What is the main purpose of bureaucracy?
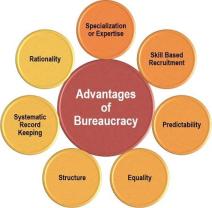
The main purpose of bureaucracy is to provide a systematic and organized structure for managing and administering large organizations. Bureaucracy is a form of organizational design characterized by a hierarchical structure, formal rules and procedures, and specialized roles. Its primary purposes include:
Efficiency:
- Bureaucracy aims to achieve efficiency in the execution of tasks and operations. By establishing clear rules, procedures, and roles, it helps streamline processes and reduce redundancy.
Organizational Control:
- Bureaucracy provides a framework for organizational control. The hierarchical structure ensures that authority and decision-making are clearly defined, promoting order and discipline within the organization.
Specialization:
- Bureaucratic organizations often encourage specialization, allowing individuals to focus on specific tasks and develop expertise. This specialization can lead to increased productivity and higher-quality output.
Predictability:
- Standardized rules and procedures create predictability in organizational behavior. This predictability is beneficial for employees, stakeholders, and the organization as a whole.
Division of Labor:
- Bureaucracy facilitates the division of labor, with different individuals or departments assigned specific responsibilities. This division helps in efficient task allocation and resource utilization.
Scalability:
- Bureaucratic structures are designed to be scalable, making it easier for organizations to expand or contract as needed. The established framework can be replicated across different units or divisions.
Decision-Making:
- Bureaucracy provides a systematic approach to decision-making. Decisions are often made based on established rules and procedures, contributing to consistency and fairness.
Resource Allocation:
- Bureaucratic organizations have established processes for resource allocation. This ensures that resources are distributed according to organizational priorities and goals.
Legal Compliance:
- Bureaucracy helps organizations comply with legal and regulatory requirements. The formal structure and adherence to rules reduce the risk of legal issues and support ethical business practices.
Accountability:
- Bureaucracy fosters accountability by clearly defining roles and responsibilities. Each level of management is accountable for specific tasks, contributing to transparency and responsibility.
While bureaucracy serves these purposes, it is important to balance its benefits with potential drawbacks, such as rigidity, slow response to change, and the risk of bureaucracy becoming a hindrance to innovation. Organizations often strive to find the right balance in their structure to optimize efficiency and effectiveness.
Identifying the primary objectives of bureaucratic structures
The primary objectives of bureaucratic structures can vary depending on the specific organization and context, but some key goals tend to be fairly consistent:
1. Efficiency and Predictability:
- Bureaucracies aim to achieve tasks in a streamlined manner, minimizing errors and maximizing output. This is achieved through standardized procedures, division of labor, and clear rules that everyone follows. Predictability comes from consistent application of these rules, promoting stability and reliability within the system.
2. Fairness and Impartiality:
- Formal rules and regulations are designed to ensure that everyone is treated equally, regardless of their personal connections or circumstances. This helps to prevent favoritism, discrimination, and corruption, upholding ethical principles and promoting public trust.
3. Rationality and Objectivity:
- Decisions are ideally made based on objective criteria and established procedures, rather than personal biases or emotions. This helps to ensure logical and consistent decision-making, minimizing human error and promoting transparency.
4. Accountability and Control:
- Clear hierarchies and chains of command establish who is responsible for what, making it easier to identify and address problems. Documentation and record-keeping further enhance accountability, providing a paper trail for actions and decisions taken.
5. Continuity and Preservation of Knowledge:
- Bureaucracies aim to maintain institutional memory by passing down knowledge and procedures through established training programs and documentation. This ensures that the organization can continue functioning effectively even as personnel changes occur.
6. Legitimacy and Public Trust:
- By adhering to established norms and procedures, bureaucracies strive to maintain public trust and legitimacy. This allows them to effectively fulfill their roles within society and achieve their broader goals.
It's important to remember that these primary objectives don't necessarily guarantee perfect bureaucratic function. Issues like inefficiency, red tape, and inflexibility can still arise. However, understanding these core goals can help us analyze and evaluate the effectiveness of bureaucratic structures in achieving their purposes.
In addition to these general objectives, specific bureaucratic structures might have additional goals tailored to their unique roles and mandates. For example, a government agency regulating food safety might focus on public health protection, while a tax agency might prioritize efficient revenue collection.
I hope this information helps! Let me know if you have any other questions.