How do you solve a density equation?
Density equations are fundamental in various scientific and engineering fields. This comprehensive guide will provide you with a practical approach to solving density equations and understanding their applications.
Understanding Density
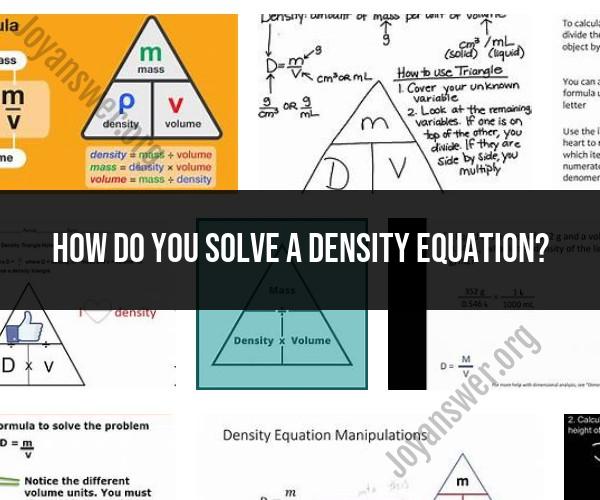
Density is the measure of mass per unit volume of a substance. It is calculated using the formula:
Density (ρ) = Mass (m) / Volume (V)
Solving for Mass or Volume
You can rearrange the density formula to solve for mass or volume:
- Mass (m) = Density (ρ) × Volume (V)
- Volume (V) = Mass (m) / Density (ρ)
Real-World Applications
Density equations are used in a wide range of applications:
- Archimedes' Principle: Used to determine the volume of irregularly shaped objects by measuring their buoyant force in a fluid.
- Material Selection: Engineers use density equations to choose materials with specific properties for various applications.
- Fluid Dynamics: Density plays a crucial role in understanding fluid behavior and flow.
Example Problems
Let's work through a couple of example problems:
Example 1: Calculating Mass
If the density of a substance is 2.5 g/cm³ and its volume is 100 cm³, what is its mass?
Mass (m) = Density (ρ) × Volume (V) = 2.5 g/cm³ × 100 cm³ = 250 g
Example 2: Determining Volume
If an object has a mass of 800 g and a density of 4 g/cm³, what is its volume?
Volume (V) = Mass (m) / Density (ρ) = 800 g / 4 g/cm³ = 200 cm³
Conclusion
Solving density equations is a valuable skill that has practical applications in science, engineering, and everyday life. By understanding the fundamentals and working through example problems, you can confidently approach and solve density-related calculations.