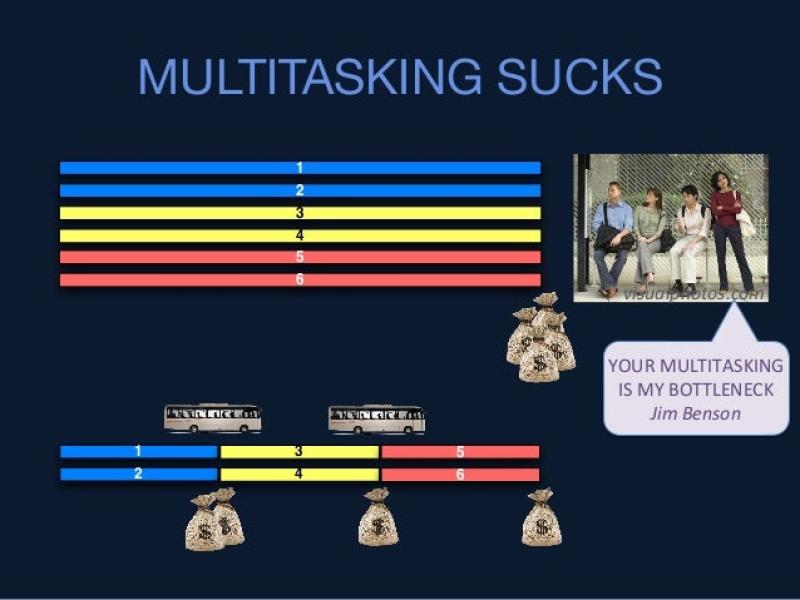
What do instructors need to know about “bottlenecks?
In the context of education, the term "bottlenecks" refers to points in the educational system where student progress is impeded or slowed down significantly. These bottlenecks can have a negative impact on student success and completion rates. Instructors can play a vital role in identifying and addressing bottlenecks to improve the educational experience for their students. Here's what instructors need to know about bottlenecks:
Identification of Bottlenecks:
- Instructors should be aware of common bottlenecks that students face in their courses and programs. These bottlenecks can include high-demand courses, prerequisite requirements, limited access to resources, and administrative barriers.
Impact on Student Success:
- Bottlenecks can hinder student progress, leading to lower retention and graduation rates. Instructors should understand that addressing these issues can have a positive impact on student success.
Prerequisite Courses: Instructors need to be aware of the prerequisites required for their courses. Prerequisite courses can become bottlenecks if they are difficult to access, have limited availability, or have high failure rates.
Course Availability: High-demand courses with limited seats or scheduling conflicts can create bottlenecks. Instructors can advocate for increased course availability or explore alternatives like online courses.
Effective Teaching Strategies: Instructors can employ teaching strategies that enhance student learning and engagement. Creating an inclusive and supportive classroom environment can help students overcome academic challenges.
Assessment and Feedback: Instructors should provide timely and constructive feedback on assignments and assessments. Effective feedback can help students understand their strengths and weaknesses, enabling them to progress more efficiently.
Mentoring and Advising: Instructors can provide guidance and mentorship to students who are struggling. This can include referring students to academic support services, offering study strategies, or helping them explore alternative courses.
Advocacy: Instructors have a voice in their academic institutions. They can advocate for changes that address bottlenecks, such as increased course availability, improved prerequisites, and streamlined administrative processes.
Collaboration: Instructors can collaborate with colleagues and administrators to identify and address bottlenecks. Cross-departmental cooperation can lead to more effective solutions.
Data Analysis: Instructors can use data to identify patterns related to student success and areas of concern. Analyzing student performance and outcomes can help pinpoint bottlenecks.
Communication: Instructors can communicate with students about potential bottlenecks and offer guidance on how to navigate them. This includes advising students on course sequencing, study strategies, and resources.
Professional Development: Instructors can participate in professional development opportunities to enhance their teaching and mentoring skills. Staying informed about best practices in education can be valuable in addressing bottlenecks.
By understanding and actively addressing bottlenecks in education, instructors can contribute to improving the overall educational experience for their students. It requires a proactive approach, collaboration with colleagues and administrators, and a commitment to enhancing student success and retention rates.
Understanding the Significance of Identifying Bottlenecks in Instruction
In an educational setting, a bottleneck refers to any hindrance or obstruction that impedes the smooth flow of learning and teaching. Identifying and addressing bottlenecks is crucial for optimizing instructional strategies, enhancing student engagement, and improving overall learning outcomes.
Benefits of Addressing Bottlenecks in Instruction
Improved Efficiency: Eliminating bottlenecks can streamline instructional processes, reducing wasted time and resources.
Enhanced Student Engagement: By addressing roadblocks that hinder student progress, instructors can foster a more engaging and stimulating learning environment.
Boosted Learning Outcomes: Addressing bottlenecks can lead to improved retention, comprehension, and overall academic performance among students.
How Can Instructors Improve Efficiency by Addressing Bottlenecks?
Analyze Instructional Processes: Identify areas where time is being lost or where students are struggling.
Seek Feedback: Gather input from students, colleagues, and administrators to identify potential bottlenecks.
Implement Technology: Utilize educational technology tools to streamline tasks, automate repetitive processes, and provide personalized learning experiences.
Refine Instructional Strategies: Adapt teaching methods and materials to address identified bottlenecks and improve student comprehension.
Tools and Strategies for Instructors to Identify and Manage Bottlenecks
Observe Student Performance: Closely monitor student behavior, engagement, and progress to identify areas of difficulty.
Analyze Assessment Data: Review test scores, assignments, and other assessments to identify patterns and pinpoint areas where students are struggling.
Gather Student Feedback: Conduct surveys, polls, or informal discussions to gather students' perspectives on instructional challenges.
Collaborate with Colleagues: Engage in peer observation and discussion to share insights and identify potential bottlenecks.
Real-World Examples of Bottlenecks in Educational Settings
Lack of Clear Instructions: Vague or poorly structured instructions can lead to confusion, frustration, and wasted time.
Inaccessible Materials: Unclear or overly complex textbooks, handouts, or online resources can hinder student understanding.
Ineffective Classroom Management: Poor classroom management can lead to disruptions, distractions, and a loss of valuable learning time.
Inadequate Feedback Mechanisms: Delayed or insufficient feedback can deprive students of timely guidance and hinder their progress.
How Can Instructors Enhance the Learning Experience by Dealing with Bottlenecks?
Provide Clear and Concise Instructions: Break down complex tasks into manageable steps, use clear language, and provide visual aids when necessary.
Utilize Diverse Learning Materials: Offer a variety of learning materials, such as interactive simulations, multimedia presentations, and hands-on activities, to cater to different learning styles.
Implement Effective Classroom Management Strategies: Establish clear rules and expectations, maintain a structured learning environment, and address disruptions promptly.
Provide Timely and Constructive Feedback: Offer regular feedback to students, focusing on specific areas for improvement and providing guidance for progress.
Incorporate Personalized Learning Techniques: Adapt instructional methods and materials to meet the individual needs and learning styles of students.
Foster a Collaborative Learning Environment: Encourage peer-to-peer learning, group projects, and class discussions to enhance engagement and promote active learning.
Continuously Evaluate and Refine Instructional Practices: Regularly assess the effectiveness of teaching methods and make adjustments as needed to address bottlenecks and improve student outcomes.
By identifying and addressing bottlenecks in instruction, educators can create a more efficient, engaging, and effective learning environment for their students.