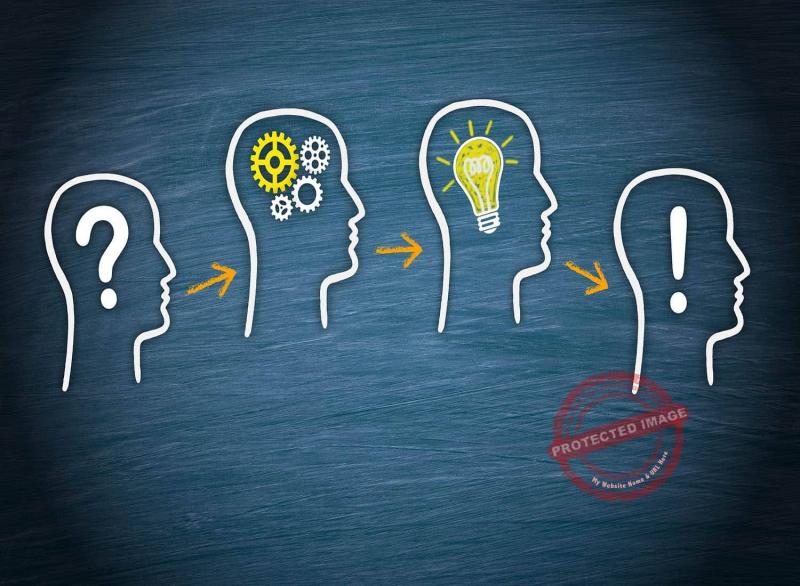
What are strategies for problem solving?
Effective problem-solving involves employing various strategies to address challenges efficiently and achieve optimal solutions. Here are several strategies to consider:
1. Define the Problem:
- Clarify the Issue: Understand the problem thoroughly by defining its scope, boundaries, and underlying causes. Ask questions to gain a comprehensive understanding.
2. Analyze the Situation:
- Gather Information: Collect relevant data and facts related to the problem. Use critical thinking to evaluate and interpret the information.
3. Generate Solutions:
- Brainstorming: Encourage creative thinking to generate multiple potential solutions without criticism. Quantity matters initially; quality comes later.
- Mind Mapping: Visualize connections between ideas to explore potential solutions and their implications.
4. Evaluate Alternatives:
- Assess Options: Consider the pros and cons of each potential solution. Evaluate their feasibility, impact, and alignment with desired outcomes.
- Prioritize: Rank solutions based on criteria such as effectiveness, cost, time, and resources required.
5. Make Decisions:
- Decision Matrix: Use a decision-making tool to objectively compare and select the best solution based on predetermined criteria.
- Risk Analysis: Assess potential risks associated with each solution and develop risk mitigation strategies.
6. Implement the Solution:
- Action Plan: Develop a clear plan outlining steps needed to execute the chosen solution.
- Allocate Resources: Assign responsibilities, allocate necessary resources, and establish timelines for implementation.
7. Monitor Progress:
- Feedback Loops: Regularly evaluate the progress of the implemented solution. Adjustments may be necessary based on feedback and changing circumstances.
- Measure Success: Establish metrics to gauge the effectiveness of the solution and whether it addresses the problem.
8. Learn and Adapt:
- Reflection: Reflect on the process and outcomes. Identify lessons learned and apply them to future problem-solving endeavors.
- Continuous Improvement: Embrace a mindset of continuous improvement, adapting strategies based on previous experiences.
9. Collaborate and Communicate:
- Teamwork: Collaborate with others to leverage diverse perspectives and expertise.
- Effective Communication: Clearly communicate ideas, expectations, and progress to stakeholders involved in the problem-solving process.
By employing these strategies systematically, individuals and teams can enhance their problem-solving skills, streamline decision-making, and achieve more effective and efficient solutions to complex challenges.
Effective problem-solving is a crucial skill that enables individuals and organizations to overcome challenges, identify solutions, and achieve desired outcomes. Here are some effective strategies that can be used for problem-solving:
1. Define and Analyze the Problem:
Before attempting to solve a problem, it is essential to clearly define and analyze its nature, scope, and root cause. This involves gathering information, identifying the problem's components, and understanding the underlying factors contributing to the issue.
2. Brainstorm and Generate Solutions:
Once the problem is well-defined, brainstorm and generate as many potential solutions as possible. Encourage creative thinking, consider unconventional approaches, and explore a wide range of options without immediately judging their feasibility.
3. Evaluate and Select the Best Solution:
Evaluate the generated solutions based on their effectiveness, feasibility, and potential consequences. Consider factors such as cost, time constraints, and impact on stakeholders. Select the solution that best addresses the problem while minimizing negative consequences.
4. Develop an Implementation Plan:
Create a detailed plan for implementing the chosen solution. This plan should outline the steps involved, assign responsibilities, establish timelines, and identify necessary resources.
5. Implement and Monitor the Solution:
Put the implementation plan into action and closely monitor the effectiveness of the solution. Be prepared to make adjustments or course corrections as needed.
6. Evaluate the Outcome and Learn from the Process:
Upon completion, evaluate the outcome of the problem-solving process. Assess whether the desired outcome was achieved, identify lessons learned, and consider how the process could be improved in the future.
Comparison of Problem-solving Methodologies:
Different problem-solving methodologies emphasize different approaches and techniques. Some common methodologies include:
Analytical problem-solving: This approach involves breaking down the problem into smaller components and analyzing each part systematically to identify the root cause and develop solutions.
Creative problem-solving: This approach emphasizes out-of-the-box thinking, brainstorming, and exploring unconventional solutions. It is often used when traditional methods fail to yield satisfactory results.
Collaborative problem-solving: This approach involves involving multiple individuals with different perspectives and expertise to work together in identifying, analyzing, and addressing the problem.
Decision-making problem-solving: This approach focuses on evaluating and selecting the best course of action among a range of potential solutions, considering various factors and potential consequences.
The choice of problem-solving methodology depends on the specific context, the nature of the problem, and the available resources. Effective problem-solvers can adapt their approach based on the situation and utilize different techniques to effectively address challenges and achieve their desired outcomes.
Real-life Examples of Successful Problem-solving Strategies:
Several real-life examples illustrate the successful application of problem-solving strategies:
The development of penicillin: Alexander Fleming's accidental discovery of penicillin and his subsequent efforts to isolate and develop the drug revolutionized the treatment of bacterial infections.
The creation of the internet: The development of the internet involved numerous problem-solving breakthroughs, from communication protocols to network architecture, resulting in a global communication infrastructure.
The eradication of smallpox: The World Health Organization's global smallpox eradication campaign, despite facing challenges and setbacks, successfully eliminated the disease from the human population.
Innovation in the automotive industry: The automotive industry has a long history of innovation, with problem-solving leading to advancements in fuel efficiency, safety features, and environmental impact.
Solving complex environmental challenges: Addressing environmental issues like climate change and pollution requires a combination of problem-solving strategies, scientific research, and international cooperation.
Effective problem-solving is an ongoing process that requires creativity, perseverance, and a willingness to adapt. By utilizing appropriate strategies, individuals and organizations can overcome obstacles, identify solutions, and achieve their goals.