What is the least to most prompting procedure?
The Least to Most Prompting Procedure is a systematic intervention technique used in Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) to teach new skills or behaviors to individuals. This procedure involves initially providing minimal assistance or prompts and gradually increasing the level of assistance until the individual successfully completes the task. The goal is to promote independence and reduce dependency on prompts over time. Here's how the procedure typically works:
Least Intrusive Prompt:
- The teaching session begins with the presentation of the least intrusive prompt. This could be a subtle cue or hint that helps the individual understand what is expected without providing direct assistance.
Wait Time:
- After presenting the least intrusive prompt, the instructor allows a brief period of wait time to give the individual an opportunity to respond independently. This wait time is essential to allow the person to process the information and attempt the task on their own.
Additional Prompts:
- If the individual does not respond correctly or does not initiate the desired behavior during the initial wait time, the instructor then provides a slightly more intrusive prompt. This could be a more explicit cue, a gesture, or additional guidance to help the individual understand and complete the task.
Gradual Increase in Prompt Intensity:
- The procedure continues with a gradual increase in the intensity of prompts until the individual successfully performs the target behavior. The progression is from the least intrusive prompts to more explicit and direct prompts.
Reinforcement:
- Positive reinforcement, such as praise or a reward, is provided when the individual successfully completes the task with the provided prompts. This reinforcement helps strengthen the association between the behavior and a positive outcome.
Data Collection:
- Throughout the teaching session, data is collected on the individual's responses and the prompts required. This data is valuable for assessing progress, determining the effectiveness of prompts, and making informed decisions about future interventions.
The Least to Most Prompting Procedure is particularly useful for individuals who may struggle with new tasks or have varying levels of skill in different areas. By starting with minimal prompts, the procedure respects the individual's current abilities and encourages independence. The gradual increase in prompting allows for differentiation based on the learner's needs, ensuring that the level of assistance provided is tailored to their specific requirements.
It's important to note that the goal of this procedure is to fade out prompts over time as the individual becomes more proficient in the targeted skill. The ultimate aim is to promote independent functioning and reduce reliance on external assistance.
Sure, here is a summary of the least-to-most prompting hierarchy, its implementation, and its benefits and applications:
Understanding the least-to-most prompting hierarchy: A framework for providing instructional support
The least-to-most prompting hierarchy (LTM) is a systematic approach to providing instructional support that gradually fades as a learner becomes more independent. It is a widely used technique in applied behavior analysis (ABA), particularly for teaching individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and other developmental disabilities.
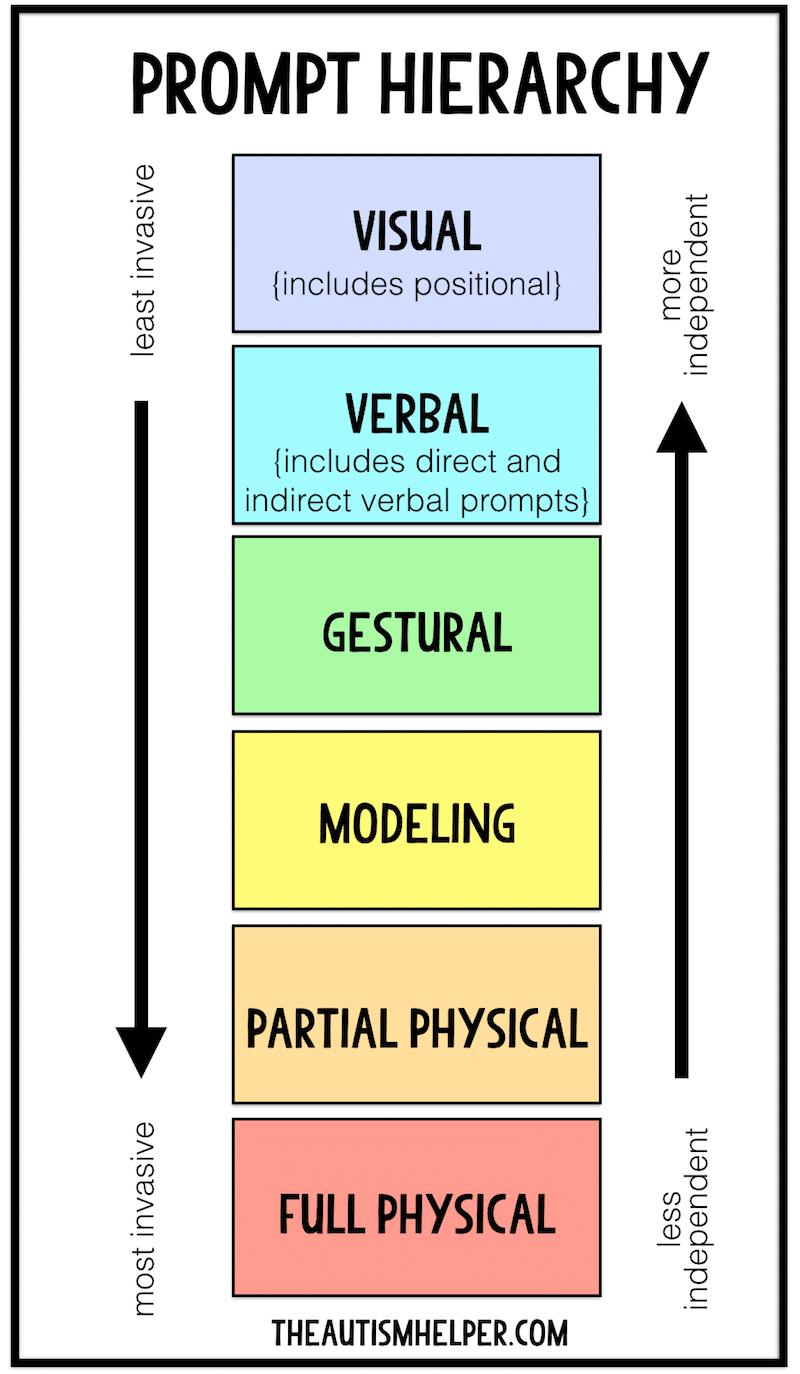
The LTM hierarchy consists of a series of prompts, ranging from the least intrusive to the most intrusive. Prompts are cues or supports that help a learner complete a task or skill. The goal of the LTM procedure is to provide just enough prompting to help the learner succeed, while gradually fading out the prompts as the learner becomes more independent.
The LTM hierarchy typically includes the following levels of prompts:
- Independent: The learner completes the task or skill without any prompts.
- Gesture: The provider gestures to indicate the correct response.
- Indirect Verbal: The provider provides verbal cues that are not specific to the task, such as "Good job!" or "Keep trying."
- Direct Verbal: The provider provides specific verbal instructions, such as "Pick up the red block."
- Model: The provider demonstrates the task or skill for the learner.
- Partial Physical Assistance: The provider physically guides the learner's hand or body to complete the task or skill.
- Full Physical Assistance: The provider physically completes the task or skill for the learner.
Implementing the least-to-most prompting procedure: Applying the hierarchy to provide gradual assistance
To implement the LTM procedure, the provider starts at the least intrusive level of prompting and gradually fades the prompts as the learner becomes more independent. The provider should only increase the level of prompting if the learner is unable to complete the task or skill with the current level of support.
Here are some general guidelines for fading prompts:
- Start with the least intrusive prompt.
- Provide just enough prompting to help the learner succeed.
- Fade prompts gradually over time.
- Wait for a correct response before fading the prompt.
- Provide praise and reinforcement for independent responses.
Benefits and applications of the least-to-most prompting procedure: Enhancing learning and reducing reliance on prompts
The LTM procedure has several benefits, including:
- Increases independence: By gradually fading prompts, the LTM procedure helps learners develop the skills and confidence to complete tasks independently.
- Enhances learning: The LTM procedure provides learners with the support they need to learn new skills effectively.
- Reduces reliance on prompts: With consistent use of the LTM procedure, learners become less reliant on prompts and more independent in their day-to-day activities.
The LTM procedure can be used to teach a wide range of skills, including:
- Communication skills: Teaching individuals with ASD to use verbal or nonverbal communication methods.
- Social skills: Teaching individuals with ASD how to interact with others in a positive way.
- Self-help skills: Teaching individuals with ASD how to complete daily living tasks such as dressing, eating, and using the toilet.
- Academic skills: Teaching individuals with ASD how to read, write, and solve math problems.
- Challenging behaviors: Reducing challenging behaviors such as tantrums and aggression.
Overall, the least-to-most prompting hierarchy is a valuable tool for providing instructional support and enhancing learning for individuals with a wide range of abilities.