What are the different types of Economics?
Economics is a diverse field with several sub-disciplines that focus on different aspects of economic behavior and phenomena. Here is an overview of some of the major types of economics:
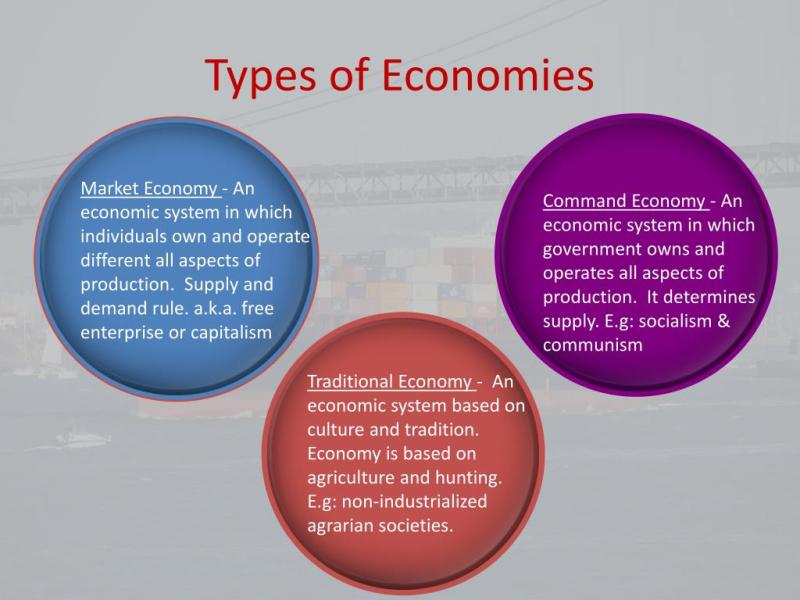
Microeconomics:
- Microeconomics is the study of individual economic agents, such as consumers, firms, and markets. It examines how these agents make decisions, interact, and allocate resources at a smaller scale.
Macroeconomics:
- Macroeconomics focuses on the economy as a whole, studying aggregate phenomena such as inflation, unemployment, economic growth, and national income. It explores the broader trends and policies that impact the entire economy.
Development Economics:
- Development economics is concerned with understanding the economic development of countries and regions. It explores factors affecting poverty, inequality, and economic growth, as well as policies for promoting development.
International Economics:
- International economics examines economic interactions between countries. It covers topics such as international trade, exchange rates, balance of payments, and the effects of globalization on economies.
Behavioral Economics:
- Behavioral economics integrates insights from psychology into economic analysis. It studies how psychological factors influence individual decision-making and economic outcomes, challenging traditional assumptions of rational behavior.
Environmental Economics:
- Environmental economics analyzes the economic impact of environmental policies and explores ways to address environmental issues such as pollution, climate change, and resource depletion.
Labor Economics:
- Labor economics focuses on the labor market, studying issues related to employment, wages, working conditions, and the overall functioning of the labor market.
Health Economics:
- Health economics examines the allocation of resources in the healthcare sector. It explores topics such as healthcare financing, insurance, and the economic impact of health policies.
Urban and Regional Economics:
- Urban and regional economics investigates economic issues related to cities and regions. This includes the study of urban development, regional growth, and the spatial distribution of economic activities.
Financial Economics:
- Financial economics studies the allocation of resources in financial markets. It includes topics such as investment, risk management, asset pricing, and the behavior of financial institutions.
Public Economics:
- Public economics examines the role of government in the economy. It covers topics such as taxation, public expenditure, public goods, and the impact of government policies on economic outcomes.
Industrial Organization:
- Industrial organization explores the structure and behavior of industries and markets. It examines issues related to market power, competition, and the impact of market structure on economic efficiency.
Institutional Economics:
- Institutional economics focuses on the role of institutions in shaping economic behavior. It explores how formal and informal institutions influence economic outcomes, including issues related to property rights, contracts, and governance.
These sub-disciplines represent just a portion of the diversity within the field of economics. Many economists specialize in one or more of these areas, and interdisciplinary approaches are common, especially as economic phenomena are often influenced by social, political, and cultural factors.
What are the main branches or specializations within the field of Economics?
Economics, as a vast and ever-evolving field, encompasses a diverse range of specializations, each focusing on different aspects of resource allocation and human behavior. Here are some of the main branches or specializations within the field:
1. Microeconomics:
- Analyzes individual decision-making and behavior, specifically how consumers and firms allocate resources under conditions of scarcity.
- Key subfields include:
- Consumer theory: Examines consumer behavior, preferences, and demand for goods and services.
- Price theory: Studies factors influencing product price and output determination in markets.
- Industrial organization: Analyzes market structure, competition, and firm behavior.
- Game theory: Applies strategic decision-making models to economic interactions.
2. Macroeconomics:
- Focuses on the performance, structure, and behavior of an economy as a whole, rather than individual units.
- Key subfields include:
- Economic growth: Studies the determinants and factors influencing economic growth over time.
- Monetary economics: Analyzes the role of money, banking systems, and monetary policy in the economy.
- Fiscal economics: Examines the impact of government spending, taxation, and fiscal policy on macroeconomic outcomes.
- International economics: Focuses on economic relations between countries, international trade, and global financial markets.
3. Econometrics:
- Applies statistical methods and data analysis to test economic theories and models.
- Uses econometric techniques to estimate relationships between economic variables and draw conclusions about economic phenomena.
4. Behavioral Economics:
- Combines insights from economics and psychology to understand how cognitive biases, emotions, and social influences impact economic decision-making.
- Focuses on understanding deviations from rational choice assumptions and their implications for markets and policy.
5. Public Economics:
- Analyzes government intervention in the economy, focusing on public goods, taxation, welfare programs, and other policy issues.
- Examines the efficiency and equity implications of government policies and seeks to optimize resource allocation in the public sector.
6. Development Economics:
- Studies the economic challenges and opportunities faced by developing countries, focusing on poverty reduction, economic growth, and human development.
- Analyzes factors like education, healthcare, infrastructure, and institutional structures in the context of developing economies.
7. Environmental Economics:
- Examines the interaction between economic activities and the environment, focusing on issues like pollution, resource depletion, and sustainability.
- Develops tools and policies to address environmental challenges and promote sustainable economic development.
8. Financial Economics:
- Analyzes financial markets, institutions, and instruments, focusing on risk management, asset pricing, and investment decisions.
- Examines the behavior of financial markets and their impact on the broader economy.
These are just a few examples of the many specializations within economics. The field is constantly evolving, and new subfields emerge as technological advancements and societal challenges create new areas of study.
Ultimately, the choice of specialization depends on your individual interests, skills, and career aspirations. Do you enjoy analyzing individual behavior and market dynamics? Or are you more interested in studying the big picture of national economies and global development? Exploring the diverse branches of economics can help you discover your passion and find a rewarding career path within this dynamic field.