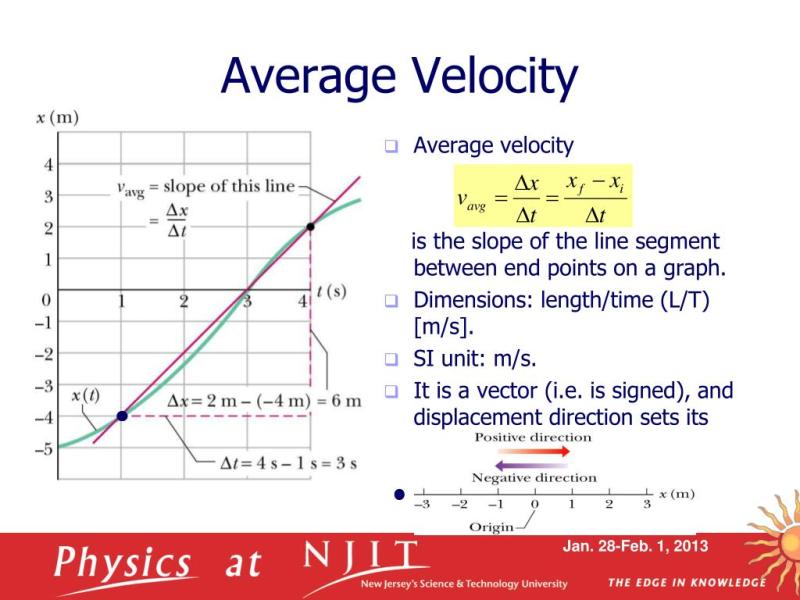
What is an average velocity vector?
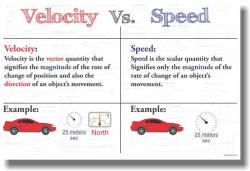
An average velocity vector is a mathematical representation of the average velocity of an object or particle during a specified time interval. It combines information about both the magnitude (speed) and direction of motion into a single vector.
Here's a more detailed explanation:
Magnitude: The magnitude of the average velocity vector represents the total distance traveled by an object during a specific time interval. It is typically expressed in units such as meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per hour (km/h), depending on the system of measurement.
Direction: The direction of the average velocity vector indicates the overall path or trajectory of the object's motion. It is usually represented using angles or vector notations (e.g., north, east, or with respect to a coordinate system).
The formula to calculate the average velocity vector is:
Average Velocity Vector (V_avg) = (Displacement Vector) / (Time Interval)
Where:
- Displacement Vector: This represents the change in the object's position during the time interval. It is a vector that points from the initial position to the final position.
- Time Interval: The duration of the motion over which you want to calculate the average velocity.
Applications of average velocity vectors are common in physics and engineering, especially when dealing with objects that move in multiple directions or undergo complex motions. It's used in various scenarios, including:
Kinematics: In the study of motion, average velocity vectors help describe how an object's position changes over time. They are crucial for understanding the behavior of particles, vehicles, and celestial bodies.
Navigation: Average velocity vectors are used in navigation systems, such as GPS, to provide information about an object's speed and direction, helping users determine their position and reach a desired destination.
Engineering Design: In fields like civil engineering and transportation planning, average velocity vectors are used to design road networks, optimize traffic flow, and ensure the safety and efficiency of transportation systems.
Astronomy: Astronomers use average velocity vectors to track the motion of celestial objects like planets, comets, and asteroids as they move through space.
Sports Analysis: Average velocity vectors can be applied in sports analytics to track the performance of athletes, such as the speed and direction of a soccer ball or the trajectory of a basketball.
Robotics: In robotics and autonomous systems, average velocity vectors help guide the movement of robots, drones, and other automated devices.
In summary, an average velocity vector combines information about an object's speed and direction during a specific time interval. It is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering, playing a critical role in understanding and predicting the motion of objects in various applications.
Understanding Average Velocity Vectors: Concepts and Significance
Average velocity is a fundamental concept in kinematics, the branch of physics that deals with motion. It describes the overall rate and direction of an object's displacement over a specified time interval. Unlike instantaneous velocity, which represents the object's velocity at a single moment, average velocity provides a summary of the object's motion over a broader period.
Significance of Average Velocity Vectors:
Quantifying Motion: Average velocity provides a quantitative measure of an object's motion, allowing us to compare the speed and direction of different objects.
Analyzing Motion Patterns: Average velocity can reveal patterns in an object's motion, indicating whether it is moving with constant speed, accelerating, or decelerating.
Solving Motion Problems: Average velocity plays a crucial role in solving various motion problems, such as determining the distance traveled or the time required for an object to reach a specific location.
Exploring the World of Average Velocity Vectors
Average velocity is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude (size) and direction. The magnitude of the average velocity represents the average speed of the object, while the direction indicates the overall direction of the object's displacement.
Calculating Average Velocity Vectors:
The formula for calculating average velocity is:
Average velocity = Δx / Δt
where:
- Δx is the displacement vector, representing the change in position of the object
- Δt is the time interval over which the displacement occurs
Interpreting Average Velocity Vectors:
Magnitude: The magnitude of the average velocity indicates the average speed of the object. A higher magnitude corresponds to a faster average speed.
Direction: The direction of the average velocity indicates the overall direction of the object's displacement. If the object moves in a straight line, the direction of the average velocity is the same as the direction of the displacement. However, if the object moves in a curved path, the direction of the average velocity may differ from the direction of the displacement at any given point.
Calculating and Interpreting Average Velocity Vectors
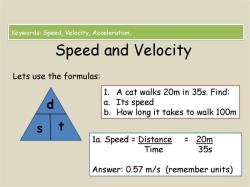
Example:
A car travels 100 meters east in 20 seconds. Calculate its average velocity.
Solution:
Δx = 100 meters east (displacement vector)Δt = 20 seconds
Average velocity = Δx / Δt = 100 meters east / 20 seconds = 5 meters per second east
Interpretation:
The average velocity is 5 meters per second east, indicating that the car's average speed was 5 meters per second, and its overall direction of motion was towards the east.