What is Morningstar risk?
Morningstar risk, often referred to as "Morningstar Risk Rating," is a measurement of the risk associated with a specific mutual fund or exchange-traded fund (ETF). It's a component of the broader risk analysis provided by Morningstar, a well-known investment research and investment management firm. Morningstar offers a risk rating to help investors assess the level of risk associated with a particular fund and make more informed investment decisions.
Morningstar Risk Rating is typically presented on a scale with stars, where a higher number of stars indicates lower risk, and a lower number of stars indicates higher risk. The specific scale may vary, but it typically ranges from one star (high risk) to five stars (low risk).
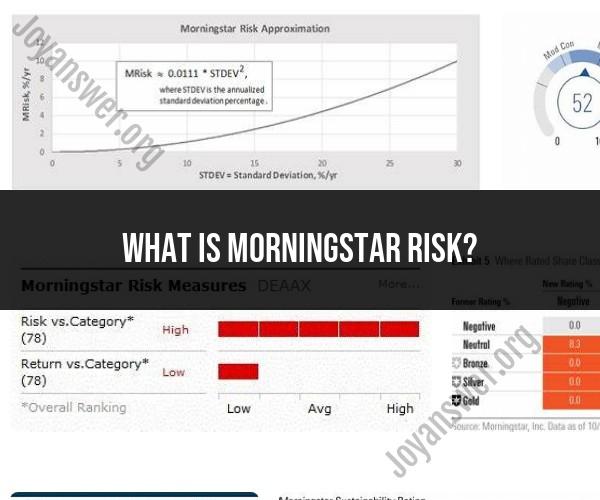
This rating is calculated based on the historical performance of the fund and its volatility compared to other funds in the same category. Factors that contribute to the Morningstar risk rating include the fund's standard deviation (a measure of price volatility), its performance compared to a benchmark index, and its historical returns. Funds with lower volatility and more consistent returns are assigned higher star ratings, indicating lower risk.
Morningstar Risk Rating is a useful tool for investors to quickly gauge the relative risk of different funds within the same investment category. However, it's important to note that past performance and volatility are not guarantees of future results. Therefore, while Morningstar risk ratings can provide valuable insights, they should be considered as just one of several factors in the decision-making process when choosing investment funds. It's advisable for investors to conduct a thorough analysis of a fund's strategy, expenses, and alignment with their investment goals and risk tolerance in addition to considering the Morningstar risk rating.
Understanding Morningstar Risk Ratings
Morningstar risk ratings are a quantitative measure of a fund's volatility, or risk of loss, over a period of time. The ratings are based on a fund's historical performance, but they are not a guarantee of future results.
Morningstar risk ratings range from 1 to 5, with 1 being the least risky and 5 being the most risky. Funds are rated within their respective categories, such as stock funds, bond funds, and hybrid funds.
How Morningstar Assesses and Rates Investment Risks
Morningstar uses a proprietary risk assessment model to calculate Morningstar risk ratings. The model takes into account a number of factors, including:
- Standard deviation: Standard deviation is a measure of how much a fund's returns have fluctuated over time. A higher standard deviation indicates higher risk.
- Downside risk: Downside risk is a measure of how much a fund's returns have fallen below its average return over time. A higher downside risk indicates higher risk.
- Tail risk: Tail risk is the risk of extreme losses. Morningstar uses a number of metrics to measure tail risk, such as the maximum drawdown and the value at risk.
Interpreting Morningstar Risk Ratings for Informed Investment Decisions
Morningstar risk ratings can be a helpful tool for investors when making investment decisions. However, it is important to note that the ratings are just one factor to consider. Investors should also consider their own risk tolerance and investment goals when making investment decisions.
For example, an investor with a low risk tolerance may want to choose funds with a Morningstar risk rating of 1 or 2. An investor with a higher risk tolerance may want to choose funds with a Morningstar risk rating of 3 or 4.
Other Factors to Consider Alongside Morningstar Risk Ratings
In addition to Morningstar risk ratings, there are a number of other factors that investors should consider when making investment decisions. These factors include:
- Fees: Fees can have a significant impact on investment returns over time. Investors should compare the fees of different funds before investing.
- Performance: Investors should also consider the performance of different funds before investing. However, it is important to note that past performance is not a guarantee of future results.
- Investment objective: Investors should also consider the investment objective of different funds. For example, an investor who is looking for capital growth may want to invest in a growth fund. An investor who is looking for income may want to invest in an income fund.
Using Morningstar Ratings as a Tool for Diversified Portfolios
Morningstar ratings can be a helpful tool for investors when building diversified portfolios. By investing in funds with different Morningstar risk ratings, investors can reduce their overall risk.
For example, an investor could invest in a mix of stock funds with Morningstar risk ratings of 1, 2, and 3. The investor could also invest in a bond fund with a Morningstar risk rating of 1 or 2. This would create a diversified portfolio with a moderate risk level.
Morningstar risk ratings are a valuable tool for investors, but they are just one factor to consider when making investment decisions. Investors should also consider their own risk tolerance, investment goals, and other factors before investing.