What product is common to reactions in cellular respiration and fermentation?
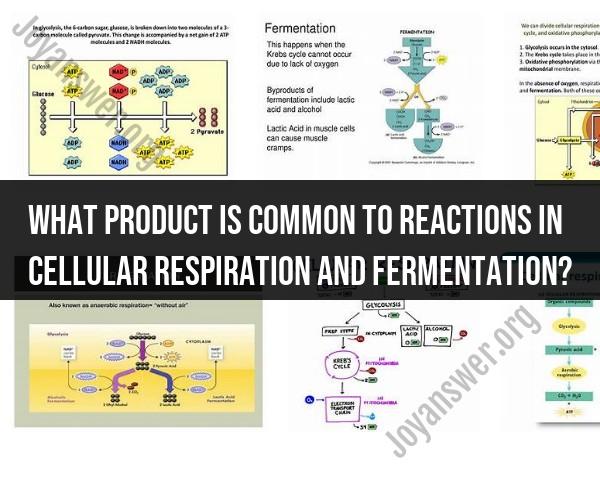
The product that is common to reactions in both cellular respiration and fermentation is adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is a molecule that serves as the primary energy currency in cells. It stores and releases energy that cells can use for various biological processes.
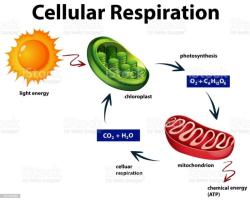
In cellular respiration, ATP is generated through a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose and other organic molecules in the presence of oxygen. This process occurs in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells and involves glycolysis, the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle), and the electron transport chain. The production of ATP in cellular respiration is highly efficient and results in a large number of ATP molecules per molecule of glucose.
In fermentation, ATP is also produced through glycolysis, a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose to generate energy. However, in the absence of oxygen, the process stops after glycolysis, and cells use fermentation pathways to regenerate molecules that can continue to participate in glycolysis. While fermentation is less efficient in terms of ATP production compared to aerobic cellular respiration, it still generates ATP to provide energy for cells, especially in anaerobic conditions.
So, ATP is a common product in both cellular respiration and fermentation, although the efficiency and quantity of ATP production differ between the two processes.
Which product is a common factor in both cellular respiration and fermentation processes?
The common product in both cellular respiration and fermentation processes is pyruvate. Pyruvate is a three-carbon molecule that is produced when glucose is broken down. During cellular respiration, pyruvate is further broken down to produce energy in the form of ATP. During fermentation, pyruvate is converted to different end products, such as lactate or ethanol, depending on the type of fermentation.
How do cellular respiration and fermentation differ in terms of end products?
Cellular respiration and fermentation differ in terms of their end products. Cellular respiration produces ATP, carbon dioxide, and water. Fermentation produces different end products, depending on the type of fermentation. For example, lactic acid fermentation produces lactate, and alcoholic fermentation produces ethanol and carbon dioxide.
The following table summarizes the end products of cellular respiration and fermentation:
| Process | End products |
|---|---|
| Cellular respiration | ATP, carbon dioxide, water |
| Lactic acid fermentation | Lactate |
| Alcoholic fermentation | Ethanol, carbon dioxide |
Can the same substrate be used in both cellular respiration and fermentation reactions?
Yes, the same substrate can be used in both cellular respiration and fermentation reactions. The most common substrate is glucose, but other substrates can also be used, such as fructose and sucrose.
The following table summarizes the substrates that can be used in cellular respiration and fermentation:
| Process | Substrates |
|---|---|
| Cellular respiration | Glucose, fructose, sucrose, other carbohydrates |
| Lactic acid fermentation | Glucose, fructose, sucrose, other carbohydrates |
| Alcoholic fermentation | Glucose, fructose, sucrose, other carbohydrates |
It is important to note that cellular respiration and fermentation are two different processes with different end products. Cellular respiration is an aerobic process, meaning that it requires oxygen. Fermentation is an anaerobic process, meaning that it does not require oxygen.
Cellular respiration is the more efficient process, producing more ATP than fermentation. However, fermentation can occur in the absence of oxygen, which is why it is important for some organisms, such as muscle cells during strenuous exercise.