What is the DSM criteria for anxiety?
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) is a widely used manual by mental health professionals to diagnose various mental health conditions, including anxiety disorders. There are several specific anxiety disorders listed in the DSM-5, each with its own set of criteria for diagnosis. I'll provide an overview of the general criteria for diagnosing an anxiety disorder based on the DSM-5:
Excessive Worry or Anxiety:
- The individual must experience excessive and persistent worry, fear, or anxiety that is difficult to control and out of proportion to the actual threat or situation.
Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms:
- Anxiety disorders often involve a range of behavioral and psychological symptoms, such as restlessness, muscle tension, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and sleep disturbances.
Duration and Impairment:
- The anxiety and related symptoms must persist for a specific duration, typically at least six months.
- These symptoms should cause significant distress or impairment in daily functioning, including social, occupational, or other important areas of life.
Specific anxiety disorders, each with their own unique criteria, include:
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Characterized by excessive worry and anxiety about various everyday events or activities.
Panic Disorder: Involves recurrent and unexpected panic attacks, along with the persistent worry about having additional attacks.
Social Anxiety Disorder (Social Phobia): Features intense fear or avoidance of social situations and performance-related situations.
Specific Phobias: Involves intense fear and avoidance of specific objects or situations, like heights, flying, animals, or blood.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): Characterized by the presence of obsessions (persistent, intrusive thoughts) and compulsions (repetitive behaviors or mental acts).
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Typically triggered by a traumatic event and includes symptoms like flashbacks, nightmares, and hyperarousal.
Separation Anxiety Disorder: Often diagnosed in children and involves excessive distress when separated from caregivers.
Selective Mutism: Primarily diagnosed in children who consistently fail to speak in specific social situations, even though they can speak in other settings.
The specific criteria for each of these anxiety disorders can be more detailed and include additional symptoms or features. Diagnosis should be made by a qualified mental health professional based on a thorough evaluation of the individual's symptoms and history.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of anxiety, it is essential to seek help from a mental health professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Anxiety disorders are treatable, and various therapeutic approaches, including cognitive-behavioral therapy and medication, can be effective in managing these conditions.
Understanding Anxiety: DSM Criteria and Diagnosis
Anxiety is a normal human emotion that everyone experiences from time to time. It is characterized by feelings of worry, nervousness, or unease, typically about an imminent event or something with an uncertain outcome. While anxiety is a normal emotion, it can become a problem if it is excessive, persistent, and interferes with your daily life.
DSM Criteria and Diagnosis
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) is the official guidebook for diagnosing mental disorders, including anxiety disorders. The DSM-5 outlines the specific criteria that must be met for a person to be diagnosed with an anxiety disorder.
There are six main types of anxiety disorders:
- Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD): Excessive worry about a variety of things for at least six months.
- Panic disorder: Sudden and unexpected panic attacks characterized by intense fear and physical symptoms.
- Social anxiety disorder (social phobia): Intense fear of social situations and being judged by others.
- Specific phobias: Intense fear of a specific object or situation.
- Agoraphobia: Fear of being in situations where escape might be difficult or help unavailable.
- Separation anxiety disorder: Excessive anxiety about being separated from a loved one.
To be diagnosed with an anxiety disorder, a person must meet the following criteria:
- The anxiety must be excessive, persistent, and interfere with their daily life.
- The anxiety must not be caused by a substance or another medical condition.
- The anxiety must not be better explained by another mental disorder.
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM) Criteria for Anxiety Disorders
The DSM-5 criteria for anxiety disorders are based on a number of factors, including:
- The type of anxiety
- The severity of the anxiety
- The duration of the anxiety
- The impact of the anxiety on the person's life
The DSM-5 criteria are used by mental health professionals to diagnose anxiety disorders and to develop treatment plans.
Identifying and Assessing Anxiety Using DSM Guidelines
There are a number of ways to identify and assess anxiety using DSM guidelines. These include:
- Clinical interviews: Mental health professionals will interview the person to gather information about their symptoms, history, and family history.
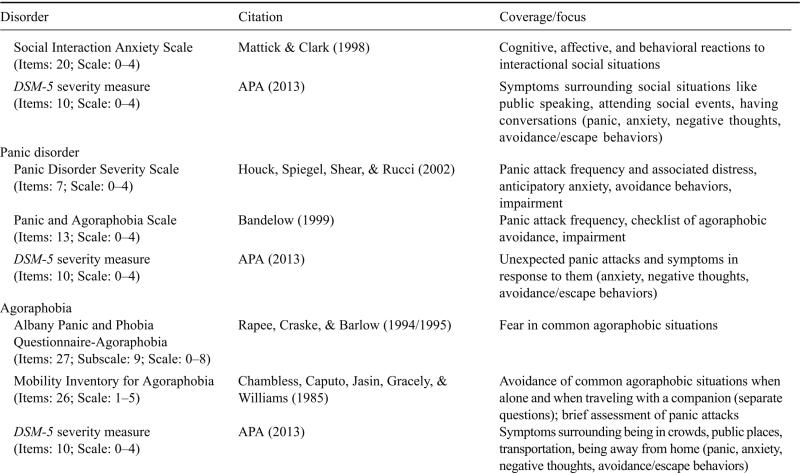
- Questionnaires and rating scales: There are a number of questionnaires and rating scales that can be used to assess anxiety symptoms.
- Physical exams: Mental health professionals may also conduct physical exams to rule out any medical conditions that could be causing the anxiety.
Once an anxiety disorder has been diagnosed, the mental health professional will develop a treatment plan. Treatment for anxiety disorders typically includes psychotherapy, medication, or a combination of both.