What is a best description of structural functionalism?
Structural functionalism is a foundational sociological perspective that seeks to understand society by examining how its various parts and institutions work together to maintain stability and order. It emphasizes the interconnectedness of different elements within a society and how they contribute to the overall functioning of the social system. Here is a comprehensive description of structural functionalism:
Basic Assumptions:
- Structural functionalism is based on several key assumptions:
- Society is a complex system composed of various interrelated parts, like institutions, norms, values, and roles.
- These parts have specific functions, roles, or purposes that contribute to the stability and survival of society.
- Society tends to seek a state of equilibrium, where all parts work harmoniously together.
- Structural functionalism is based on several key assumptions:
Function and Dysfunction:
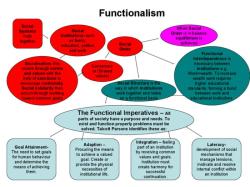
- The core concept of structural functionalism is the idea of "function." Each element of society, such as family, education, religion, and government, serves a function that contributes to the overall well-being of society.
- Functions can be manifest (intended and recognized) or latent (unintended and not always recognized).
- Dysfunctions, on the other hand, are aspects of society that disrupt or harm its stability. Structural functionalists seek to understand how society addresses these dysfunctions and restores equilibrium.
Interconnected Parts:
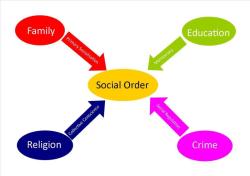
- Structural functionalism highlights the interconnectedness of different parts of society. For example, the family, education, and the economy are all interrelated and depend on each other to function effectively.
- Changes in one part of society can have ripple effects throughout the system, leading to adjustments in other parts to maintain stability.
Social Order and Stability:
- This perspective places a strong emphasis on the role of social order and stability in society. It suggests that societies tend to develop norms, values, and institutions that promote order and prevent chaos.
Evolution and Adaptation:
- Structural functionalism recognizes that societies evolve and adapt over time. As circumstances change, institutions and norms may also change to ensure that society continues to function smoothly.
Critiques and Limitations:
- Critics argue that structural functionalism can oversimplify complex social phenomena and downplay issues of conflict, inequality, and power dynamics within society.
- This perspective has been criticized for its conservative and status quo-preserving tendencies, as it tends to focus on the functions that maintain the existing social order.
Contributions:
- Despite its limitations, structural functionalism has made significant contributions to sociology by providing a framework for understanding the stability and functioning of societies. It has influenced the study of institutions, social roles, and the relationship between individuals and society.
In summary, structural functionalism is a sociological perspective that views society as a complex system of interrelated parts, each with specific functions that contribute to the overall stability and order of the social system. While it has been criticized for its limitations, it remains a valuable framework for analyzing how different aspects of society work together to maintain equilibrium.
Exploring Structural Functionalism: A Comprehensive Overview
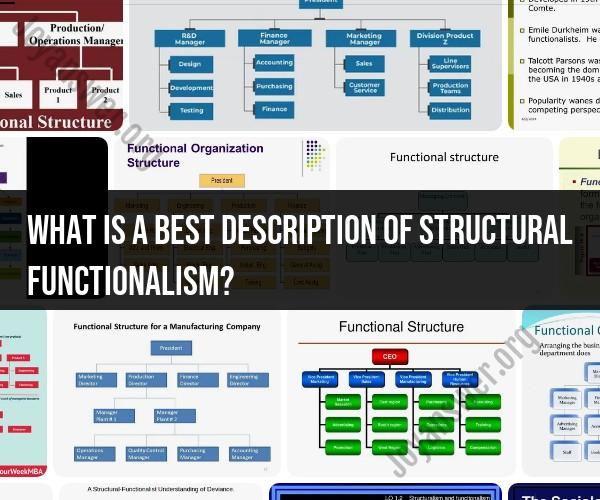
Structural functionalism is a macro theory in sociology that focuses on the relationship between the different parts of society and how they work together to maintain social order and stability. It is a systems theory, meaning that it sees society as a complex system made up of interconnected parts.
Structural functionalists believe that each part of society plays an important role in maintaining the whole. For example, the family institution is responsible for socializing children and providing them with emotional support. The education system is responsible for educating children and preparing them for the workforce. The economy is responsible for providing jobs and opportunities for people to support themselves and their families.
Structural functionalists also believe that social institutions are interrelated. For example, the family institution is interconnected with the education system and the economy. Parents are responsible for sending their children to school, and children need to be educated in order to get good jobs and support their families.
The Core Principles and Concepts of Structural Functionalism
The core principles and concepts of structural functionalism include:
- Social structure: Social structure refers to the patterned arrangements of social relationships and institutions in a society.
- Social functions: Social functions refer to the ways in which social institutions meet the needs of society.
- Social order: Social order refers to the stability and predictability of social life.
- Manifest functions: Manifest functions are the intended consequences of social institutions.
- Latent functions: Latent functions are the unintended consequences of social institutions.
Structural Functionalism in Sociology: A Closer Look
Structural functionalism has been used by sociologists to study a wide range of social phenomena, including:
- The family
- Education
- The economy
- Religion
- Politics
- Crime and deviance
Structural functionalism has been criticized for a number of reasons, including:
- It is a conservative theory that tends to view the status quo as desirable.
- It does not take into account conflict or social change.
- It focuses on the functions of social institutions, but it does not adequately explain how social institutions came to be or how they change over time.
Despite these criticisms, structural functionalism remains an important theoretical framework for understanding society. It provides a useful way to think about how social institutions work together to meet the needs of society.
Examples of Structural Functionalism in Action
Here are a few examples of structural functionalism in action:
- The family institution socializes children and provides them with emotional support.
- The education system educates children and prepares them for the workforce.
- The economy provides jobs and opportunities for people to support themselves and their families.
- Religion provides individuals with a sense of meaning and purpose in life.
- The government provides social order and protection for its citizens.
Conclusion
Structural functionalism is a valuable theory for understanding how society works. It provides a framework for thinking about the relationship between the different parts of society and how they work together to maintain social order and stability.