How do compression fractures affect the spine?
Compression fractures of the spine occur when one or more vertebrae collapse or become compressed, leading to a reduction in vertebral height. These fractures can have various causes, including osteoporosis, trauma, or certain medical conditions. Here's a comprehensive overview of how compression fractures affect the spine:
1. Causes of Compression Fractures:
- Osteoporosis: This is a common cause, especially in older adults, where bones become porous and fragile, making them more prone to fractures.
- Trauma: A sudden and forceful impact, such as a fall or car accident, can lead to compression fractures.
- Tumors: Cancerous or non-cancerous growths on the spine can weaken the vertebrae and contribute to compression fractures.
- Infections: Certain infections affecting the spine can weaken bone structures, leading to fractures.
2. Location of Compression Fractures:
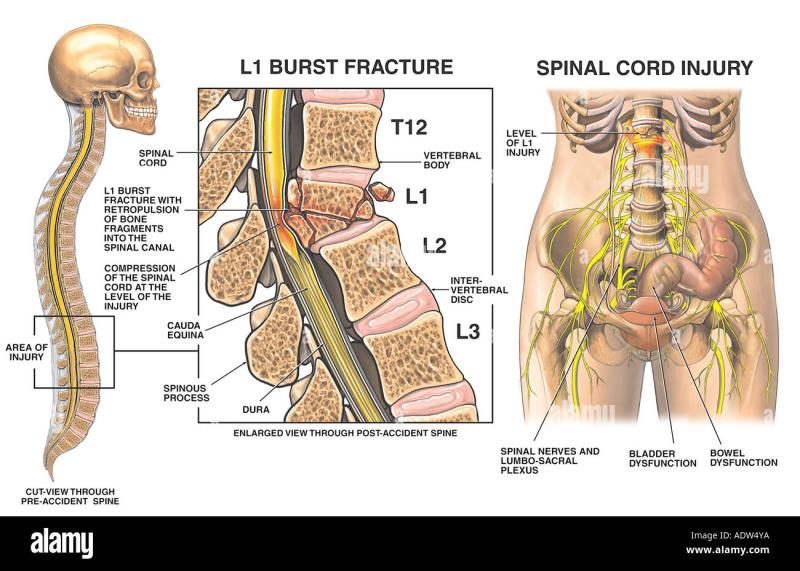
- Compression fractures often occur in the thoracic (upper/mid-back) and lumbar (lower back) regions of the spine. Thoracic compression fractures are less common but can occur, particularly in severe trauma or conditions like osteoporosis.
3. Symptoms:
- Back Pain: The most common symptom is sudden, severe back pain at the site of the fracture.
- Limited Spinal Mobility: Individuals may experience difficulty bending or twisting the spine.
- Height Loss: Compression fractures can lead to a reduction in height over time.
- Deformity: In some cases, particularly with multiple fractures, the spine may develop a forward curvature known as kyphosis, leading to a hunched appearance.
4. Diagnostic Methods:
- X-rays: Imaging studies, such as X-rays, can reveal compression fractures and their severity.
- MRI or CT Scans: These tests can provide detailed images of the spine and help identify other potential causes, such as tumors.
5. Treatment Options:
- Conservative Treatment: Mild compression fractures may be managed with rest, pain medication, and bracing.
- Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty: These minimally invasive procedures involve injecting bone cement into the fractured vertebra to stabilize and relieve pain.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to improve posture, strengthen the back muscles, and enhance mobility.
- Surgery: In severe cases or if conservative measures are ineffective, surgery may be considered. Procedures may involve spinal fusion or the use of hardware to stabilize the spine.
6. Complications:
- Chronic Pain: Some individuals may experience persistent pain even after treatment.
- Reduced Mobility: Compression fractures can lead to a reduction in spinal mobility, affecting daily activities.
- Decreased Quality of Life: Severe compression fractures, especially if multiple, can significantly impact an individual's overall quality of life.
7. Prevention:
- Osteoporosis Management: For fractures related to osteoporosis, managing and preventing further bone loss is essential. This may include medications, calcium supplementation, and lifestyle modifications.
- Fall Prevention: Taking measures to prevent falls, such as ensuring a safe home environment, using assistive devices, and staying physically active.
8. Long-Term Management:
- Individuals with compression fractures, especially those related to osteoporosis, may require long-term management to prevent further fractures. This often involves a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and ongoing monitoring.
It's important for individuals experiencing back pain or suspected compression fractures to seek prompt medical attention for proper diagnosis and appropriate management. The specific treatment approach will depend on the cause, severity, and individual circumstances.
Impact on the spine: How do compression fractures affect the spine?
Compression fractures are small breaks in the vertebrae, the bones that make up the spine. They can occur anywhere in the spine, but they are most common in the thoracic (upper back) and lumbar (lower back) regions.
Compression fractures can be caused by a variety of factors, including osteoporosis, trauma, and cancer. They can also occur as a result of normal aging.
When a compression fracture occurs, the vertebra collapses, which can lead to a number of problems, including:
- Pain: Compression fractures can cause pain in the back and neck. The pain is often worse when standing or walking and may improve with rest.
- Loss of height: Compression fractures can cause the spine to shorten, which can lead to loss of height.
- Deformity: Compression fractures can cause the spine to curve, which can lead to deformity.
- Nerve damage: Compression fractures can put pressure on the nerves in the spine, which can cause numbness, weakness, and tingling in the arms and legs.
Exploring the consequences and implications of compression fractures on spinal health
Compression fractures can have a significant impact on spinal health. They can lead to pain, loss of height, deformity, and nerve damage. Compression fractures can also make it difficult to perform everyday activities, such as walking, standing, and lifting objects.
In addition to the physical consequences, compression fractures can also have a negative impact on mental health. People with compression fractures may experience anxiety, depression, and social isolation.
Tips for managing and seeking treatment for compression fractures in the spine
There are a number of things that people with compression fractures can do to manage their condition and seek treatment.
Management tips:
- Rest: Getting plenty of rest can help to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Pain medication: Over-the-counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, can help to relieve pain.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help to strengthen the muscles around the spine and improve flexibility.
- Bracing: A brace can help to support the spine and reduce pain.
Treatment options:
- Medication: There are a number of medications that can be used to treat compression fractures. These medications can help to strengthen bones and reduce the risk of future fractures.
- Surgery: Surgery may be necessary in some cases to repair compression fractures. Surgery is usually reserved for people who have severe pain or nerve damage.
If you think you may have a compression fracture, it is important to see a doctor right away. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent further complications.
Here are some additional tips for managing and seeking treatment for compression fractures in the spine:
- Eat a healthy diet. A healthy diet can help to strengthen bones and reduce the risk of compression fractures.
- Exercise regularly. Exercise can help to strengthen the muscles around the spine and improve flexibility.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can weaken bones and increase the risk of compression fractures.
- Talk to your doctor about your risk factors. If you have osteoporosis or other risk factors for compression fractures, talk to your doctor about ways to reduce your risk.
By following these tips, you can manage your compression fractures and maintain your spinal health.