How to calculate the angular velocity in physics?
Angular velocity is a measure of how quickly an object rotates around a specific axis. It is usually expressed in radians per second (rad/s) and is an important concept in physics, particularly in the study of rotational motion. To calculate angular velocity, you can follow these steps:
Step 1: Understand the VariablesBefore you start calculating angular velocity, make sure you understand the variables involved:
- θ (Theta): This represents the angular displacement, which is the change in the angle through which the object has rotated. It is measured in radians (rad).
- t (Time): The time it takes for the object to rotate through the angular displacement. It is usually measured in seconds (s).
- ω (Angular Velocity): This is what you want to calculate and is measured in radians per second (rad/s).
Step 2: Identify the Initial and Final AnglesDetermine the initial and final angles through which the object has rotated. You can use degrees, but they must be converted to radians because angular velocity is usually expressed in radians.
Step 3: Calculate the Change in Angle (θ)Use the following formula to calculate the angular displacement:
θ = θ_final - θ_initial
Make sure to use radians for both θ_final and θ_initial.
Step 4: Calculate the Angular Velocity (ω)Use the following formula to calculate angular velocity:
ω = θ / t
Where:
- ω is the angular velocity (in radians per second).
- θ is the angular displacement (in radians) calculated in step 3.
- t is the time taken for the rotation (in seconds).
Step 5: Complete the CalculationSubstitute the values you obtained in steps 3 and 4 into the formula. This will give you the angular velocity in radians per second (rad/s).
Here's a step-by-step example:
Suppose an object rotates from an initial angle of 30 degrees to a final angle of 150 degrees in 5 seconds.
Step 1: Understand the Variables
- θ_initial = 30 degrees (convert to radians)
- θ_final = 150 degrees (convert to radians)
- t = 5 seconds
Step 2: Convert Degrees to Radiansθ_initial = 30 degrees × (π radians / 180 degrees) = 0.5236 radiansθ_final = 150 degrees × (π radians / 180 degrees) = 2.6179 radians
Step 3: Calculate the Change in Angle (θ)θ = θ_final - θ_initial = 2.6179 radians - 0.5236 radians = 2.0943 radians
Step 4: Calculate Angular Velocity (ω)ω = θ / t = 2.0943 radians / 5 seconds = 0.4189 rad/s
So, the angular velocity of the object is approximately 0.4189 radians per second.
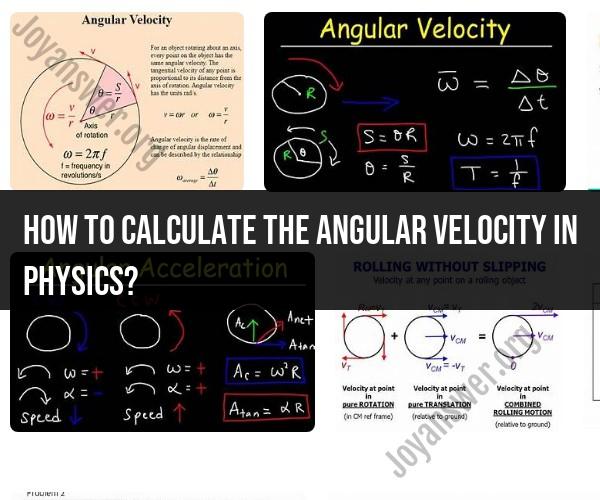
Calculating Angular Velocity in Physics
Angular velocity, denoted by the Greek letter omega (ω), is the measure of how fast an object is rotating around an axis. It is defined as the rate of change of angular displacement, which is the angle that the object has rotated. Angular velocity is a vector quantity, meaning that it has both magnitude and direction. The direction of the angular velocity vector is perpendicular to the plane of rotation.
The SI unit of angular velocity is radians per second (rad/s). One radian is the angle subtended by an arc length equal to the radius of the circle.
To calculate the angular velocity of an object, we can use the following formula:
ω = Δθ / Δt
where:
- ω is the angular velocity in rad/s
- Δθ is the angular displacement in radians
- Δt is the time interval in seconds
Example:
A merry-go-round rotates 40 times in 1 minute. What is its angular velocity in rad/s?
ω = 40 revolutions / 1 minute * 2π radians / revolution * 1 minute / 60 seconds
ω = 4.19 rad/s
The Concepts and Units of Angular Velocity
Angular velocity is a fundamental concept in rotational mechanics. It is related to other important quantities, such as angular momentum and torque, by the following equations:
- Angular momentum = L = Iω
- Torque = τ = dL/dt = Iα
where:
- L is the angular momentum in kg⋅m^2/s
- I is the moment of inertia in kg⋅m^2
- α is the angular acceleration in rad/s^2
Angular velocity is also used in other fields of science and engineering, such as astronomy, electrical engineering, and robotics. For example, the angular velocity of a planet can be used to calculate its orbital period, and the angular velocity of a motor can be used to calculate its speed.
Formulas and Equations for Angular Velocity
In addition to the basic formula for angular velocity (ω = Δθ / Δt), there are a number of other formulas and equations that can be used to calculate angular velocity in different situations.
For example, the following formula can be used to calculate the angular velocity of an object that is rotating at a constant speed:
ω = v / r
where:
- ω is the angular velocity in rad/s
- v is the linear velocity in m/s
- r is the radius of rotation in m
The following formula can be used to calculate the angular velocity of an object that is rotating with a constant acceleration:
ω = ω0 + αt
where:
- ω is the angular velocity at time t in rad/s
- ω0 is the angular velocity at time t = 0 in rad/s
- α is the angular acceleration in rad/s^2
- t is the time in seconds
Practical Applications and Examples of Angular Velocity
Angular velocity is used in a wide variety of practical applications, including:
- Transportation: The angular velocity of a car's wheels is used to calculate its speed. The angular velocity of a propeller is used to calculate the thrust of an airplane.
- Manufacturing: The angular velocity of a machine tool is used to control the speed at which it cuts or shapes a material.
- Energy production: The angular velocity of a wind turbine is used to generate electricity. The angular velocity of a hydroelectric turbine is used to generate electricity from the flow of water.
- Consumer products: The angular velocity of a CD or DVD player is used to determine the speed at which the disc spins. The angular velocity of a washing machine is used to control the speed at which the clothes are washed.
Angular Velocity in Different Fields of Science and Engineering
Angular velocity is used in a variety of different fields of science and engineering, including:
- Astronomy: The angular velocity of a planet is used to calculate its orbital period. The angular velocity of a star is used to calculate its rotation period.
- Electrical engineering: The angular velocity of a motor is used to calculate its speed. The angular velocity of a generator is used to calculate the frequency of the electricity it produces.
- Robotics: The angular velocity of a robot's joints is used to control its movement.
Conclusion
Angular velocity is a fundamental concept in rotational mechanics. It is used in a wide variety of practical applications in transportation, manufacturing, energy production, and consumer products