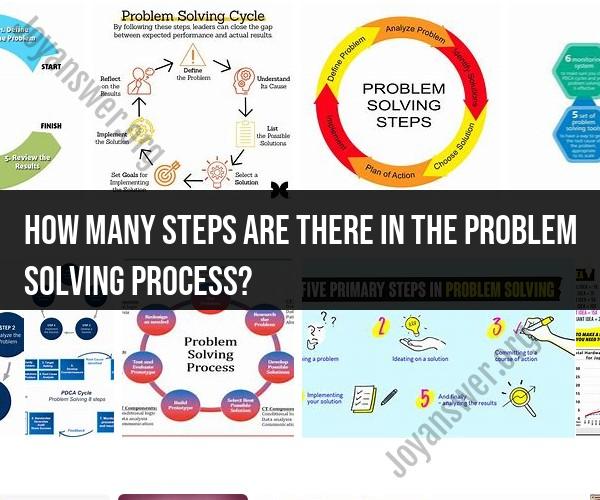
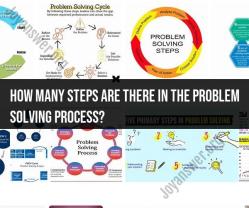
How many steps are there in the problem solving process?
The problem-solving process involves a series of steps designed to identify, analyze, and resolve issues or challenges effectively. Here are the steps in the problem-solving process:
1. Problem Identification:
- Recognize and define the problem or challenge clearly. Ensure a thorough understanding of the situation, its impact, and the desired outcome.
2. Information Gathering:
- Collect relevant data, information, and facts related to the problem. This step may involve research, surveys, interviews, or data analysis.
3. Problem Analysis:
- Analyze the information collected to understand the underlying causes, factors, and constraints contributing to the problem. Identify any patterns or trends.
4. Goal Setting:
- Define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals or objectives. Clearly articulate what you want to achieve by solving the problem.
5. Solution Generation:
- Brainstorm potential solutions and alternatives. Encourage creativity and diverse perspectives during this phase.
6. Evaluation of Options:
- Assess the pros and cons of each solution. Consider feasibility, potential risks, costs, and benefits associated with each option.
7. Decision-Making:
- Select the most suitable solution based on the evaluation. Make informed decisions that align with your goals and values.
8. Implementation Planning:
- Develop a detailed plan for implementing the chosen solution. Define action steps, responsibilities, timelines, and necessary resources.
9. Implementation:
- Put the plan into action, following the defined steps and timelines. Monitor progress and address any issues or obstacles that arise during implementation.
10. Monitoring and Evaluation:- Continuously assess the progress and effectiveness of the implemented solution. Collect feedback, data, and metrics to gauge success.
11. Adjustment and Refinement:- If the solution is not achieving the desired results, be open to adjustments and refinements. Modify the plan as needed to improve outcomes.
12. Closure:- Once the problem is resolved or the goal is achieved, formally close the project or initiative. Celebrate successes and acknowledge the efforts of those involved.
13. Documentation and Learning:- Document the problem-solving process, including the steps taken, decisions made, and outcomes achieved. Share lessons learned for future reference and improvement.
14. Continuous Improvement:- Encourage a culture of continuous improvement by applying insights gained from past problem-solving experiences to future challenges.
15. Communication:- Maintain clear and effective communication with stakeholders throughout the problem-solving process. Keep them informed of progress, changes, and outcomes.
16. Ethical Considerations:- Consider ethical principles and implications in every step of the problem-solving process. Ensure that solutions are aligned with ethical standards and values.
17. Collaboration and Teamwork:- Many problems require collaborative efforts. Engage relevant experts, stakeholders, and team members to leverage diverse perspectives and expertise.
Effective problem-solving often involves adaptability, critical thinking, and a structured approach. While these steps provide a framework, it's essential to be flexible and open to revisiting earlier steps or iterating through the process as needed to arrive at the best solution.