How many perspectives are there in sociology?
Sociology is a diverse field with multiple perspectives and approaches to understanding human society and social behavior. While it's difficult to assign an exact number to the perspectives in sociology, there are several major theoretical perspectives that sociologists often use to analyze and explain various aspects of society. These include:
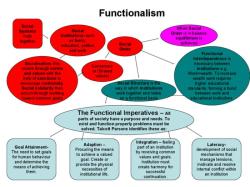
Structural Functionalism: This perspective views society as a complex system made up of various institutions and structures that work together to maintain stability and order. It focuses on how different parts of society function to meet the needs of individuals and the broader society.
Conflict Theory: Conflict theory emphasizes the role of power, inequality, and social conflict in shaping society. It examines how different groups in society compete for resources, influence, and social change, often leading to tension and inequality.
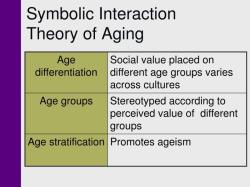
Symbolic Interactionism: Symbolic interactionism explores how individuals and groups create and interpret symbols and meanings in their interactions. It emphasizes the role of symbols, language, and communication in shaping social reality.
Feminist Theory: Feminist theory analyzes the role of gender in society and the ways in which patriarchy and gender inequality impact individuals and social structures. It seeks to understand and challenge gender-based discrimination and oppression.
Social Constructionism: Social constructionism argues that many aspects of social reality, such as gender, race, and identity, are socially constructed through shared beliefs, language, and cultural practices. It examines how these constructions influence our perceptions and experiences.
Conflict Perspective: The conflict perspective, often associated with Marxism, focuses on class struggle and the exploitation of the working class by the capitalist class. It emphasizes economic inequality and the role of social classes in shaping society.
Interactionist Perspective: Interactionist perspectives, including symbolic interactionism, examine how individuals interact with each other and interpret symbols and meanings in their daily lives. They emphasize the importance of small-scale interactions in shaping society.
Rational Choice Theory: Rational choice theory views individuals as rational actors who make decisions based on their self-interest. It explores how individuals make choices in various social contexts, including economics, politics, and relationships.
Postmodernism: Postmodernism challenges traditional sociological theories and emphasizes the fragmented and complex nature of contemporary society. It questions the idea of a single, objective truth and highlights the diversity of human experiences.
Queer Theory: Queer theory examines issues related to sexuality, gender identity, and sexual norms. It challenges traditional notions of binary gender and heteronormativity and explores the fluidity of identities.
These are some of the major perspectives in sociology, but there are many other specialized and hybrid perspectives that sociologists may use to analyze specific social phenomena. Sociological research often draws from multiple perspectives to provide a comprehensive understanding of complex social issues.
Sociology Perspectives: A Multifaceted Exploration of Society
Sociology is the study of human society and social behavior. It is a broad and diverse field, with many different perspectives on society.
One of the most important aspects of sociology is its use of multiple perspectives. This means that sociologists do not rely on a single theory or approach to explain social phenomena. Instead, they draw on a variety of perspectives to gain a more complete understanding of society.
Sociology's Many Lenses: Diverse Perspectives on Human Interaction
Some of the most common sociological perspectives include:
- Functionalism: Functionalism views society as a system made up of interrelated parts. Each part of the system plays a role in maintaining the stability and functioning of the whole.
- Conflict theory: Conflict theory views society as a place of conflict between different groups. These groups compete for power and resources.
- Symbolic interactionism: Symbolic interactionism focuses on the meaning that people attach to their social interactions. It is concerned with how people use symbols and language to communicate with each other and make sense of the world around them.
Other sociological perspectives include feminist theory, queer theory, and critical race theory. These perspectives focus on the experiences of marginalized groups and the ways in which power and inequality operate in society.
Sociological Frameworks: Understanding the Varied Perspectives in the Field
Sociological frameworks provide a way to organize and understand the different sociological perspectives. One common framework is the micro-macro distinction. Micro-sociological perspectives focus on the individual and small-group interactions. Macro-sociological perspectives focus on large-scale social structures and processes.
Another common framework is the theory-method distinction. Sociological theories provide general explanations of social phenomena. Sociological methods are the tools that sociologists use to collect and analyze data to test their theories.
Conclusion
Sociology perspectives provide a multifaceted exploration of society. By drawing on a variety of perspectives, sociologists can gain a more complete understanding of the complex forces that shape our social world.