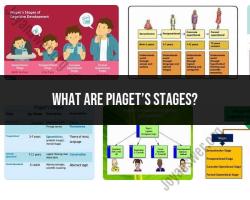
What does cognitive psychology focus on?
Cognitive psychology is a branch of psychology that focuses on the study of mental processes, including how people think, perceive, remember, learn, problem-solve, and make decisions. It explores the internal mental processes that are involved in the way individuals process information and interact with the world. Here are some key focus areas of cognitive psychology:
Memory:
- Cognitive psychologists study how information is encoded, stored, and retrieved in the human memory. This includes short-term memory, long-term memory, and factors that influence memory recall.
Perception:
- Perception involves the interpretation of sensory information from the environment. Cognitive psychologists investigate how individuals perceive and make sense of the world around them, including the processes related to visual perception, auditory perception, and more.
Attention:
- Attention refers to the ability to selectively focus on certain aspects of the environment while ignoring others. Cognitive psychologists study attentional processes, such as how attention is allocated, sustained, and divided.
Language:
- Cognitive psychology explores the mental processes involved in language acquisition, comprehension, and production. This includes studying how people understand and generate language, as well as the cognitive mechanisms behind language development.
Problem-Solving and Decision Making:
- Cognitive psychologists examine how individuals solve problems and make decisions. This includes investigating problem-solving strategies, decision-making biases, and the factors that influence the decision-making process.
Learning:
- Learning is a central focus in cognitive psychology, encompassing the study of how individuals acquire new knowledge and skills. Cognitive psychologists explore different learning theories, memory processes related to learning, and the cognitive aspects of educational practices.
Cognitive Development:
- Cognitive psychology investigates the development of cognitive abilities across the lifespan. This includes the study of cognitive changes in children, adolescents, adults, and older adults.
Cognitive Neuroscience:
- Cognitive psychologists often collaborate with neuroscientists to study the neural mechanisms underlying cognitive processes. Cognitive neuroscience combines psychological theories with neuroscientific methods to understand the biological basis of cognition.
Information Processing:
- Cognitive psychologists adopt an information processing perspective to understand how individuals acquire, store, and use information. This approach views the mind as a system that processes information in a series of stages, similar to a computer.
Artificial Intelligence and Cognitive Modeling:
- Cognitive psychologists use computer models and simulations to create artificial intelligence that mimics human cognitive processes. These models help test theories and provide insights into how the mind works.
Cognitive psychology has applications in various fields, including education, clinical psychology, human-computer interaction, and artificial intelligence. Researchers and practitioners in cognitive psychology aim to understand and improve cognitive processes to enhance human performance and well-being.
What is the primary focus of cognitive psychology?
Cognitive psychology is a branch of psychology that studies the mental processes involved in human cognition, including perception, attention, memory, language, problem-solving, and decision-making. It aims to understand how we take in, transform, store, and retrieve information from the world around us. Cognitive psychologists use a variety of methods to study cognition, including experiments, surveys, and brain imaging techniques.
How does cognitive psychology explore and analyze human cognition?
Cognitive psychologists use a variety of methods to explore and analyze human cognition. These methods can be broadly divided into two categories:
Behavioral methods: These methods focus on measuring and observing people's overt behavior, such as their responses to stimuli or their performance on tasks. Some examples of behavioral methods include reaction time experiments, error analysis, and eye tracking.
Cognitive neuroscience methods: These methods use brain imaging techniques to study the neural basis of cognition. Some examples of cognitive neuroscience methods include functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), electroencephalography (EEG), and positron emission tomography (PET).
What cognitive processes are of utmost interest to cognitive psychologists?
Cognitive psychologists are interested in a wide range of cognitive processes, including:
Perception: How do we take in and interpret information from our senses?
Attention: How do we select and focus on relevant information while filtering out distractions?
Memory: How do we encode, store, and retrieve information?
Language: How do we understand, produce, and use language?
Problem-solving: How do we solve problems and make decisions?
Creativity: How do we generate new ideas and solutions?
Cognitive psychologists are also interested in understanding how these cognitive processes interact with each other and how they are affected by factors such as age, education, and culture.