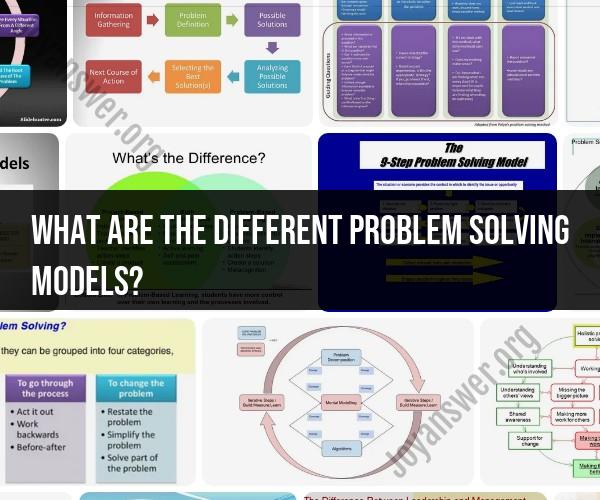
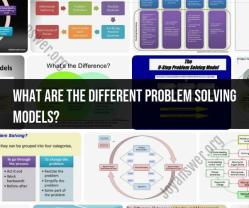
What are the different problem solving models?
Problem-solving models provide structured approaches to address challenges, make decisions, and find solutions in various fields and situations. Here's a comprehensive overview of the key elements and steps in navigating problem-solving models:
1. Problem Identification:
- The first step in problem-solving is recognizing and defining the problem or challenge clearly. It involves understanding the situation, its impact, and the desired outcome.
2. Information Gathering:
- Collect relevant data, information, and facts related to the problem. This step may involve research, surveys, interviews, or data analysis.
3. Problem Analysis:
- Analyze the information collected to understand the underlying causes, factors, and constraints contributing to the problem. Identify any patterns or trends.
4. Goal Setting:
- Define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals or objectives. Clearly articulate what you want to achieve by solving the problem.
5. Solution Generation:
- Brainstorm potential solutions and alternatives. Encourage creativity and diverse perspectives during this phase.
6. Evaluation of Options:
- Assess the pros and cons of each solution. Consider feasibility, potential risks, costs, and benefits associated with each option.
7. Decision-Making:
- Select the most suitable solution based on the evaluation. Make informed decisions that align with your goals and values.
8. Implementation Planning:
- Develop a detailed plan for implementing the chosen solution. Define action steps, responsibilities, timelines, and necessary resources.
9. Implementation:
- Put the plan into action, following the defined steps and timelines. Monitor progress and address any issues or obstacles that arise during implementation.
10. Monitoring and Evaluation:- Continuously assess the progress and effectiveness of the implemented solution. Collect feedback, data, and metrics to gauge success.
11. Adjustment and Refinement:- If the solution is not achieving the desired results, be open to adjustments and refinements. Modify the plan as needed to improve outcomes.
12. Closure:- Once the problem is resolved or the goal is achieved, formally close the project or initiative. Celebrate successes and acknowledge the efforts of those involved.
13. Documentation and Learning:- Document the problem-solving process, including the steps taken, decisions made, and outcomes achieved. Share lessons learned for future reference and improvement.
14. Continuous Improvement:- Encourage a culture of continuous improvement by applying insights gained from past problem-solving experiences to future challenges.
15. Communication:- Maintain clear and effective communication with stakeholders throughout the problem-solving process. Keep them informed of progress, changes, and outcomes.
16. Ethical Considerations:- Consider ethical principles and implications in every step of the problem-solving process. Ensure that solutions are aligned with ethical standards and values.
17. Collaboration and Teamwork:- Many problems require collaborative efforts. Engage relevant experts, stakeholders, and team members to leverage diverse perspectives and expertise.
Different problem-solving models, such as the scientific method, decision trees, SWOT analysis, Six Sigma, and more, may emphasize specific steps or approaches. The choice of model depends on the nature of the problem and the context in which it arises. Effective problem-solving often involves a combination of models and approaches to address complex challenges comprehensively.