Is a vertebral compression fracture serious?
Yes, a vertebral compression fracture can be a serious medical condition, and its severity depends on various factors, including the degree of vertebral collapse, the presence of associated symptoms, and the underlying cause of the fracture. Vertebral compression fractures commonly occur in the thoracic (upper back) or lumbar (lower back) regions of the spine and are often associated with conditions such as osteoporosis or trauma.
Key considerations regarding the seriousness of vertebral compression fractures include:
Pain and Disability: Vertebral compression fractures can cause significant pain, which may be acute and intense. The pain can limit mobility and daily activities, impacting a person's quality of life.
Loss of Height and Postural Changes: As a vertebral body collapses, it can lead to a reduction in overall height and changes in posture. These alterations can affect the individual's appearance and contribute to a stooped or bent-forward posture.
Impact on Breathing and Organ Function: Severe compression fractures, especially those involving the thoracic spine, can affect the space within the chest cavity, potentially impacting respiratory function and the functioning of internal organs.
Neurological Complications: In some cases, a vertebral compression fracture may result in nerve compression or damage, leading to neurological symptoms. These symptoms can include radiating pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the extremities.
Underlying Conditions: The seriousness of a vertebral compression fracture may be influenced by the underlying cause. For example, fractures associated with osteoporosis may indicate an increased risk of additional fractures in the future.
Fracture Stability: The stability of the fracture is an important factor. Stable fractures are less likely to progress or cause significant complications, while unstable fractures may require more immediate intervention to prevent further damage.
Treatment Options: The severity of the fracture also influences the approach to treatment. Conservative measures such as pain management, bracing, and physical therapy may be sufficient for stable fractures, while more severe or unstable fractures may require surgical intervention.
It is essential for individuals experiencing back pain, especially after trauma or in the presence of risk factors such as osteoporosis, to seek medical attention promptly. Diagnosis typically involves imaging studies such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans. A healthcare professional can assess the severity of the fracture and recommend an appropriate treatment plan based on the specific circumstances.
Early intervention and appropriate management are crucial for minimizing pain, preventing further complications, and promoting recovery in individuals with vertebral compression fractures.
Understanding the Severity of Vertebral Compression Fractures:
1. Seriousness of a Vertebral Compression Fracture:
The seriousness of a vertebral compression fracture depends on several factors, including:
- Location of the fracture: Fractures in the upper thoracic spine may be less serious, while those in the lower thoracic or lumbar spine can be more concerning due to their proximity to nerves and the spinal cord.
- Severity of the compression: Minor fractures with minimal height loss may be less urgent compared to severe fractures with significant deformity or instability.
- Underlying medical conditions: Individuals with osteoporosis or other bone weakeners are at a higher risk of complications.
- Neurological involvement: Fractures affecting the spinal cord or nerve roots can be life-threatening and require immediate intervention.
Generally, most vertebral compression fractures are not life-threatening, but they can be quite painful and significantly impact quality of life. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are crucial to prevent complications and ensure optimal recovery.
2. Untreated Compression Fracture Complications:
Untreated compression fractures can lead to several complications, including:
- Chronic pain: Persistent pain can significantly affect daily activities and well-being.
- Kyphosis (hunchback): Worsening spinal curvature can lead to cosmetic concerns and breathing difficulties.
- Neurological deficits: In severe cases, nerve damage can cause weakness, numbness, or even paralysis.
- Increased risk of future fractures: Weakened bones are more susceptible to further fractures.
- Reduced lung capacity: Compressed vertebrae can put pressure on the lungs, hindering their function.
- Mental health impact: Chronic pain and disability can contribute to anxiety and depression.
3. Long-Term Consequences of Multiple Fractures:
Multiple compression fractures can have long-term consequences, including:
- Increased risk of spinal deformity: Repeated fractures can worsen kyphosis or lead to scoliosis (curvature sideways).
- Chronic pain and disability: Persistent pain and reduced mobility can impact daily activities and independence.
- Osteoporosis progression: Fractures are often a sign of worsening osteoporosis, requiring increased management efforts.
- Reduced quality of life: Pain, disability, and cosmetic concerns can significantly impact overall well-being.
4. Permanent Damage from Compression Fractures:
While most compression fractures heal successfully with proper treatment, permanent damage is possible in some cases, especially if left untreated. This includes:
- Severe kyphosis: Significant spinal curvature can be difficult to completely correct and cause ongoing pain and functional limitations.
- Neurological deficits: Nerve damage caused by severe fractures may not fully recover, leading to lasting weakness, numbness, or paralysis.
- Reduced lung capacity: In severe cases, permanent compression of the lungs can affect breathing function.
5. Treatment Options for Severe Compression Fractures:
Severe compression fractures with significant deformity, instability, or neurological involvement may require more aggressive treatment options, including:
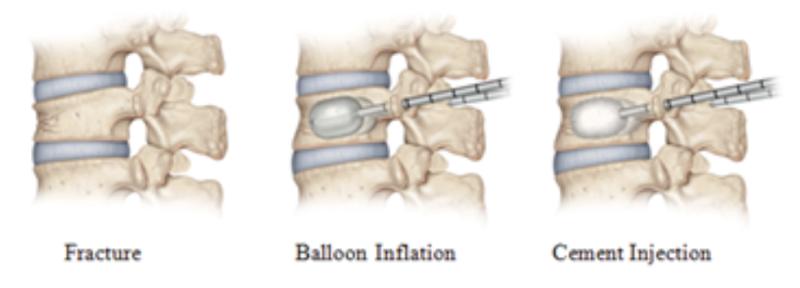
- Vertebral augmentation: Minimally invasive procedures like kyphoplasty or vertebroplasty inject cement into the fractured vertebra to stabilize it and restore height.
- Surgery: In rare cases, open surgery may be necessary to decompress the spinal cord, reconstruct damaged vertebrae, or remove bone tumors.
- Bracing: Spinal braces can help stabilize the spine and prevent further deformity while the fracture heals.
- Pain management: Medication and physical therapy play a crucial role in managing pain and improving mobility.
Remember, seeking prompt medical attention for any suspected vertebral compression fracture is crucial. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can significantly improve outcomes and minimize the risk of complications.
Please consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and evaluation of your specific condition.