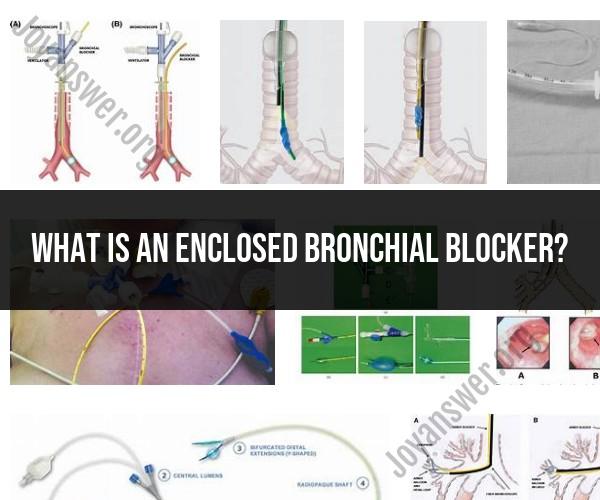
What is an enclosed bronchial blocker?
An enclosed bronchial blocker is a medical device used in the field of anesthesiology and critical care medicine to selectively block or isolate one of the lungs during certain surgical procedures or when managing patients with lung-related conditions. It is designed to be inserted into a patient's airway and positioned within the bronchus (the main airway leading to each lung) to prevent airflow to one of the lungs while maintaining ventilation to the other lung. This selective lung isolation is particularly useful in situations where it is necessary to work on or treat one lung while keeping the other lung functioning normally.
Here are some key points about enclosed bronchial blockers:
Purpose: Enclosed bronchial blockers are primarily used during surgeries, such as thoracic surgery or certain procedures involving the lungs, to facilitate better visualization and access to the lung being operated on. They are also used in critical care settings to manage conditions like pneumonia or lung injury.
Isolation: The device consists of a tube with an inflatable cuff at its tip. Once inserted into the patient's airway, the cuff is inflated to seal off the bronchus leading to the non-operated lung. This effectively prevents air from entering or leaving that lung, allowing the surgeon or healthcare provider to work on the isolated lung without interference from the other.
Advantages: Enclosed bronchial blockers offer advantages over other lung isolation techniques, such as double-lumen endotracheal tubes or bronchial blockers that are not enclosed. They can provide a better seal and improved isolation, reducing the risk of contamination between the lungs and minimizing the risk of complications during surgery.
Safety: The use of bronchial blockers requires proper training and experience to ensure safe and effective lung isolation. Healthcare professionals should be skilled in their placement, maintenance, and monitoring during procedures.
Patient Monitoring: Patients undergoing procedures with enclosed bronchial blockers typically require close monitoring, including continuous assessment of oxygenation, ventilation, and lung compliance.
Removal: After the procedure or treatment is completed, the bronchial blocker is deflated and carefully removed, allowing both lungs to resume normal function.
It's important to note that the use of enclosed bronchial blockers is a specialized medical technique performed by trained healthcare providers in specific clinical situations. The choice of lung isolation method depends on the patient's condition and the requirements of the procedure. The safety and effectiveness of these devices are paramount, and they should only be used by qualified medical professionals.