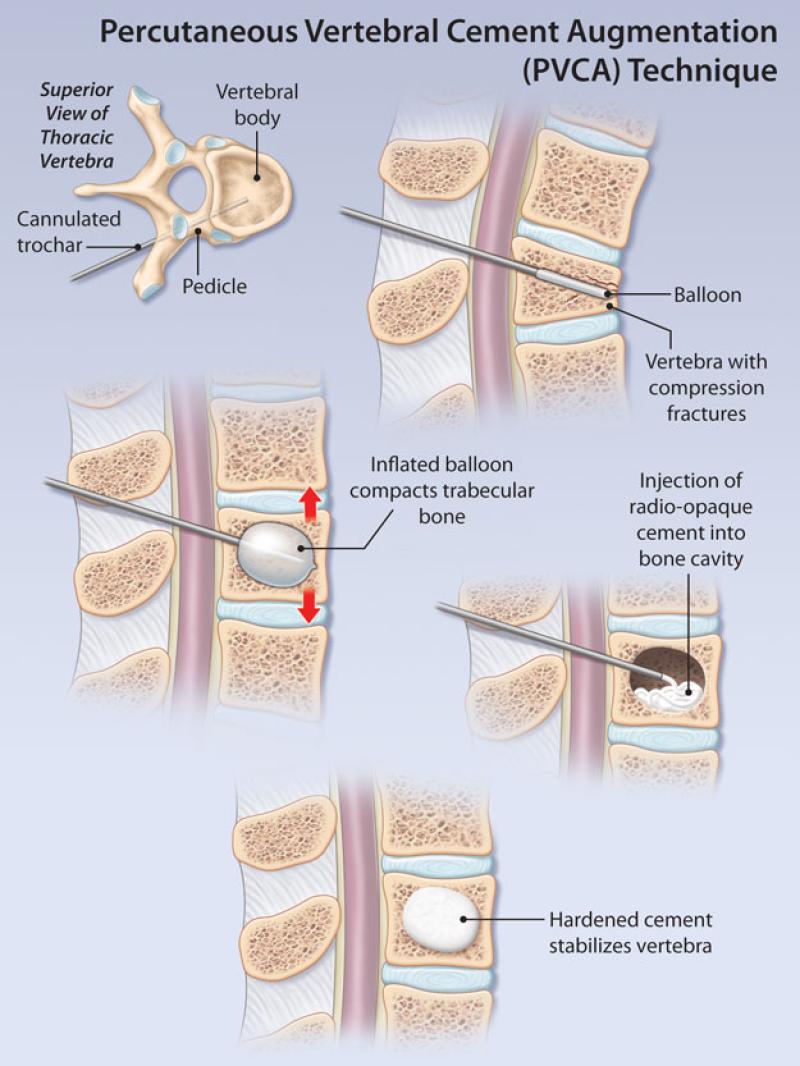
How is compression fracture diagnosed?
Diagnosing compression fractures typically involves a combination of medical history assessment, physical examination, and imaging studies. Here are the common methods and procedures used in the diagnosis of compression fractures:
Medical History and Physical Examination:
- The healthcare provider will begin by taking a detailed medical history, asking about symptoms, recent injuries, or any relevant medical conditions. A physical examination may involve assessing the spine's range of motion, checking for tenderness or deformities, and evaluating neurological symptoms.
Pain Assessment:
- The patient's description of the pain, including its location, intensity, and any exacerbating or alleviating factors, is crucial in guiding the diagnostic process.
X-rays:
- X-rays are often the initial imaging study used to diagnose compression fractures. X-rays can reveal changes in the structure of the vertebrae, such as compression, fractures, or collapses. They provide a quick and relatively low-cost assessment of the spine.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
- An MRI scan is more detailed than X-rays and can provide a clearer view of soft tissues, ligaments, and the spinal cord. It is particularly useful for identifying acute fractures, evaluating the extent of damage, and detecting other associated conditions.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan:
- A CT scan may be recommended to provide more detailed images of the spine. It is especially helpful in assessing the bones and detecting fractures that may not be as easily visible on X-rays.
Bone Scan:
- A bone scan may be performed to identify areas of increased bone activity, which can be indicative of fractures, infections, or tumors. While less common than X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs, bone scans may be used in specific cases.
DEXA Scan:
- Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scans are often used to assess bone density and the risk of osteoporosis, which can contribute to compression fractures. Osteoporosis is a common underlying cause of vertebral compression fractures.
Laboratory Tests:
- Blood tests may be ordered to assess calcium levels, thyroid function, and other factors related to bone health. These tests can help identify potential causes of decreased bone density or increased fracture risk.
Biopsy (Rarely):
- In some cases, a biopsy may be recommended to examine a sample of bone tissue. This is usually reserved for situations where the cause of the compression fracture is uncertain or when a more detailed analysis is needed.
Neurological Examination:
- If the compression fracture is affecting the spinal cord, a neurological examination may be conducted to assess sensory and motor function, reflexes, and other signs of spinal cord injury.
The combination of these diagnostic methods allows healthcare professionals to accurately identify and understand the nature and extent of the compression fracture. Once diagnosed, the appropriate treatment plan can be determined, which may include pain management, physical therapy, bracing, and, in some cases, surgical intervention.
Diagnosing spinal issues: How is a compression fracture diagnosed?
Compression fractures are a common type of spinal injury. They occur when the bones in the spine (vertebrae) collapse. This can happen from a sudden impact, such as a fall or car accident, or from overuse, such as osteoporosis.
Symptoms of a compression fracture include:
- Pain in the back or neck, especially when standing or sitting
- Loss of height
- Kyphosis (hunchback)
- Muscle weakness
- Numbness or tingling in the arms or legs
To diagnose a compression fracture, your doctor will likely:
- Ask you about your medical history and symptoms
- Perform a physical exam to check for tenderness, swelling, and muscle weakness
- Order imaging tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs, to see the bones in your spine
Methods and procedures for diagnosing compression fractures in the spine
The following methods and procedures are commonly used to diagnose compression fractures in the spine:
- X-rays: X-rays are the most common type of imaging test used to diagnose compression fractures. They can show the bones in your spine and reveal any signs of a fracture.
- CT scans: CT scans create cross-sectional images of your spine. They can provide more detailed images of the bones and soft tissues in your spine than X-rays.
- MRIs: MRIs use magnetic fields and radio waves to create images of the soft tissues in your spine. They can be used to diagnose compression fractures that are not visible on X-rays or CT scans.
Tips for seeking medical attention and understanding diagnostic processes for spinal conditions
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms of a compression fracture, it is important to seek medical attention right away. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent complications, such as chronic pain, deformity, and nerve damage.
Here are some tips for seeking medical attention and understanding diagnostic processes for spinal conditions:
- Find a doctor who specializes in spinal conditions. This could be an orthopedic surgeon, neurosurgeon, or physical medicine and rehabilitation doctor.
- Ask your doctor about the diagnostic tests that they recommend. Be sure to understand the risks and benefits of each test before agreeing to it.
- If you have any questions or concerns, be sure to ask your doctor. They should be able to explain the diagnostic process to you in a way that you understand.
Here are some additional tips:
- Be prepared to give your doctor a detailed medical history. This includes any previous injuries, illnesses, and surgeries.
- Tell your doctor about any medications or supplements that you are taking.
- Be honest about your symptoms and pain levels. This will help your doctor to make a diagnosis and recommend the best course of treatment.
By following these tips, you can ensure that you receive the best possible care for your spinal condition.