What is the general reaction for cellular respiration?
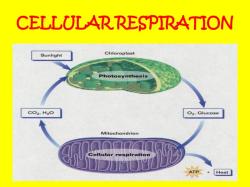
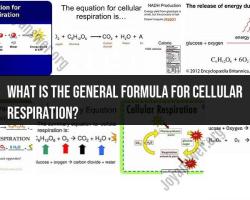
The general reaction for cellular respiration is a complex process that involves the breakdown of glucose (or other organic molecules) to produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) within cells. There are three main stages of cellular respiration: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle), and the electron transport chain. The overall chemical equation for cellular respiration is as follows:
C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2 (oxygen) → 6CO2 (carbon dioxide) + 6H2O (water) + ATP (energy)
This equation summarizes the complete oxidation of one molecule of glucose, which results in the production of carbon dioxide, water, and energy (in the form of ATP). Cellular respiration is an exothermic process, meaning it releases energy in the form of heat. The energy stored in glucose is gradually released in a controlled manner through a series of enzymatic reactions in the three stages of respiration. The majority of ATP is produced in the electron transport chain as electrons move through a series of protein complexes, generating a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis.
It's important to note that cellular respiration is not limited to glucose; it can also involve other organic molecules such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. The breakdown of these molecules ultimately leads to the production of ATP and the release of carbon dioxide and water. Cellular respiration is a fundamental metabolic process in living organisms, providing the energy necessary for various cellular activities and maintaining life.
What is the general chemical reaction for cellular respiration?
The general chemical reaction for cellular respiration is:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
This equation shows that glucose (C6H12O6) is oxidized (combines with oxygen, O2) to produce carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and energy in the form of ATP.
How is glucose oxidized during cellular respiration to produce energy?
Glucose is oxidized during cellular respiration in a series of chemical reactions that occur in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of the cell. These reactions break down glucose into smaller molecules, and the energy released from these reactions is used to produce ATP.
The first step in cellular respiration is glycolysis. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and does not require oxygen. In glycolysis, glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate.
Pyruvate is then transported to the mitochondria, where it is further oxidized in a series of reactions called the Krebs cycle. The Krebs cycle requires oxygen, and it produces carbon dioxide, water, and ATP.
The final step in cellular respiration is oxidative phosphorylation. Oxidative phosphorylation occurs on the inner mitochondrial membrane and requires oxygen. In oxidative phosphorylation, electrons are transferred from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen, and ATP is produced.
What are the reactants and products in the cellular respiration equation?
The reactants in the cellular respiration equation are glucose and oxygen. The products of the cellular respiration equation are carbon dioxide, water, and ATP.
ATP is the energy currency of the cell. It is used to power all of the cell's activities, including muscle contraction, protein synthesis, and active transport.
Cellular respiration is a complex process, but it is essential for life. Without cellular respiration, cells would not be able to produce the energy they need to survive and function.