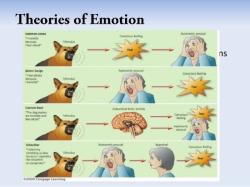
What is the James-Lange theory of emotion?
The James-Lange theory of emotion, developed independently by American psychologist William James and Danish physiologist Carl Lange in the late 19th century, proposes that our emotional experiences are the result of our physiological responses to external stimuli. This theory suggests that emotions are essentially perceptions of bodily changes or physiological reactions in response to specific events or situations. Here's a brief overview of the James-Lange theory:
Sequence of Events: According to the James-Lange theory, the sequence of events leading to an emotional experience is as follows:a. An external event or stimulus triggers a physiological response in the body. For example, encountering a bear in the woods leads to increased heart rate and sweating.b. The individual perceives and interprets these physiological changes as emotions. In the example, the person interprets the increased heart rate and sweating as fear.c. Emotions are therefore a result of the bodily responses to the stimulus.
Distinctive Physiological Responses: The theory suggests that different emotions are associated with specific and distinct patterns of physiological responses. For example, fear might be associated with an increased heart rate and a sense of trembling, while anger could result in increased blood pressure and muscle tension.
Variability: The theory acknowledges that individual differences in physiological responses can lead to variations in emotional experiences. How one person's body reacts to a particular stimulus may differ from another person's response.
Implications: The James-Lange theory has significant implications for understanding the relationship between the body and emotions. It suggests that altering physiological responses could potentially influence emotional states. For example, deliberately inducing a calm and relaxed physiological state might help reduce feelings of anxiety.
While the James-Lange theory made important contributions to the study of emotions by emphasizing the role of the body in emotional experiences, it also faced challenges and criticisms. Critics argued that emotions are not solely the result of bodily changes and that cognitive appraisal and mental processes also play a crucial role in emotional experiences.
Subsequent theories, such as the Cannon-Bard theory and the Schachter-Singer theory (two-factor theory), built upon and refined the understanding of emotions by incorporating cognitive and situational factors into the emotional process.