime hours at a 1.5x overtime rate, their overtime pay would be:
Overtime Pay = $25/hour * 1.5 * 5 hours = $75
Bonuses, which are additional payments given to employees based on performance, achievements, or other factors, also influence hourly pay calculations. If an employee receives a bonus, their overall compensation increases, and their effective hourly wage for the period also increases.
To accurately reflect the impact of overtime and bonuses, it is essential to consider these factors when calculating hourly pay, especially when assessing employee compensation over extended periods.