What are nursing interventions for myocardial infarction?
Nursing interventions for myocardial infarction (heart attack) are crucial in managing the condition and promoting recovery. These interventions aim to stabilize the patient, alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and support the patient's overall health. Some key nursing interventions include:
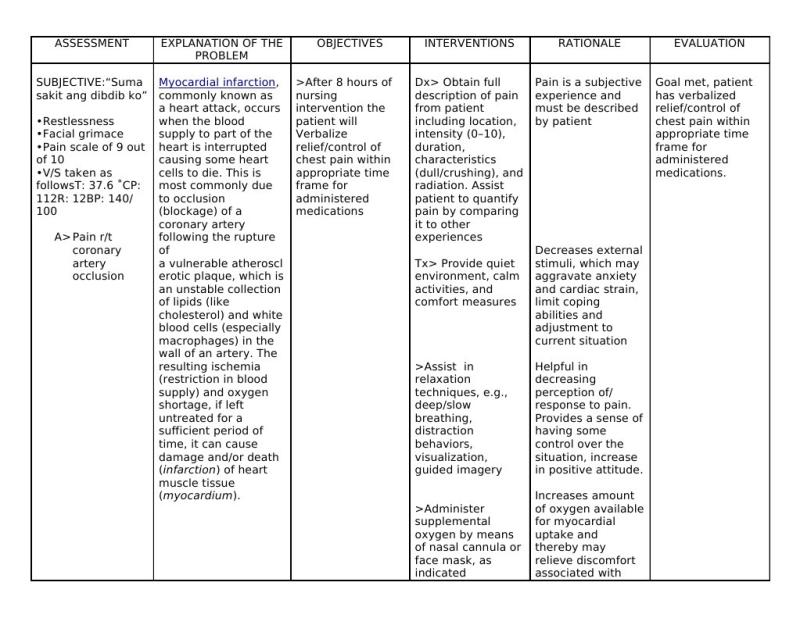
Monitoring Vital Signs: Continuously assessing and monitoring vital signs such as blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen saturation, and temperature to detect any changes or complications.
Pain Management: Providing prompt pain relief using medications (such as nitroglycerin) to alleviate chest pain or discomfort. Assessing pain levels regularly and administering pain relief as needed.
Oxygen Therapy: Administering supplemental oxygen to ensure adequate oxygenation and relieve respiratory distress if present.
ECG Monitoring: Continuous electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring to assess cardiac rhythm and detect any abnormalities. Promptly reporting any changes in the ECG readings.
Medication Administration: Administering prescribed medications such as antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants, beta-blockers, and ACE inhibitors to reduce cardiac workload, prevent clot formation, and manage blood pressure.
Assistance with Thrombolytic Therapy or PCI: Collaborating with the healthcare team to assist in the administration of thrombolytic therapy or preparing the patient for percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or angioplasty, which restores blood flow to the blocked artery.
Education and Support: Providing patient and family education on lifestyle modifications, medication adherence, diet, exercise, stress management, and signs of complications. Offering emotional support and addressing concerns.
Monitoring and Managing Complications: Monitoring for potential complications such as arrhythmias, heart failure, or cardiogenic shock. Taking prompt action if complications arise.
Assessment of Fluid Balance: Monitoring intake and output, assessing for signs of fluid overload or dehydration, and adjusting fluid therapy accordingly.
Preparation for Discharge: Preparing the patient for discharge by ensuring they understand their medications, follow-up appointments, lifestyle modifications, and the signs and symptoms that require immediate medical attention.
Collaboration and Referral: Collaborating with other healthcare professionals, including cardiologists, dietitians, physical therapists, and social workers, to ensure comprehensive care and support for the patient's recovery.
These interventions aim to address the immediate needs of the patient during a myocardial infarction while also focusing on long-term management and prevention of future cardiovascular events.
Nursing interventions for myocardial infarction (MI), also known as a heart attack, are aimed at minimizing heart damage, preventing complications, and promoting healing. Nurses play a crucial role in providing prompt and comprehensive care to patients experiencing an MI.
Immediate Nursing Interventions
Pain Management: Administer pain medication, such as morphine, to relieve the severe chest pain associated with an MI.
Oxygen Therapy: Provide supplemental oxygen to maintain adequate oxygen levels and support heart function.
Electrocardiogram (ECG) Monitoring: Continuously monitor the ECG to assess heart rhythm, identify potential arrhythmias, and track the extent of the MI.
Aspirin Administration: Administer aspirin to reduce blood clot formation and improve blood flow to the heart.
Nitroglycerin Administration: If appropriate, administer nitroglycerin to improve blood flow to the heart and relieve chest pain.
Ongoing Nursing Interventions
Fluid Management: Monitor fluid intake and output to maintain fluid balance and prevent complications such as congestive heart failure.
Medication Administration: Administer prescribed medications, such as beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and statins, to reduce heart rate, lower blood pressure, and prevent further heart damage.
Patient Education: Provide patient education about the MI, its causes, risk factors, and lifestyle modifications to promote recovery and prevent future occurrences.
Emotional Support: Offer emotional support and counseling to help patients cope with the stress, anxiety, and fear associated with an MI.
Discharge Planning: Coordinate discharge planning with other healthcare providers to ensure a smooth transition from hospital care to home or rehabilitation settings.
Nurses play a critical role in managing patients with MI, providing comprehensive care that encompasses both immediate and ongoing interventions. Their expertise and dedication contribute significantly to improving patient outcomes and promoting long-term recovery.