What is SWOT analysis?
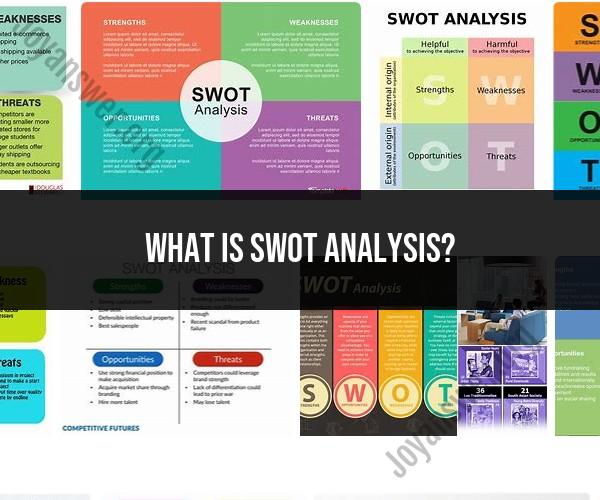
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning framework used by organizations to evaluate their current position and develop strategies for the future. SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats, and it provides a structured way to assess both internal and external factors that can impact an organization's performance. Here's a breakdown of each component of SWOT analysis:
Strengths (S):
- Strengths are internal factors that give an organization a competitive advantage or a unique edge in its industry.
- These can include the organization's assets, resources, capabilities, brand reputation, skilled workforce, and any other positive attributes that set it apart.
Weaknesses (W):
- Weaknesses are also internal factors, but they represent areas where the organization falls short or faces challenges.
- Identifying weaknesses helps an organization recognize areas that need improvement, such as outdated technology, limited resources, or inefficiencies in operations.
Opportunities (O):
- Opportunities are external factors in the business environment that an organization can leverage to its advantage.
- These can include market trends, emerging technologies, new customer segments, regulatory changes, or any external conditions that present growth or expansion prospects.
Threats (T):
- Threats are external factors that can potentially harm or hinder the organization's success.
- Threats may come from competitors, economic downturns, changing consumer preferences, legal or regulatory issues, or any external challenges that could negatively impact the organization.
The process of conducting a SWOT analysis typically involves the following steps:
Data Collection: Gather relevant information about the organization, its industry, and the external environment. This may involve surveys, market research, internal assessments, and stakeholder input.
SWOT Matrix: Create a SWOT matrix or grid with four quadrants, one for each component (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats). Populate each quadrant with key points or factors.
Analysis: Evaluate the factors listed in each quadrant and prioritize them based on their impact and significance. Consider how strengths can be leveraged, weaknesses addressed, opportunities seized, and threats mitigated.
Strategy Development: Use the insights gained from the SWOT analysis to develop strategic goals and action plans. Align your organization's strengths with opportunities, work on improving weaknesses, and create strategies to counter threats.
Monitoring and Revision: SWOT analysis is an ongoing process. Regularly revisit and update the analysis as the business environment evolves. This helps ensure that your organization remains adaptable and responsive to changing conditions.
SWOT analysis is a versatile tool used in various fields, including business, marketing, healthcare, education, and nonprofit sectors. It provides a structured framework for decision-making, helping organizations make informed choices and better position themselves in their respective industries.