What is the goal of CPIM certification?
The goal of CPIM (Certified in Production and Inventory Management) certification is to enhance an individual’s knowledge and expertise in supply chain and operations management, particularly in areas related to production, inventory, and materials management.
Key objectives include:
Deepening Understanding of Supply Chain Concepts – Equip professionals with knowledge of demand management, procurement, production planning, and inventory control.
Improving Operational Efficiency – Help organizations optimize production processes, reduce waste, and manage resources more effectively.
Enhancing Career Opportunities – Provide recognized credentials that demonstrate expertise in supply chain management, boosting professional credibility and career growth.
Supporting Strategic Decision-Making – Enable professionals to make data-driven decisions regarding inventory, production schedules, and resource allocation.
In short, CPIM certification aims to develop highly skilled professionals capable of improving supply chain performance and supporting organizational goals.
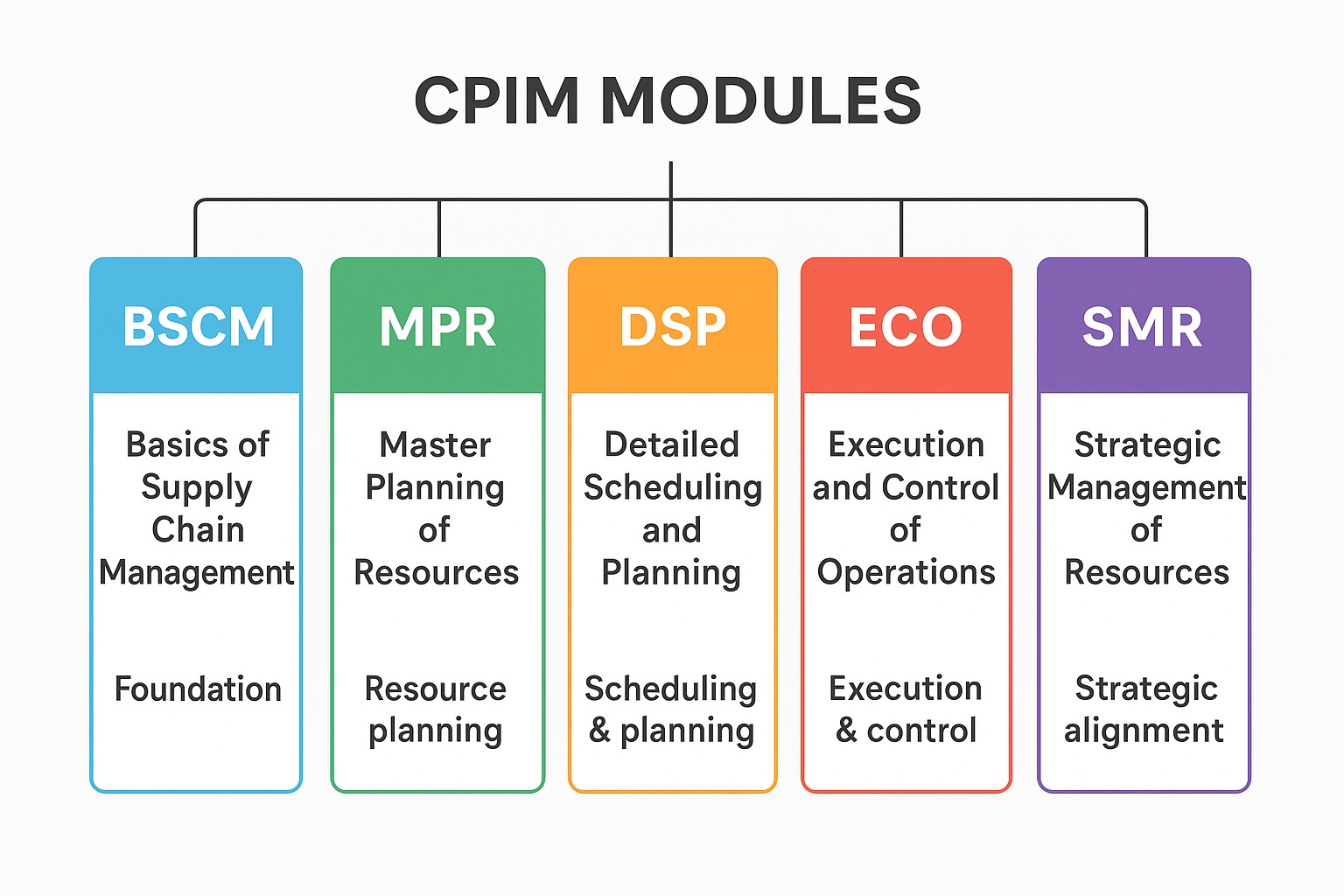
The CPIM (Certified in Production and Inventory Management) certification is offered by APICS/ASCM and is structured into five key modules. Each module focuses on a specific area of supply chain and operations management:
1. Basics of Supply Chain Management (BSCM)
Focus: Foundation of supply chain and operations management.
Knowledge Covered:
Supply chain terminology and concepts
Functions of operations management
Demand planning and forecasting
Inventory management fundamentals
Supplier and customer relationship basics
Basic financial concepts related to supply chain
2. Master Planning of Resources (MPR)
Focus: Planning resources to meet demand efficiently.
Knowledge Covered:
Sales and operations planning (S&OP)
Demand management and forecasting
Production planning strategies (make-to-stock, make-to-order, assemble-to-order)
Capacity planning and resource requirements planning (RRP)
Master scheduling and inventory policies
Coordination across departments to meet customer demand
3. Detailed Scheduling and Planning (DSP)
Focus: Translating plans into actionable schedules.
Knowledge Covered:
Material requirements planning (MRP)
Shop floor scheduling and sequencing
Inventory replenishment techniques
Managing lead times and order priorities
Integrating production and procurement schedules
Using planning tools to optimize efficiency
4. Execution and Control of Operations (ECO)
Focus: Managing day-to-day operations to meet production and service goals.
Knowledge Covered:
Shop floor operations and order execution
Quality management and control
Inventory tracking and adjustments
Performance measurement and key metrics
Continuous improvement and problem-solving in operations
5. Strategic Management of Resources (SMR)
Focus: Aligning operations with organizational strategy.
Knowledge Covered:
Supply chain strategy and competitive advantage
Process improvement and Lean principles
Supply chain risk management
Financial and performance analysis for strategic decisions
Leadership and change management in operations
Summary:
BSCM: Fundamentals
MPR: Resource planning
DSP: Scheduling & planning
ECO: Execution & control
SMR: Strategic alignment
These modules together equip professionals with end-to-end knowledge of production, inventory, and supply chain management, making them capable of improving efficiency, reducing costs, and supporting strategic decisions.
The primary objective of obtaining CPIM (Certified in Planning and Inventory Management) certification is to demonstrate a professional's expertise in a company's internal supply chain operations.
What is the primary objective of obtaining CPIM certification?
The primary objective of obtaining CPIM certification is to validate a professional's knowledge and skills in managing internal supply chain operations.
What skills and knowledge does CPIM certification provide to supply chain professionals?
CPIM certification provides a wide range of practical skills and knowledge, including:
Demand Management: Techniques for forecasting demand and aligning production plans to meet customer needs.
Inventory Optimization: Strategies to manage inventory levels, reduce costs, and avoid stockouts or overstocking.
Production Planning: The ability to create and manage production schedules, perform capacity planning, and ensure efficient operations.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): A deep understanding of how to use and leverage ERP systems for effective supply chain management.
Risk Management: Skills to manage supply chain risks and disruptions, ensuring business continuity.
How can CPIM certification improve a professional's career and salary?
CPIM certification can significantly improve a professional's career and salary by:
Increasing Credibility and Marketability: It serves as a globally recognized standard of competence, making certified individuals more attractive to employers and recruiters.
It demonstrates a commitment to professional development and a mastery of industry best practices. Opening Career Advancement Opportunities: The certification can lead to promotions and new roles in areas like production planning, materials management, and supply chain management.
Many organizations prioritize CPIM-certified individuals for leadership positions. Increasing Earning Potential: According to a 2024 report, professionals with at least one certification from ASCM (the certifying body for CPIM) earned a median salary 18% higher than their non-certified colleagues.
How does CPIM certification benefit an organization's efficiency and productivity?
CPIM certification benefits an organization's efficiency and productivity by equipping its employees with the skills to:
Optimize Internal Operations: Certified professionals can streamline processes, reduce waste, and improve the flow of materials within the company.
Enhance Decision-Making: They can make informed decisions by analyzing business environments and aligning supply chain strategies with organizational goals.
Improve Inventory Control: By applying best practices, they can reduce inventory holding costs, improve inventory accuracy, and enhance customer satisfaction by ensuring product availability.
Boost Agility: CPIM-certified staff are better equipped to manage supply disruptions and demand variations, making the organization's supply chain more resilient.
What are the key topics covered in the CPIM certification program?
The CPIM certification program is structured to provide a comprehensive understanding of internal operations.
Supply Chains and Strategy: Understanding fundamental supply chain concepts and how they relate to business strategy.
Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP): Aligning demand and supply plans to optimize resources.
Demand Management: Forecasting, managing, and measuring customer demand.
Supply: Planning and managing procurement and supplier relationships.
Inventory: Techniques for managing and controlling inventory, including inventory costs, valuation, and metrics.
Detailed Schedules: Creating and managing production and service schedules.
Quality, Technology, and Continuous Improvement: Principles of quality management, using technology like ERP, and implementing continuous improvement practices.