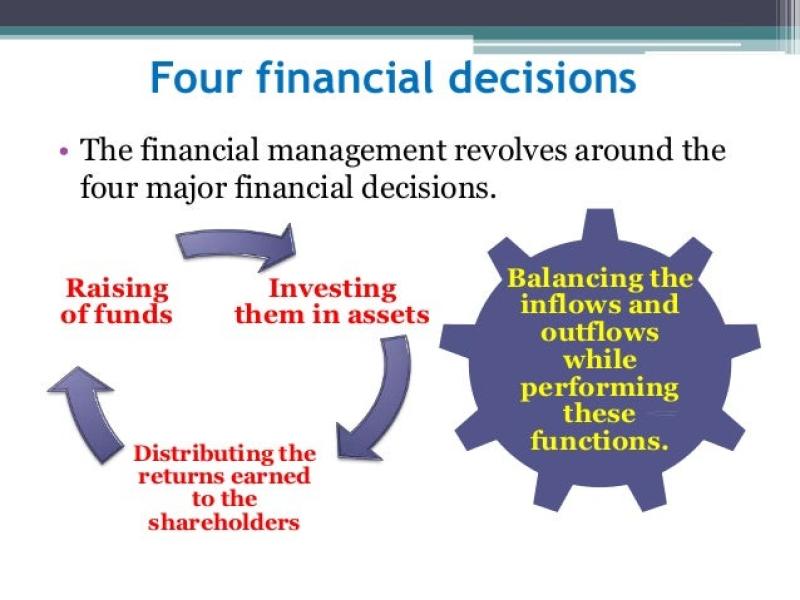
What are the three types of financial management decisions?
Financial management decisions encompass various aspects of managing a company's finances to achieve its financial goals. While there are more than three types of financial decisions, the primary categories include:
Capital Budgeting Decisions (Investment Decisions):
- Capital budgeting decisions involve the allocation of funds to long-term investment opportunities. These decisions determine where a company should invest its capital to generate returns in the future. Key components of capital budgeting include:
- Evaluating investment proposals or projects.
- Estimating cash flows and expected returns.
- Assessing the risks associated with each project.
- Selecting projects that align with the company's strategic goals and have a positive net present value (NPV).
- Capital budgeting decisions involve the allocation of funds to long-term investment opportunities. These decisions determine where a company should invest its capital to generate returns in the future. Key components of capital budgeting include:
Financing Decisions:
- Financing decisions pertain to how a company raises capital to fund its operations and investments. This involves determining the optimal mix of debt and equity to maintain financial stability and achieve growth. Key aspects of financing decisions include:
- Issuing debt (e.g., bonds, loans) or equity (e.g., stocks) to raise funds.
- Evaluating the cost of capital associated with different financing options.
- Assessing the company's leverage and debt levels.
- Ensuring that the financing structure aligns with the company's risk tolerance and financial objectives.
- Financing decisions pertain to how a company raises capital to fund its operations and investments. This involves determining the optimal mix of debt and equity to maintain financial stability and achieve growth. Key aspects of financing decisions include:
Working Capital Management Decisions:
- Working capital management decisions involve the day-to-day management of a company's short-term assets and liabilities. These decisions are essential for maintaining liquidity and operational efficiency. Key components of working capital management include:
- Managing cash and cash equivalents.
- Handling accounts receivable and accounts payable to optimize cash flow.
- Monitoring inventory levels to balance carrying costs and stockouts.
- Ensuring that the company has adequate liquidity to meet its short-term obligations.
- Working capital management decisions involve the day-to-day management of a company's short-term assets and liabilities. These decisions are essential for maintaining liquidity and operational efficiency. Key components of working capital management include:
In addition to these primary categories, financial management decisions may also include dividend decisions (related to the distribution of profits to shareholders), risk management decisions (such as hedging against financial risks), and strategic financial decisions related to mergers, acquisitions, and alliances.
Effective financial management requires a balance among these various decisions to ensure a company's financial health, growth, and sustainability. The specific financial decisions a company makes will depend on its industry, size, goals, and the economic environment in which it operates.
What is the significance of capital budgeting in financial management?
Capital budgeting is a crucial aspect of financial management that involves evaluating and selecting long-term investment projects. It plays a significant role in firms' financial planning and decision-making by ensuring that capital resources are allocated efficiently to projects that maximize shareholder value.
The significance of capital budgeting lies in its ability to:
Enhance profitability: Capital budgeting helps firms identify and select projects that are expected to generate positive returns, thereby enhancing overall profitability and shareholder wealth.
Optimize resource allocation: By evaluating potential projects, capital budgeting ensures that limited capital resources are allocated to those projects with the highest potential returns, maximizing the firm's financial efficiency.
Support strategic goals: Capital budgeting aligns investment decisions with the firm's long-term strategic goals, ensuring that investments contribute to the firm's overall growth and competitive position.
Reduce financial risk: Capital budgeting techniques, such as net present value (NPV) and internal rate of return (IRR), help assess the financial viability of projects, reducing the risk of investing in unprofitable or high-risk ventures.
Facilitate informed decision-making: Capital budgeting provides a structured framework for evaluating investment alternatives, enabling firms to make informed decisions based on quantitative analysis and risk assessment.
How do financing decisions contribute to a firm's capital structure?
Financing decisions determine how a firm raises the capital needed to fund its operations, acquisitions, and growth initiatives. These decisions play a crucial role in shaping the firm's capital structure, which refers to the mix of debt, equity, and other sources of financing used by the firm.
The impact of financing decisions on capital structure includes:
Cost of capital: The cost of capital is the rate a firm must pay to attract financing. Financing decisions influence the cost of capital by determining the proportion of debt and equity in the capital structure.
Financial risk: The risk associated with a firm's capital structure is influenced by the mix of debt and equity. Debt financing typically carries higher risk due to fixed interest payments and the potential for default.
Financial flexibility: A firm's ability to raise additional capital in the future is affected by its capital structure. A balanced capital structure can enhance financial flexibility, making it easier to raise capital when needed.
Tax implications: Financing decisions can have tax implications, as interest payments on debt are tax-deductible, while dividends paid to shareholders are not.
Shareholder value: Financing decisions can indirectly impact shareholder value by influencing the firm's profitability, risk profile, and financial flexibility.
In what ways do dividend decisions affect shareholder value?
Dividend decisions determine how much of a firm's profits are distributed to shareholders and how much is retained for reinvestment. These decisions can have a significant impact on shareholder value through various channels:
Dividend payout ratio: The dividend payout ratio is the percentage of profits paid out to shareholders as dividends. A higher payout ratio can enhance shareholder satisfaction and attract dividend-seeking investors.
Share repurchase programs: Share repurchases involve the firm buying back its own shares from the market. This can reduce the number of outstanding shares, increasing earnings per share (EPS) and potentially boosting share prices.
Signal to the market: Dividend decisions can send signals about the firm's financial health and future prospects. Consistent dividend payments may indicate stability and growth potential, while dividend cuts or suspensions may signal financial difficulties.
Investor preferences: Different investors have varying preferences regarding dividends. Dividend-seeking investors may favor firms with high payout ratios, while growth-oriented investors may prefer firms that retain profits for reinvestment.
Overall shareholder value: Ultimately, the impact of dividend decisions on shareholder value depends on a complex interplay of factors, including the firm's financial situation, growth prospects, investor preferences, and overall market conditions.