How can you use CPI to calculate the inflation rate?
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) can be used to calculate the inflation rate, which measures the average change in prices for a basket of goods and services over time. To calculate the inflation rate using the CPI, follow these steps:
Obtain CPI Data:
- You'll need historical CPI data for the specific time period you want to calculate the inflation rate. CPI data is typically published by government agencies, such as the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics in the United States.
Select Two Time Points:
- Choose two time points: a starting date (e.g., last year) and an ending date (e.g., this year). These dates should represent the period you want to calculate the inflation rate for.
Retrieve CPI Values:
- Find the CPI values for both the starting date (CPI₁) and the ending date (CPI₂). The CPI values are indices that represent the price level at each time point.
Calculate the Inflation Rate:
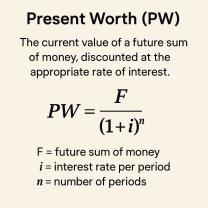
Use the following formula to calculate the inflation rate (I):
Subtract the CPI value at the starting date from the CPI value at the ending date. Then, divide this difference by the CPI value at the starting date. Multiply the result by 100 to express the inflation rate as a percentage.
Interpret the Result:
- The calculated inflation rate represents the percentage change in the price level between the two selected time points. A positive inflation rate indicates that prices have risen, while a negative rate suggests a decrease in prices. Zero percent inflation means that prices have remained constant.
Additional Considerations:
- Make sure the CPI data you're using is relevant to the specific region or country you're interested in because different places may have different CPI values.
- You can calculate the inflation rate for various time intervals (e.g., monthly, quarterly, or annually) depending on the availability of CPI data and your analytical needs.
Keep in mind that the CPI is a measure of general price changes for a basket of goods and services and may not reflect the specific price changes for individual products or services. Additionally, the choice of the starting and ending dates can impact the calculated inflation rate, so it's important to select relevant time points for your analysis.
Sure, here is a detailed explanation of the five topics you mentioned:
Using the Consumer Price Index (CPI) to Calculate Inflation
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a measure of the average change in prices paid by urban consumers for a basket of consumer goods and services. It is used to calculate inflation, which is the rate at which prices for goods and services are rising.
To calculate inflation using the CPI, the following formula is used:
Inflation = (CPI_CurrentYear - CPI_PreviousYear) / CPI_PreviousYear * 100
Where:
- CPI_CurrentYear is the CPI for the current year
- CPI_PreviousYear is the CPI for the previous year
Components and Calculation of CPI
The CPI is calculated by measuring the price changes for a basket of consumer goods and services. The basket includes a variety of items, such as food, housing, transportation, medical care, and recreation. The weights of the items in the basket are based on their importance in the consumer budget.
The prices of the items in the CPI basket are collected from a sample of stores and businesses. The prices are then averaged and compared to the prices in the previous year. The change in the average prices is then used to calculate the CPI.
Interpreting CPI Data for Inflation Trends
The CPI is a valuable tool for understanding inflation trends. By tracking changes in the CPI over time, economists can identify periods of high inflation and low inflation. This information can be used to make informed decisions about economic policy.
For example, if the CPI is rising rapidly, the Federal Reserve may raise interest rates in an effort to slow down the economy and reduce inflation.
Limitations and Criticisms of CPI as an Inflation Indicator
The CPI is not without its limitations. One criticism is that the basket of goods and services used to calculate the CPI may not be representative of the spending habits of all consumers. Additionally, the CPI can be slow to reflect changes in prices for some items, such as new technologies.
Despite its limitations, the CPI is still the most widely used measure of inflation. It is a valuable tool for understanding inflation trends and making informed economic decisions.
Combining CPI with Other Economic Indicators for Inflation Analysis
Economists often use the CPI in conjunction with other economic indicators to get a more comprehensive picture of inflation. Other indicators that are commonly used include:
- The Producer Price Index (PPI), which measures changes in prices paid by producers for goods and services
- The Employment Cost Index (ECI), which measures changes in wages and salaries
- The Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Price Index, which measures changes in prices paid by consumers for a broader range of goods and services than the CPI
By using a variety of indicators, economists can get a more accurate picture of inflation and the factors that are driving it.