What are the two basic components to the emotion theory?
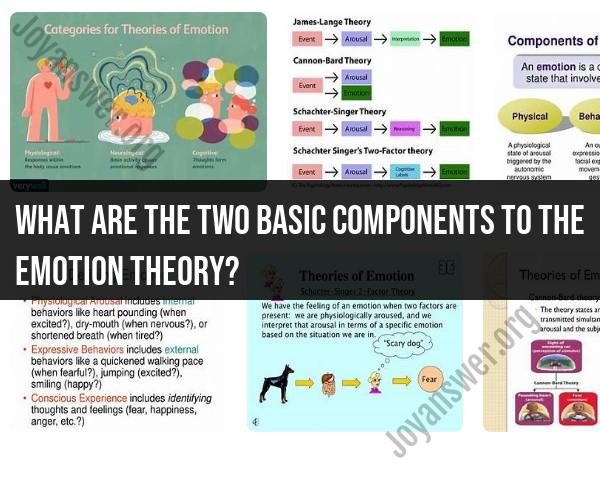
In the realm of emotion theory, two fundamental components are often highlighted:
Physiological Component: This component involves the physiological changes that occur within the body in response to emotional stimuli. For instance, when experiencing fear, the body might undergo changes such as increased heart rate, sweating, or adrenaline release. These bodily responses are often associated with specific emotions and are part of the fight-or-flight response.
Cognitive Component: This aspect refers to the cognitive appraisal or the mental interpretation of the emotional stimuli. It involves how individuals perceive, interpret, and evaluate the situation, leading to the experience of a particular emotion. For example, if encountering a challenging situation, the cognitive component involves assessing whether it's threatening, enjoyable, or neutral, subsequently influencing the emotional response.
These two components work together in the process of experiencing emotions. The physiological changes occur in response to stimuli, while cognitive appraisal helps interpret and label these physiological changes as specific emotions, contributing to the overall emotional experience.
Physiological Component: Bodily changes associated with emotions
Emotions trigger a cascade of physiological changes in the body, including:
Increased heart rate and respiration: This prepares the body for action or fight-or-flight response.
Increased adrenaline and cortisol: These hormones enhance alertness and energy, while also suppressing the immune system.
Changes in facial expression, muscle tension, and sweating: These bodily signals communicate emotions to others.
Changes in digestion and sleep patterns: Emotions can disrupt the body's normal rhythms.
Cognitive Component: Thoughts, interpretations, and appraisals of emotions
Our thoughts and interpretations play a crucial role in shaping our emotional experiences. When we encounter a situation, our minds automatically analyze it and assess its significance for our well-being. This appraisal process determines how we feel about the situation. For instance, if we perceive a situation as threatening, we may experience fear or anxiety. If we perceive it as positive, we may experience joy or excitement.
3. Interplay between the Physiological and Cognitive Components in Shaping Emotional Experiences
The physiological and cognitive components of emotions interact dynamically. The physiological changes initiated by an emotional response can influence our thoughts and interpretations, while our thoughts and interpretations can modulate the physiological responses. For example, if we interpret a situation as relatively harmless, our heart rate and breathing may not increase as significantly as if we perceive it as dangerous.
Individual differences in the expression and regulation of emotions
Individuals vary in their tendencies to express and regulate their emotions. Some people are more expressive than others, while others are more reserved. Some people are better at managing their emotions, while others find it more challenging. These differences can be influenced by genetics, personality traits, and life experiences.
The role of emotions in influencing behavior and decision-making
Emotions play a significant role in guiding our behavior and decision-making. They can motivate us to pursue certain goals, avoid potential threats, and connect with others. Positive emotions can enhance creativity and problem-solving, while negative emotions can motivate us to take action. However, it's important to strike a balance, as excessive emotional reactivity can lead to impulsive or harmful behaviors.