What is considered a good EFC from FAFSA?
The Expected Family Contribution (EFC) is a crucial part of the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) process, as it determines a student's eligibility for federal financial aid. Understanding what constitutes a "good" EFC can help you better gauge your financial aid prospects.
What is EFC?
The EFC is a measure of your family's financial strength and is calculated according to a formula established by law. The information you provide on your FAFSA form, such as your family's taxed and untaxed income, assets, and benefits (such as unemployment or Social Security), is used to calculate the EFC. The EFC is reported as a number and represents the amount your family is expected to contribute to your education for one academic year.
What Constitutes a Good EFC?
A "good" EFC largely depends on the context of your financial situation and the cost of the colleges you are considering. Here’s a breakdown to help you understand:
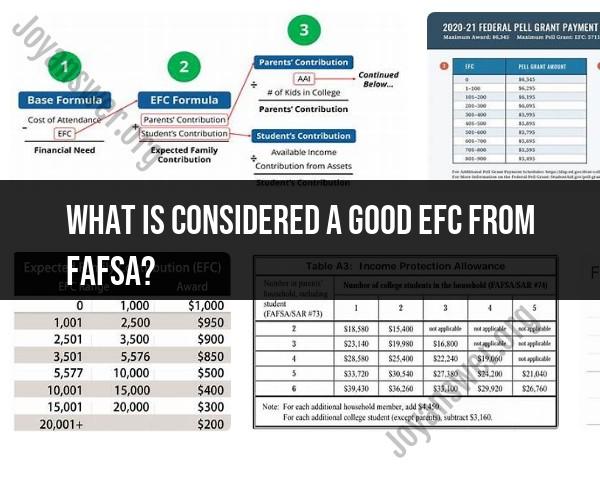
1. Lower EFC (0 to 5,000)
- Eligibility for Financial Aid: Typically, a lower EFC means you are more likely to qualify for need-based financial aid, including federal Pell Grants, work-study programs, and subsidized student loans.
- Grant Aid: Students with an EFC close to zero are often eligible for the maximum amount of federal Pell Grants and may also qualify for additional state and institutional grants.
- Considered Good: For many students, an EFC in this range is considered "good" because it indicates a higher likelihood of receiving significant financial aid.
2. Moderate EFC (5,001 to 20,000)
- Mixed Aid: Students with a moderate EFC might still qualify for some need-based aid but will also likely need to rely on loans and family contributions.
- Institutional Support: Some colleges with higher costs may provide substantial institutional aid to bridge the gap for students in this range.
- Context Matters: Whether this EFC is considered good depends on the cost of the college and the family’s financial situation. It may still be beneficial if the family can reasonably cover the expected contribution.
3. Higher EFC (20,001 and above)
- Less Need-Based Aid: Students with higher EFCs are less likely to qualify for federal need-based aid but may still access federal loans and merit-based scholarships.
- Family Contribution: A high EFC suggests that the family has a greater ability to pay for college expenses out of pocket.
- Variable Perspective: For families with sufficient income and savings, a high EFC might be manageable and not a significant concern. However, for others, it may mean more reliance on loans and savings.
Key Factors Influencing EFC
- Income: Both parent and student income are major factors.
- Assets: Savings, investments, and other assets are considered but with different weights for parents and students.
- Household Size: The number of people in your household can affect your EFC.
- Number of Family Members in College: If more than one family member is attending college simultaneously, your EFC may be lower.
Conclusion
A "good" EFC is one that aligns with your family's ability to pay for college without undue financial strain. For many, a lower EFC is ideal as it opens up more opportunities for financial aid. However, the context of your family's finances and the cost of the institutions you are considering will ultimately determine whether an EFC is manageable or not. It’s important to consider not just the EFC number but also the total cost of attendance and other financial resources available to you.
What range of Expected Family Contribution (EFC) from FAFSA is considered favorable?
A lower Expected Family Contribution (EFC) on your FAFSA is generally considered more favorable for financial aid purposes. This is because it indicates a higher level of financial need, making you eligible for more federal and state aid, as well as grants and scholarships from colleges and universities.
There's no single "favorable" EFC range, but here's a breakdown to help you understand how EFC affects aid:
- EFC of $0: This indicates the highest level of financial need and could potentially qualify you for the maximum amount of federal and state aid, along with scholarships and grants from institutions.
- Low EFC (Below national average): An EFC lower than the national average (which fluctuates year to year) is still favorable and can lead to significant financial aid awards.
- Moderate EFC (Around national average): An EFC around the national average may still qualify you for some federal and state aid, but the amount might be lower. You might need to look more into scholarships and work-study programs to bridge the gap.
- High EFC (Above national average): A higher EFC suggests a lower financial need. You might receive minimal federal aid and need to rely more on private loans or merit-based scholarships.
Here are some resources to help you get a better understanding of your EFC:
- Federal Student Aid website: Expected Family Contribution (EFC) This website explains how EFC is calculated and what it means for financial aid eligibility.
- FAFSA Expected Family Contribution (EFC) calculator: The FAFSA application process itself includes an EFC calculator that will give you an estimated EFC based on your financial information.
Remember, even with a higher EFC, exploring scholarship opportunities and work-study programs can significantly reduce your out-of-pocket college costs.