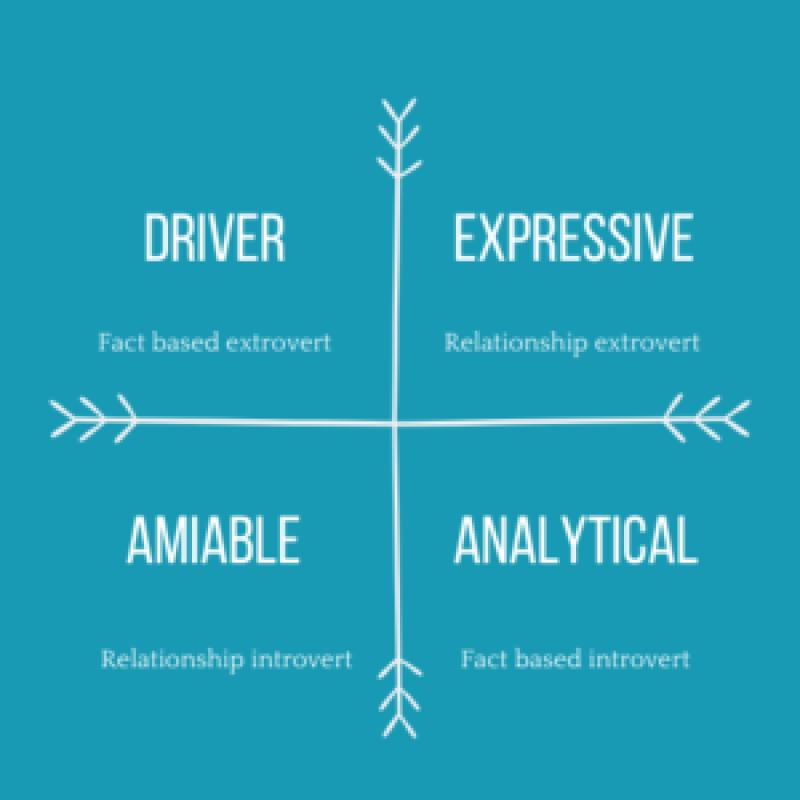
What are the four personality traits?
The Big Four personality traits, also known as the Five Factor Model or OCEAN model, are a widely accepted framework in psychology for describing and understanding personality. These traits are:
Openness to Experience (O): This trait reflects a person's willingness to explore new ideas, engage in creative thinking, and be open to new experiences. Individuals high in openness tend to be imaginative, curious, and open-minded, while those low in openness may prefer routine and familiarity.
Conscientiousness (C): Conscientiousness refers to the degree of organization, responsibility, and reliability in a person. Individuals high in conscientiousness are often diligent, detail-oriented, and disciplined, while those low in conscientiousness may be more spontaneous and less focused on order and structure.
Extraversion (E): Extraversion measures the extent to which a person is outgoing, sociable, and energetic. Extraverted individuals tend to be talkative, assertive, and enjoy social interactions, while introverted individuals may be quieter, more reserved, and prefer solitary activities.
Agreeableness (A): Agreeableness reflects a person's interpersonal style and how they relate to others. Individuals high in agreeableness are typically empathetic, cooperative, and considerate, while those low in agreeableness may be more competitive or skeptical.
There is a fifth factor, often included in the Five Factor Model, known as:
- Neuroticism (N) or Emotional Stability: This trait measures the tendency to experience negative emotions such as anxiety, depression, and irritability. High neuroticism individuals may be more prone to stress and emotional instability, while low neuroticism individuals tend to be more emotionally resilient and stable.
These traits are considered to be relatively stable over time and have been found to be consistent across various cultures. The Big Four personality traits provide a comprehensive framework for understanding and describing individual differences in personality.
1. The Four Key Personality Traits (According to the Big Five Model)
The Big Five personality model is a widely accepted framework that identifies five broad dimensions of personality:
1. Openness to Experience:
- High in openness: Curious, imaginative, interested in new things and ideas.
- Low in openness: Traditional, prefers familiar routines, less interested in abstract concepts.
2. Conscientiousness:
- High in conscientiousness: Organized, efficient, reliable, goal-oriented.
- Low in conscientiousness: Disorganized, impulsive, less focused on achievement.
3. Extraversion:
- High in extraversion: Outgoing, talkative, energetic, enjoys social interaction.
- Low in extraversion: Introverted, prefers solitude, gets drained by social interaction.
4. Agreeableness:
- High in agreeableness: Trustworthy, helpful, cooperative, empathetic.
- Low in agreeableness: Competitive, assertive, less concerned with maintaining harmony.
5. Neuroticism:
- High in neuroticism: Tends to experience negative emotions like anxiety, worry, and sadness.
- Low in neuroticism: Emotionally stable, calm, resilient to stress.
2. How Personality Traits Influence Behavior and Interactions
- Motivation and Goals: Traits like conscientiousness and extraversion can influence what goals individuals set and how they pursue them.
- Social Interactions: Agreeableness and neuroticism can impact how individuals relate to others, build relationships, and navigate conflict.
- Emotional Responses: Neuroticism and openness influence how individuals experience and react to emotions, both positive and negative.
- Decision-Making: Conscientiousness and openness can affect how individuals gather information, evaluate options, and make choices.
- Stress and Coping: Traits like neuroticism and resilience can influence how individuals handle stress and adapt to challenging situations.
It's important to remember that personality traits are not fixed categories, but rather spectrums on which individuals fall. Everyone displays a unique combination of these traits, and their expression can vary depending on context and situational factors.
3. Standardized Personality Assessments
Yes, there are several standardized personality assessments designed to measure the Big Five traits and other personality dimensions. Some common examples include:
- NEO Personality Inventory-Revised (NEO-PI-R)
- Five Factor Inventory (FFI)
- Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)
- Big Five Inventory (BFI)
These assessments typically use surveys or questionnaires to assess an individual's self-reported preferences, behaviors, and experiences. However, it's crucial to interpret these assessments with caution as they are not perfect indicators of complex human personality and should be used in conjunction with other methods for a comprehensive understanding of an individual.
I hope this helps! Let me know if you have any further questions.