What are the principles of bureaucracy?
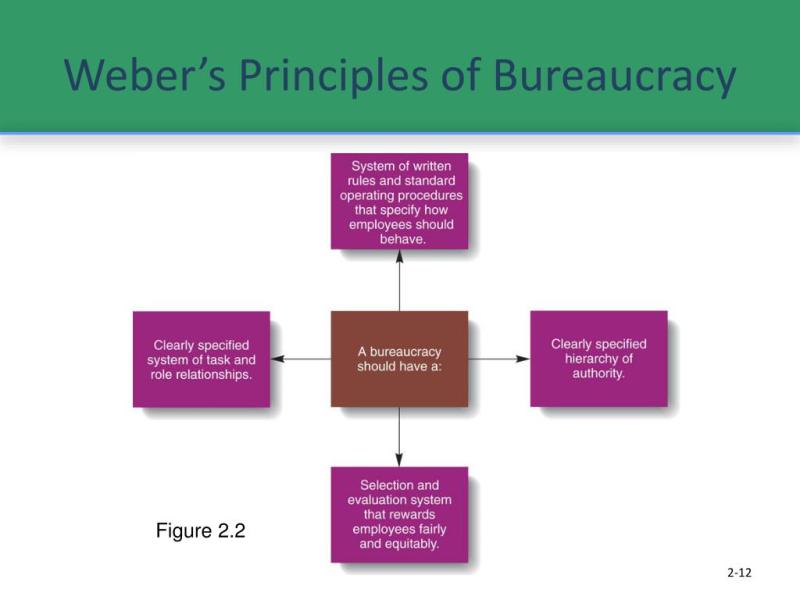
Max Weber, a German sociologist, identified several principles underlying bureaucracy. These principles provide a framework for understanding the key tenets of bureaucratic organizations. Here are the main principles of bureaucracy:
Division of Labor:
- Bureaucracy involves the division of labor, where tasks are broken down into specialized roles. This specialization allows individuals to focus on specific functions, leading to increased efficiency and expertise.
Hierarchy of Authority:
- Bureaucratic organizations have a clear hierarchy of authority, with levels of management and supervision. Each level has its own set of responsibilities, and lower levels are subordinate to higher ones.
Formal Rules and Procedures:
- Bureaucracy relies on formal rules and procedures to govern organizational behavior. These rules provide a standardized framework for decision-making and operations, ensuring consistency and predictability.
Impersonality:
- Bureaucracy emphasizes impersonality, where decisions are based on rules and not on personal relationships. This helps in avoiding favoritism or bias and contributes to fair and objective treatment.
Career Meritocracy:
- Bureaucratic organizations promote a system of career advancement based on merit. Individuals advance in their careers based on their qualifications, skills, and performance rather than personal connections.
Specialization and Expertise:
- Bureaucracy encourages specialization and the development of expertise in specific roles. Employees become specialists in their areas, contributing to increased efficiency and effectiveness.
Formal Recordkeeping:
- Bureaucratic organizations maintain detailed and formal records of decisions, actions, and transactions. This recordkeeping ensures transparency, accountability, and a historical reference for organizational activities.
Professionalism:
- Bureaucracy promotes a sense of professionalism among its members. Employees are expected to adhere to ethical standards and conduct themselves in a manner consistent with the organization's values.
Predictability:
- The use of formal rules and procedures in bureaucracy contributes to predictability. This predictability is essential for organizational stability and the efficient execution of tasks.
Separation of Personal and Professional Life:
- Bureaucracy advocates for the separation of personal and professional life. Personal emotions and relationships should not interfere with the objective and impartial execution of organizational duties.
These principles, as outlined by Max Weber, form the foundation of bureaucratic organizations. While bureaucracy has its advantages, it's important to note that excessive adherence to these principles can lead to rigidity and bureaucracy becoming an obstacle to innovation and adaptability. Organizations often seek to strike a balance between the benefits of bureaucracy and the need for flexibility in a dynamic environment.
Core principles defining bureaucratic systems
The core principles defining bureaucratic systems were outlined by German sociologist Max Weber in the early 20th century. These principles aimed to create organizations that were rational, efficient, and fair. They continue to influence bureaucratic structures around the world even today.
Here are the key principles:
- Hierarchy and chain of command: A clear hierarchy with well-defined lines of authority and responsibility. This ensures order and accountability, with each level reporting to the one above it.
- Formal rules and regulations: Standardized procedures and written rules govern every aspect of work, ensuring consistency and fairness in decision-making.
- Division of labor and specialization: Work is divided into specialized tasks, with each employee focusing on a specific area of expertise. This leads to increased efficiency and productivity, as workers become highly skilled in their particular roles.
- Impersonality and neutrality: Decisions are based on objective criteria and procedures, not personal relationships or emotions. This promotes fairness and prevents favoritism.
- Meritocratic recruitment and promotion: Selection and advancement are based on qualifications and performance, not personal connections or nepotism. This ensures that the most qualified people are in positions of power.
- Career orientation: Employees are encouraged to develop their skills and advance through the ranks, creating a stable and committed workforce.
It is important to note that while these principles have been influential, bureaucratic systems can also be criticized for being inflexible, slow-moving, and resistant to change. Additionally, the focus on rules and procedures can sometimes lead to red tape and a lack of common sense. Nevertheless, understanding the core principles of bureaucracy can help us to better understand and evaluate these complex systems.
Here are some additional points that can be made about bureaucratic systems:
- Bureaucratic systems are often associated with negative stereotypes, such as being inefficient, slow-moving, and resistant to change. However, it is important to remember that these systems can also be effective in achieving their goals.
- Bureaucracy is not a monolithic entity. There are many different types of bureaucratic systems, each with its own unique characteristics.
- Bureaucracy is a dynamic system that is constantly evolving. As the world changes, so too do bureaucratic systems.
I hope this helps! Let me know if you have any other questions.